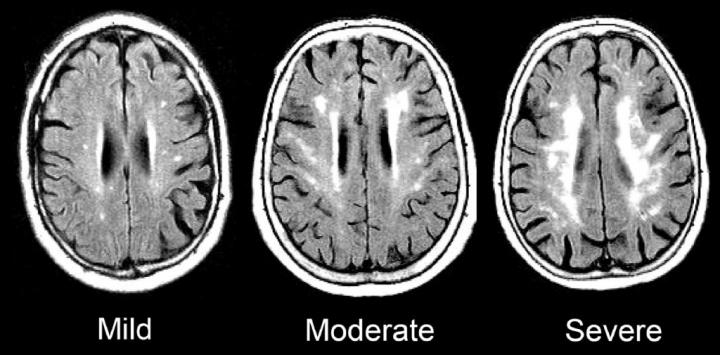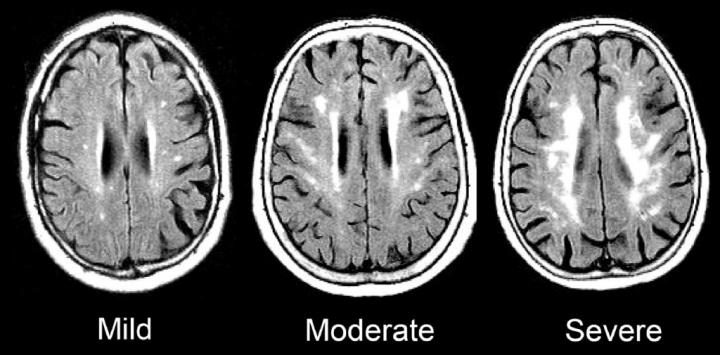
Credit: Gottesman lab
Researchers at Johns Hopkins have added to evidence that rising and chronic inflammation as measured by a biomarker in the blood in middle and late age are linked to visible structural changes in the brains of people with poor cognition and dementia.
The authors say results of their study, based on data gathered from a federally funded study on more than 1,500 people, suggests that efforts to curb inflammation with drugs or lifestyle changes midlife or earlier may be key to delaying or preventing cognitive decline in old age.
"We found that individuals who had an increase in inflammation during midlife that was maintained from mid to late life have greater abnormalities in the brain's white matter structure, as measured with MRI scans," says Keenan Walker, Ph.D., lead author and postdoctoral fellow in the Department of Neurology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
"This suggests to us that inflammation may have to be chronic, rather than temporary, to have an adverse effect on important aspects of the brain's structure necessary for cognitive function," he adds.
Researchers have long gathered evidence that chronic inflammation and the biochemicals associated with it may damage the brain. C-reactive protein, an inflammatory factor made in the liver, for example, already has become a marker for chemical damage to heart and blood vessel tissue indicative of heart attack.
So far, however, according to Walker, studies linking inflammation to brain abnormalities have not looked at these factors and features over an extended period of time in the same population.
In their new study, described in the August issue of Neurobiology of Aging, Walker and his colleagues took data from the atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study that looked at brain structure and integrity, as well as a marker of inflammation over a 21-year period spanning middle age to late life.
Specifically, the investigators focused on and compared data on 1,532 participants recruited from 1987 to 1989 from Washington County, Maryland; Forsyth County, North Carolina; Minneapolis, Minnesota; and Jackson, Mississippi. Sixty-one percent of participants were women, and 28 percent were African-American. At the final visit, participants were an average age of 76.
Over the course of the ARIC study, each participant had five visits with study coordinators, averaging every three years. At the last visit, each participant underwent an MRI of their brain to examine evidence of damage to so-called white matter — the part of the brain responsible for transmitting messages. Damaged white matter appears superwhite on a scan, similar to overexposure on a photograph, and was measured using an automated program.
At visits 2, 4 and 5, the researchers took blood samples to measure for high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, a standard measure of inflammation throughout the body. Those with levels below 3 milligrams per liter were considered to have low inflammation, whereas those with 3 or more milligrams per liter of C-reactive protein were considered to have elevated inflammation.
Even after adjusting for demographics (e.g., sex and education) and cardiovascular disease risk, the researchers found that the 90 people who transitioned from low to persistently elevated C-reactive protein during midlife, indicating increasing inflammation, showed the greatest damage to the white matter in the brain.
Using a program that measures structural integrity at the microscopic level, the researchers estimate that the brains of the people who had escalating C-reactive protein in middle age appear similar to that of a person 16 years older.
Walker says because their findings overall showed that increasing and chronic inflammation were associated with the most damage to white matter, there is more reason to infer a cause and effect relationship between growing and persistent inflammation and evidence of dementia. But he emphasized that theirs was an "observational" study not designed to determine cause and effect, or to prove it. More studies would need to be done to prove cause and effect and figure out the precise pathways to brain damage, he added.
"Our work is important because currently there aren't treatments for neurodegenerative diseases, and inflammation may be a reversible factor to prolong or prevent disease onset," says Rebecca Gottesman, M.D., Ph.D., senior author and professor of neurology and epidemiology at Johns Hopkins. "Now, researchers have to look at how we might reduce inflammation to reduce cognitive decline and neurodegeneration."
Walker says that common causes of chronic inflammation include cardiovascular disease, heart failure, diabetes, high blood pressure and infections such as hepatitis C or HIV. He also says that inflammation is a normal byproduct of aging, but poor physical health and injuries seem to exacerbate it.
Some studies suggest that reducing inflammation in the short term can be accomplished by treating and controlling common cardiovascular diseases and maintaining a healthy weight.
###
Additional authors include Elizabeth Selvin of Johns Hopkins; B. Gwen Windham of the University of Mississippi Medical Center; Melinda Power of George Washington University; Ron Hoogeveen and Christie Ballantyne of Baylor College; Aaron Folsom of the University of Minnesota and David Knopman and Clifford Jack of Mayo Clinic.
The study is supported by contracts from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) (HHSN268201100005C, HHSN268201100006C, HHSN268201100007C, HHSN268201100008C, HHSN268201100009C, HHSN268201100010C, HHSN268201100011C and HHSN268201100012C) and grants from the NHLBI (HL096814, HL096899, HL096902, HL096917, R01-HL70825), the National Institute of Aging (T32AG027668 and K24 AG052573) and the National Institute of Diabetes.
Media Contact
Vanessa McMains
[email protected]
410-502-9410
@HopkinsMedicine
http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org
Original Source
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/news/media/releases/mid__to_late_life_increases_in_marker_of_chronic_inflammation_tied_to_dementia?preview=true