Credit: Michael Bremner/cqc2t.org
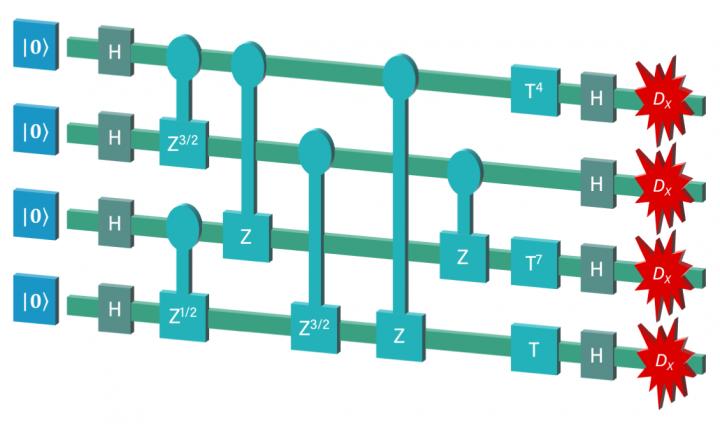
A team of researchers from Australia and the UK have developed a new theoretical framework to identify computations that occupy the 'quantum frontier' — the boundary at which problems become impossible for today's computers and can only be solved by a quantum computer. Importantly, they demonstrate that these computations can be performed with near-term, intermediate, quantum computers.
"Until recently it has been difficult to say definitively when quantum computers can outperform classical computers," said Professor Michael Bremner, Chief Investigator at the Centre for Quantum Computation and Communication Technology and founding member of the UTS Centre for Quantum Software and Information (UTS:QSI).
"The big challenge for quantum complexity theorists over the last decade has been to find stronger evidence for the existence of the quantum frontier, and then to identify where it lives. We're now getting a sense of this, and beginning to understand the resources required to cross the frontier to solve problems that today's computers can't."
The team has identified quantum computations that require the least known physical resources required to go beyond the capabilities of classical computers, significant because of the technological challenges associated with scaling up quantum computers.
Prof Bremner said that the result also indicates that full fault-tolerance may not be required to outperform classical computers. "To date, it has been widely accepted that error correction would be a necessary component of future quantum computers, but no one has yet been able to achieve this at a meaningful scale," said Bremner.
"Our work shows that while some level of error mitigation is needed to cross the quantum frontier, we may be able to outperform classical computers without the added design complexity of full fault tolerance," he said.
Dr Ashley Montanaro of the University of Bristol collaborated with Bremner to develop the framework.
"We started out with the goal of defining the minimum resources required to build a post-classical quantum computer, but then found that our model could be classically simulated with a small amount of noise, or physical imperfection," said Montanaro.
"The hope among scientists had always been that if the amount of noise in a quantum system was small enough then it would still be superior to a classical computer, however we have now shown that this probably isn't the case, at least for this particular class of computations," he said.
"We then realised that it is possible to use a classical encoding on a quantum circuit to overcome 'noise' in a much simpler way to mitigate these errors. The effectiveness of this approach was surprising. What it suggests is that we could use such structures to develop new quantum algorithms in a way that can directly avoid certain types of errors."
"This is a result that could lead to useful 'intermediate' quantum computers in the medium term, while we continue to pursue the goal of a full-scale universal quantum computer."
###
The paper detailing this research was selected for an editorial in the inaugural issue of Quantum journal, a new initiative in open-source, community-run academic publishing. UTS:QSI authors have been featured prominently in the journal's first edition. The work is supported with funding from the Australian Research Council through the Centre of Excellence and Future Fellowship programs.
Media Contact
Grainne Murphy
[email protected]
61-427-564-973
@cqc2t_
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag