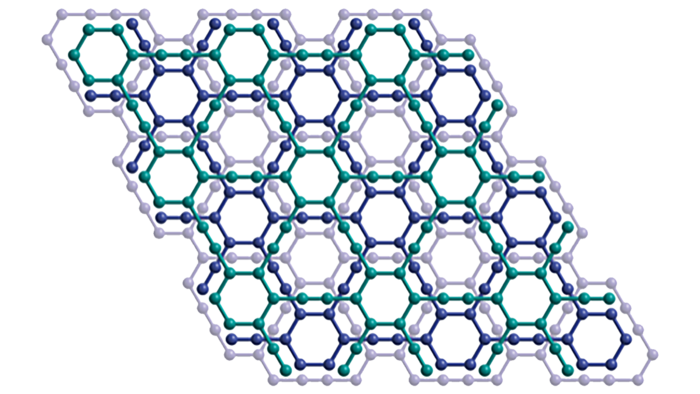
For over a decade, scientists have attempted to synthesize a new form of carbon called graphyne with limited success. That endeavor is now at an end, though, thanks to new research from the University of Colorado Boulder.
Credit: Yiming Hu
For over a decade, scientists have attempted to synthesize a new form of carbon called graphyne with limited success. That endeavor is now at an end, though, thanks to new research from the University of Colorado Boulder.
Graphyne has long been of interest to scientists because of its similarities to the “wonder material” graphene—another form of carbon that is highly valued by industry whose research was even awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2010. However, despite decades of work and theorizing, only a few fragments have ever been created before now.
This research, announced last week in Nature Synthesis, fills a longstanding gap in carbon material science, potentially opening brand-new possibilities for electronics, optics and semiconducting material research.
“The whole audience, the whole field, is really excited that this long-standing problem, or this imaginary material, is finally getting realized,” said Yiming Hu, lead author on the paper and 2022 doctoral graduate in chemistry.
Scientists have long been interested in the construction of new or novel carbon allotropes, or forms of carbon, because of carbon’s usefulness to industry, as well as its versatility.
There are different ways carbon allotropes can be constructed depending on how sp2, sp3 and sp hybridized carbon (or the different ways carbon atoms can bind to other elements), and their corresponding bonds, are utilized. The most well-known carbon allotropes are graphite (used in tools like pencils and batteries) and diamonds, which are created out of sp2 carbon and sp3 carbon, respectively.
Using traditional chemistry methods, scientists have successfully created various allotropes over the years, including fullerene (whose discovery won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1996) and graphene.
However, these methods don’t allow for the different types of carbon to be synthesized together in any sort of large capacity, like what’s required for graphyne, which has left the theorized material—speculated to have unique electron conducting, mechanical and optical properties—to remain that: a theory.
But it was also that need for the nontraditional that led those in the field to reach out to Wei Zhang’s lab group.
Zhang, a professor of chemistry at CU Boulder, studies reversible chemistry, which is chemistry that allows bonds to self-correct, allowing for the creation of novel ordered structures, or lattices, such as synthetic DNA-like polymers.
After being approached, Zhang and his lab group decided to give it a try.
Creating graphyne is a “really old, long-standing question, but since the synthetic tools were limited, the interest went down,” Hu, who was a PhD student in Zhang’s lab group, commented. “We brought out the problem again and used a new tool to solve an old problem that is really important.”
Using a process called alkyne metathesis—which is an organic reaction that entails the redistribution, or cutting and reforming, of alkyne chemical bonds (a type of hydrocarbon with at least one carbon-carbon triple covalent bond)—as well as thermodynamics and kinetic control, the group was able to successfully create what had never been created before: A material that could rival the conductivity of graphene but with control.
“There’s a pretty big difference (between graphene and graphyne) but in a good way,” said Zhang. “This could be the next generation wonder material. That’s why people are very excited.”
While the material has been successfully created, the team still wants to look into the particular details of it, including how to create the material on a large scale and how it can be manipulated.
“We are really trying to explore this novel material from multiple dimensions, both experimentally and theoretically, from atomic-level to real devices,” Zhang said of next steps.
These efforts, in turn, should aid in figuring out how the material’s electron-conducting and optical properties can be used for industry applications like lithium-ion batteries.
“We hope in the future we can lower the costs and simplify the reaction procedure, and then, hopefully, people can really benefit from our research,” said Hu.
For Zhang, this never could have been accomplished without the support of an interdisciplinary team, adding: “Without the support from the physics department, without some support from colleagues, this work probably couldn’t be done.”
Other authors on the paper include Chenyu Wu, Qingyan Pan and Yingjie Zhao from Qingdao University of Science and Technology; and Yinghua Jin, Rui Lyu, Vikina Martinez, Shaofeng Huang, Jingyi Wu, Lacey J. Wayment, Noel A. Clark, Markus B. Raschke from CU Boulder.
Journal
Nature Synthesis
DOI
10.1038/s44160-022-00068-7
Article Title
Synthesis of γ-graphyne using dynamic covalent chemistry
Article Publication Date
9-May-2022




