Credit: RUDN University
An associate professor from RUDN University developed a computer model that describes all types of vehicle body damage caused by fatigue failure. According to his computer simulation, low speed on bumpy roads can be more dangerous for a vehicle body than moderate. The results of the study can help measure fatigue resistance in vehicles more accurately. An article about this study was published in the Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory journal.
A car on a bumpy road is subjected to different dynamic loads that causes fatigue failure. Cyclic stress leads to the formation of micro-cracks, and after some time, spot welded joints fail. The vehicle body structure is the main load-bearing part among other parts of the car. A vehicle body with damaged spot welded joints has lower level of vehicle crashworthiness. The level of fatigue resistance can be measured experimentally, but it requires a lot of expendable supplies and a testing site with special equipment. An associate professor from RUDN University created a mathematical model that describes all possible damages of spot welded joints caused by fatigue failure. Using this model, one can assess fatigue resistance of a car without conducting expensive experiments.
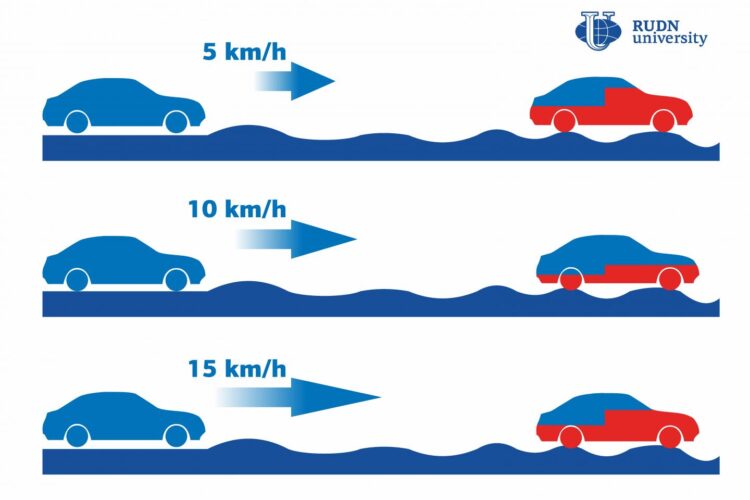
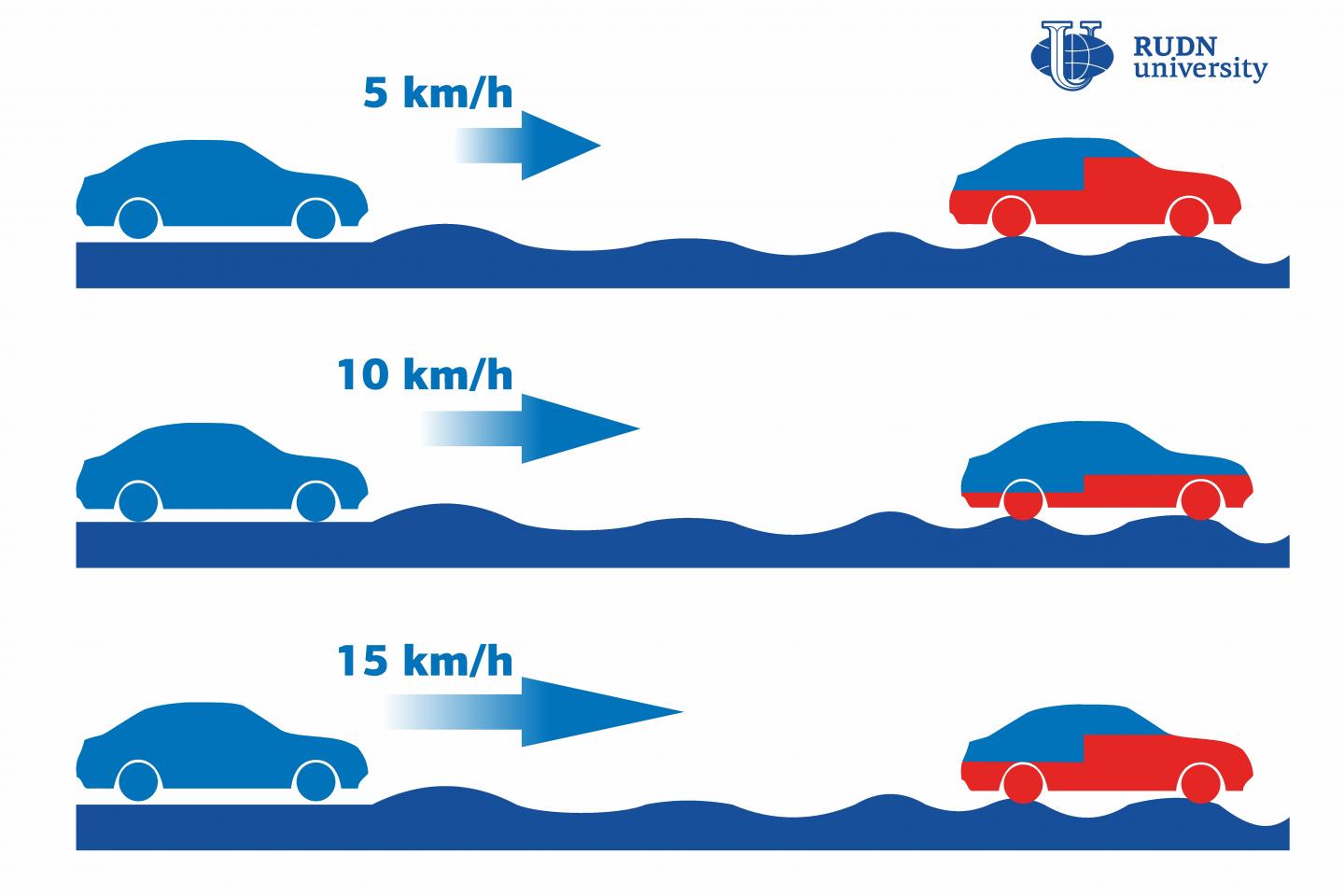
To develop this model, scientists used the so-called multibody dynamic method. It describes interactions within a system of details that move relative to one another. Then, the research team created a computer simulation in which the ‘car’ moved on different types of roads at different speeds. For example, type B was an almost perfectly smooth road with no bumps and the model moved on it at the speed of 50, 70, and 90 km/h. Type E was assigned to the bumpiest of all roads on which the speed was only 5, 10, and 15 km/h. With 4 types of roads and 3 speeds on each of them, the team conducted 12 experiments in total.
“We modeled the movement of a vehicle on different types of roads and at different speeds and measured force and momentum at 12 suspension attachment points, that is, the points at which the suspension transmits the load to the body. Each of these 12 points is affected by six force and momentum components. So, 72 values had to be calculated for each experiment,” said Kazem Reza Kasyzadeh, an associate professor at the Department of Mechanical and Instrumental Engineering of the Engineering Academy, RUDN University.
The results of this studyshow that low speeds on bumpy roads can cause more body damage than medium ones. For example, 100 spot weld joints were damaged when the model moved on a type E road at the speed of 5 km/h; 50–at 15 km/h, and only 40–at 10 km/h. Moreover, the front of a vehicle body turned out to be twice more prone to damage than the rear, regardless of the speed and road type. The team also found out that the service life of a vehicle body can be affected by the nugget diameter of spot welding joints (connection points at which two sheets are welded together). With the increase of the nugget diameter, the durability and service life of a body decreases.
###
Media Contact
Valeriya Antonova
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.