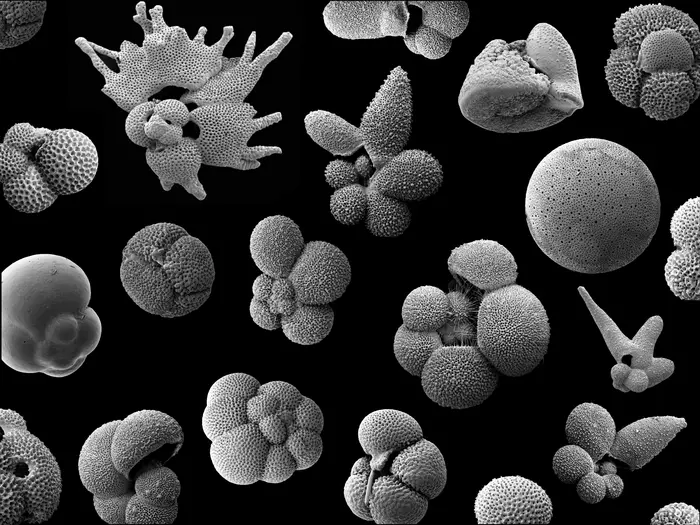
For hundreds of millions of years, the oceans have teemed with single-celled organisms called foraminifera, hard-shelled, microscopic creatures at the bottom of the food chain. The fossil record of these primordial specks offers clues into future changes in global biodiversity, related to our warming climate.
Credit: Tracy Aze / University of Leeds
For hundreds of millions of years, the oceans have teemed with single-celled organisms called foraminifera, hard-shelled, microscopic creatures at the bottom of the food chain. The fossil record of these primordial specks offers clues into future changes in global biodiversity, related to our warming climate.
Using a high-resolution global dataset of planktonic foraminifera fossils that’s among the richest biological archives available to science, researchers have found that major environmental stress events leading to mass extinctions are reliably preceded by subtle changes in how a biological community is composed, acting as a pre-extinction early warning signal.
The results are in Nature, co-led by Anshuman Swain, a Junior Fellow in the Harvard Society of Fellows, researcher in the Department of Organismic and Evolutionary Biology, and affiliate of the Museum of Comparative Zoology. A physicist by training who applies networks to biological and paleontological data, Swain teamed with co-first author Adam Woodhouse at the University of Bristol to probe the global, community structure of ancient marine plankton that could serve as an early warning system for future extinction of ocean life.
“Can we leverage the past to understand what might happen in the future, in the context of global change?” said Swain, who previously co-authored a study about the formation of polar ice caps driving changes in marine plankton communities over the last 15 million years. “Our work offers new insight into how biodiversity responds spatially to global changes in climate, especially during intervals of global warmth, which are relevant to future warming projections.”
The researchers used the Triton database, developed by Woodhouse, to ascertain how the composition of foraminifera communities changed over millions of years – orders of magnitude longer time spans than are typically studied at this scale. They focused on the Early Eocene Climatic Optimum, the last major period of sustained high global temperatures since the dinosaurs, analogous to worst-case global warming scenarios.
They found that, before an extinction pulse of 34 million years ago, marine communities became highly specialized everywhere but southern high latitudes, implying that these micro-plankton migrated en masse to higher latitudes and away from the tropics. This finding indicates that community-scale changes like the ones seen in these migration patterns are evident in fossil records long before actual extinctions and losses in biodiversity occur.
The researchers thus think it’s important to place emphasis on monitoring the structure of biological communities to predict future extinctions.
According to Swain, the results from the foraminifera studies open avenues of inquiry into other organismal groups, including other marine life, sharks, and insects. Such studies may spark a revolution in an emerging field called paleoinformatics, or using large spatiotemporally resolved databases of fossil records to glean new insights into the future Earth.
The researchers’ study was made possible by a longstanding National Science Foundation field study aboard the JOIDES Resolution research vessel, which over the last 55 years has conducted ocean drilling around the world. The project is set to expire this year.
Journal
Nature
DOI
10.1038/s41586-024-07337-9
Method of Research
Data/statistical analysis
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Biogeographic response of marine plankton to Cenozoic environmental changes
Article Publication Date
17-Apr-2024