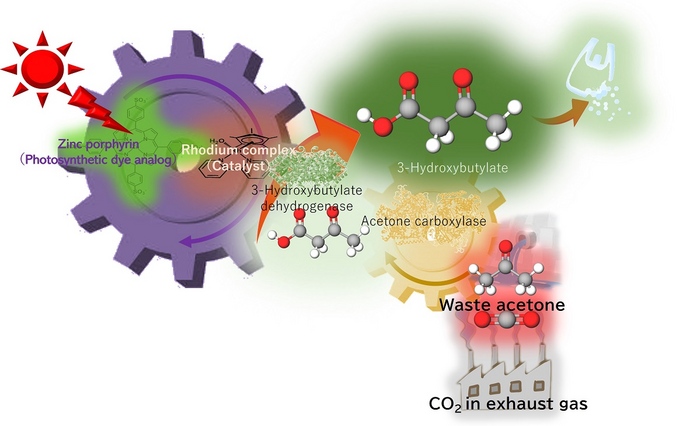
Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate—a biodegradable plastic—is a strong water-resistant polyester often used in packaging materials, made from 3-hydroxybutyrate as a precursor. In previous studies, a research team led by Professor Yutaka Amao from the Research Center for Artificial Photosynthesis at Osaka Metropolitan University, found that 3-hydroxybutyrate can be synthesized from CO2 and acetone with high efficiency, but only demonstrated this at higher concentrations of CO2 or sodium bicarbonate.
This new study aimed to reuse waste acetone from permanent marker ink and low concentrations of CO2—equivalent to exhaust gas from power plants, chemical plants, or steel factories. Acetone is a relatively inexpensive and reasonably harmless chemical used in many different laboratory settings, either for reactions or as a cleaning agent, which produces waste acetone. The acetone and CO2 acted as raw materials to synthesize 3-hydroxybutyrate using artificial photosynthesis, powered by light equivalent to sunlight.
“We focused our attention on the importance of using CO2 created by exhaust gas from thermal power plants and other sources to demonstrate the practical application of artificial photosynthesis,” explained Professor Amao.
After 24 hours, more than 60% of acetone had been successfully converted to 3-hydroxybutyrate. Their findings were published in Green Chemistry.
“In the future, we aim to develop artificial photosynthesis technology further, so that it can use acetone from liquid waste and as well as exhaust gas from the laboratory as raw materials,” stated Professor Amao.
###
Credit: Yutaka Amao, OMU
Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate—a biodegradable plastic—is a strong water-resistant polyester often used in packaging materials, made from 3-hydroxybutyrate as a precursor. In previous studies, a research team led by Professor Yutaka Amao from the Research Center for Artificial Photosynthesis at Osaka Metropolitan University, found that 3-hydroxybutyrate can be synthesized from CO2 and acetone with high efficiency, but only demonstrated this at higher concentrations of CO2 or sodium bicarbonate.
This new study aimed to reuse waste acetone from permanent marker ink and low concentrations of CO2—equivalent to exhaust gas from power plants, chemical plants, or steel factories. Acetone is a relatively inexpensive and reasonably harmless chemical used in many different laboratory settings, either for reactions or as a cleaning agent, which produces waste acetone. The acetone and CO2 acted as raw materials to synthesize 3-hydroxybutyrate using artificial photosynthesis, powered by light equivalent to sunlight.
“We focused our attention on the importance of using CO2 created by exhaust gas from thermal power plants and other sources to demonstrate the practical application of artificial photosynthesis,” explained Professor Amao.
After 24 hours, more than 60% of acetone had been successfully converted to 3-hydroxybutyrate. Their findings were published in Green Chemistry.
“In the future, we aim to develop artificial photosynthesis technology further, so that it can use acetone from liquid waste and as well as exhaust gas from the laboratory as raw materials,” stated Professor Amao.
###
About OMU
Osaka Metropolitan University is a new public university established by a merger between Osaka City University and Osaka Prefecture University in April 2022. For more science news, see https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/, and follow @OsakaMetUniv_en, or search #OMUScience.
Journal
Green Chemistry
DOI
10.1039/D3GC00247K
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Visible-light driven 3-hydroxybutyrate production from acetone and low concentrations of CO2 with the system of hybridized photocatalytic NADH regeneration and multi-biocatalysts
Article Publication Date
1-Mar-2023