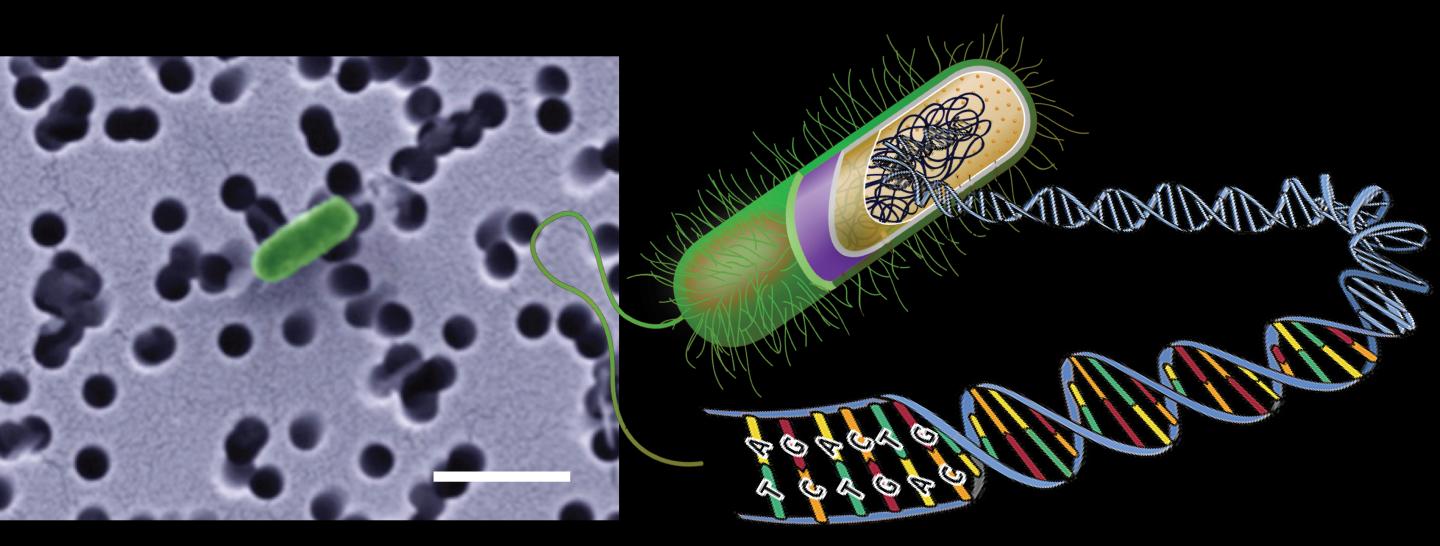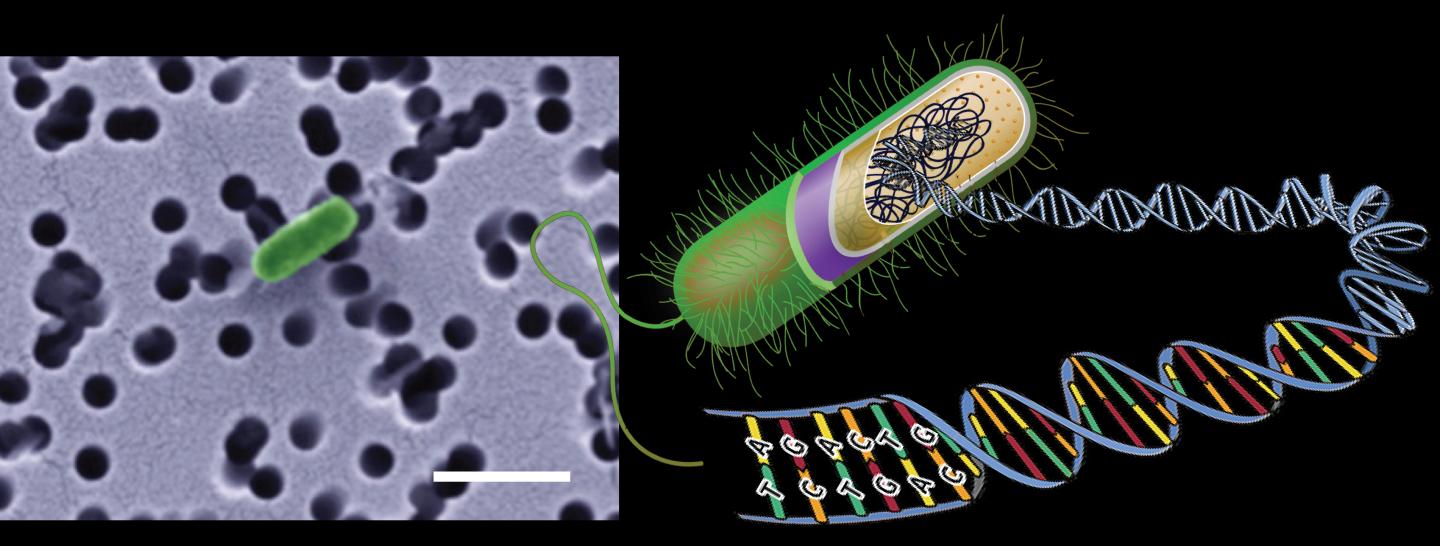
Credit: Photo: Stefan Braun. Graphic modified from Wikipedia and www.genesandhealth.org.
Researchers at the Center for Geomicrobiology at Aarhus University, Denmark, have sequenced the genomes of several microorganisms inhabiting the subsurface seabed in Aarhus Bay. The results reveal the extreme evolutionary regime controlling microbial life in the deep biosphere.
A life in slow motion
Microbial evolution is arrested in the subsurface seabed as cells are buried in under a continuously growing layer of deposited mud and their genetic material therefore remains unchanged during the millennia.
"This means that these buried microorganisms presumably have a very low adaptability, unlike the microbial life that otherwise surrounds us in our environment" says Kasper U. Kjeldsen, associate professor at the Center for Geomicrobiology, who participated in the research project.
Through genetic mutations microorganisms normally have the ability to develop new properties over a short time scale, thereby quickly adapting in response to their environment. But the researchers have shown that microbes grow in slow motion in the deep seabed with generation times of up to 100 years. Mutations therefore appear and spread very slowly in the subsurface populations. For comparison, intestinal bacteria typically have generation times of 20 minutes.
The microorganisms in the deep seabed live in an environment, which is extremely poor in food. Put simply, they chew on a lunch box, which has fed their ancestors for thousands of years, and the availability of energy is therefore minimal.
Buried alive
The microbial species we find in the deep seabed, are the same as those who lived at the seafloor for thousands of years ago. Unlike the majority of the members of surface community, these microorganisms survive burial deeper and deeper in to the subsurface.
It remains a mystery why these microorganisms have an inherent ability to grow under the extreme conditions that occur in the deep seabed.
The researchers hope that the new findings could ultimately help us to understand and reconstruct past environmental and climatic conditions based on analysis of the microbial species composition in deep marine sediment cores.
The discovery, which has changed our understanding of microbial life in the soil deep biosphere, was recentlt published in the highly acclaimed international journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States America (PNAS).
###
CONTACT
Associate Professor Kasper U. Kjeldsen
Email: [email protected]
www: http://pure.au.dk/portal/en/
Phone: +45 8715 6506
Professor Andreas Schramm
Email: [email protected]
www: http://pure.au.dk/portal/en/
Phone: +45 8715 6541
Center for Geomicrobiology and Section for Microbiology, Department of Bioscience, Aarhus University.
Media Contact
Associate Professor Kasper U. Kjeldsen
[email protected]
0045-87-15-65-06
@aarhusuni
http://www.au.dk