Researchers from National Institute for Physiological Sciences in Japan identify the mechanism underlying environmental stress-induced cardiac vulnerability to hemodynamic load in mice
Credit: National Institute for Physiological Sciences
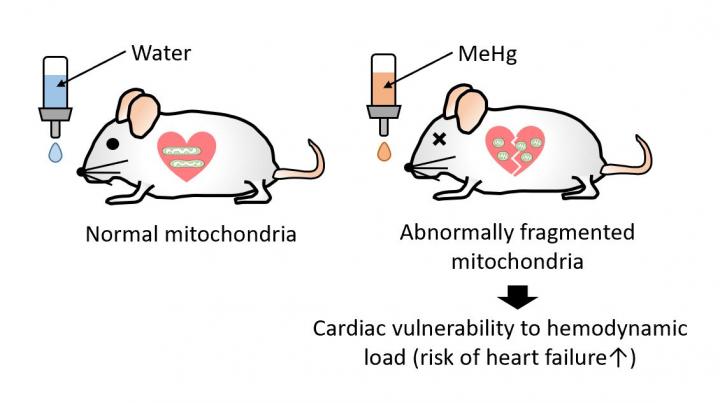
Okazaki, Japan – Although the widespread environmental contaminant methylmercury is largely associated with neurotoxic effects, it is also associated with increased risk for cardiovascular disease. Nishimura et al. found that mice exposed to a dose of methylmercury that was too low to cause neurotoxicity were more vulnerable to heart failure in response to pressure overload. Methylmercury removed a polysulfide group from Drp1, thereby removing an inhibitory brake on this protein, which resulted in increased Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission. Treating mice or human cardiomyocytes with a polysulfide group-releasing compound reversed fragility to mechanical overload induced by methylmercury. These results provide a molecular mechanism for the cardiotoxic effects of methylmercury and a possible strategy to avert these effects.
Chronic exposure to methylmercury (MeHg), an environmental electrophilic pollutant, reportedly increases the risk of human cardiac events. We report that exposure to a low, non-neurotoxic dose of MeHg precipitated heart failure induced by pressure overload in mice. Exposure to MeHg at 10 ppm did not induce weight loss typical of higher doses but caused mitochondrial hyperfission in myocardium through the activation of Drp1 by its guanine nucleotide exchange factor filamin-A. Treatment of neonatal rat cardiomyocytes (NRCMs) with cilnidipine, an inhibitor of the interaction between Drp1 and filamin-A, suppressed mitochondrial hyperfission caused by low-dose MeHg exposure. Modification of cysteine residues in proteins with polysulfides is important for redox signaling and mitochondrial homeostasis in mammalian cells. We found that MeHg targeted rat Drp1 at Cys624, a redox-sensitive residue whose SH side chain forms a bulky and nucleophilic polysulfide (Cys624-S(n)H). MeHg exposure induced the depolysulfidation of Cys624-S(n)H in Drp1, which led to filamin-dependent activation of Drp1 and mitochondrial hyperfission. Treatment with NaHS, which acts as a donor for reactive polysulfides, reversed MeHg-evoked Drp1 depolysulfidation and vulnerability to mechanical load in rodent and human cardiomyocytes and mouse hearts. These results suggest that depolysulfidation of Drp1 at Cys624-S(n)H by low-dose MeHg increases cardiac fragility to mechanical load through filamin-dependent mitochondrial hyperfission.
This work newly suggests the molecular mechanism how low-dose methylmercury makes hearts more fragile.
###
Media Contact
Motohiro Nishid
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




