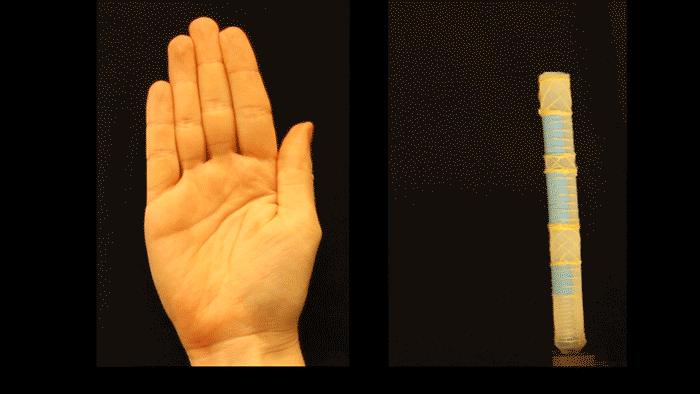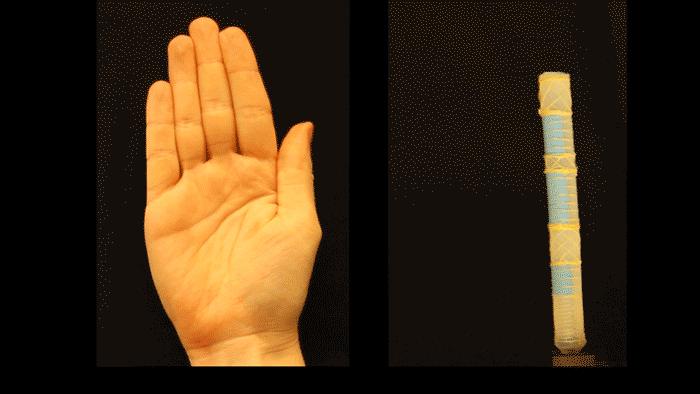
Credit: Harvard SEAS
Designing a soft robot to move organically — to bend like a finger or twist like a wrist — has always been a process of trial and error. Now, researchers from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences and the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering have developed a method to automatically design soft actuators based on the desired movement.
The research is published in The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
"Rather than designing these actuators empirically, we wanted a tool where you could plug in a motion and it would tell you how to design the actuator to achieve that motion," said Katia Bertoldi, the John L. Loeb Associate Professor of the Natural Sciences and coauthor of the paper.
Designing a soft robot that can bend like a finger or knee may seem simple but the motion is actually incredibly complex.
"The design is so complicated because one actuator type is not enough to produce complex motions," said Fionnuala Connolly, a graduate student at SEAS and first author of the paper. "You need a sequence of actuator segments, each performing a different motion and you want to actuate them using a single input."
The method developed by the team uses mathematical modeling of fluid-powered, fiber-reinforced actuators to optimize the design of an actuator to perform a certain motion. The team used this model to design a soft robot that bends like an index finger and twists like a thumb when powered by a single pressure source.
"This research streamlines the process of designing soft robots that can perform complex movements," said Conor Walsh, the John L. Loeb Associate Professor of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Core Faculty Member at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering and coauthor of the paper. "It can be used to design a robot arm that moves along a certain path or a wearable robot that assists with motion of a limb."
The new methodology will be included in the Soft Robotic Toolkit, an online, open-source resource developed at SEAS to assist researchers, educators and budding innovators to design, fabrication, model, characterize and control their own soft robots.
###
Media Contact
Leah Burrows
[email protected]
617-496-1351
@hseas
http://www.seas.harvard.edu/
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag