Credit: Canadian Journal of Cardiology
Philadelphia, January 31, 2018 – A new study published in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology determined that patients with acute cardiac syndrome (ACS) and cardiogenic shock (CS), who live far from the only cardiac catheterization facility in Nova Scotia, Canada, have a survival rate about half that of patients with more direct access.
ACS includes various forms of acute myocardial infarction ("heart attacks") and is a major medical emergency. CS is one of the most serious complications and leading causes of mortality among patients hospitalized with ACS. Both conditions require immediate treatment and invasive cardiac care. The optimal management of patients with ACS usually requires access to invasive coronary diagnostic and intervention such as percutaneous coronary interventions (PCI) to open up blocked arteries. The only institution capable of providing invasive cardiac catheterization for PCI and coronary artery bypass surgery in Nova Scotia is the Queen Elizabeth II Health Sciences Centre (QEII-HSC) in Halifax. This study evaluated whether the distances involved in getting patients to QEII-HSC affect survival rates.
'While PCI is often considered the preferred mode of reperfusion if performed by an experienced team in a timely fashion, it may not always be possible," explained lead investigator Jean-François Légaré, MD, FRCSC, Head of Cardiac Surgery at the New Brunswick Heart Centre, Saint John, NB, Canada. "This is particularly true in Nova Scotia where a large proportion of the population lives in rural communities that are several hours from the single cardiac catheterization laboratory located centrally in Halifax. Furthermore, this is compounded by logistic challenges in arranging ambulance services (air versus ground), lack of onsite physician coverage, and limited resources."
Using data from the clinical database of Cardiovascular Health Nova Scotia, 418 consecutive patients diagnosed with ACS and CS and admitted to hospital in 2009-2013 were included. Of these, 309 (73.9 percent) were close to or directly admitted to QEII-HSC and were classified as having direct access to invasive care. Of the 109 patients in other parts of the province, 64.2 percent were transferred to QEII-HSC. The mortality rate among the 309 patients with direct access to invasive care was significantly lower than the 109 patients who did not have access (41.7 percent vs. 83.5 percent, p
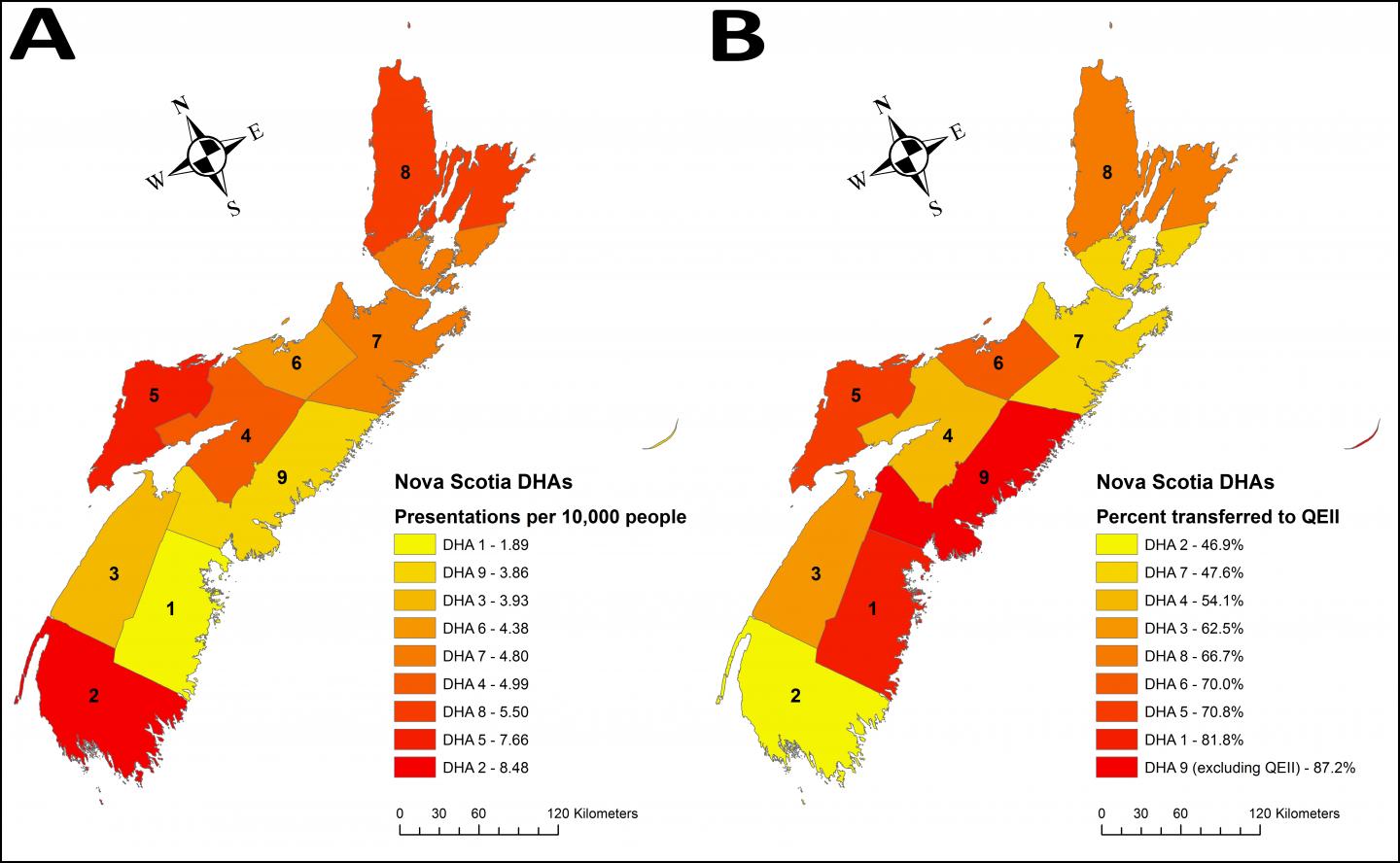
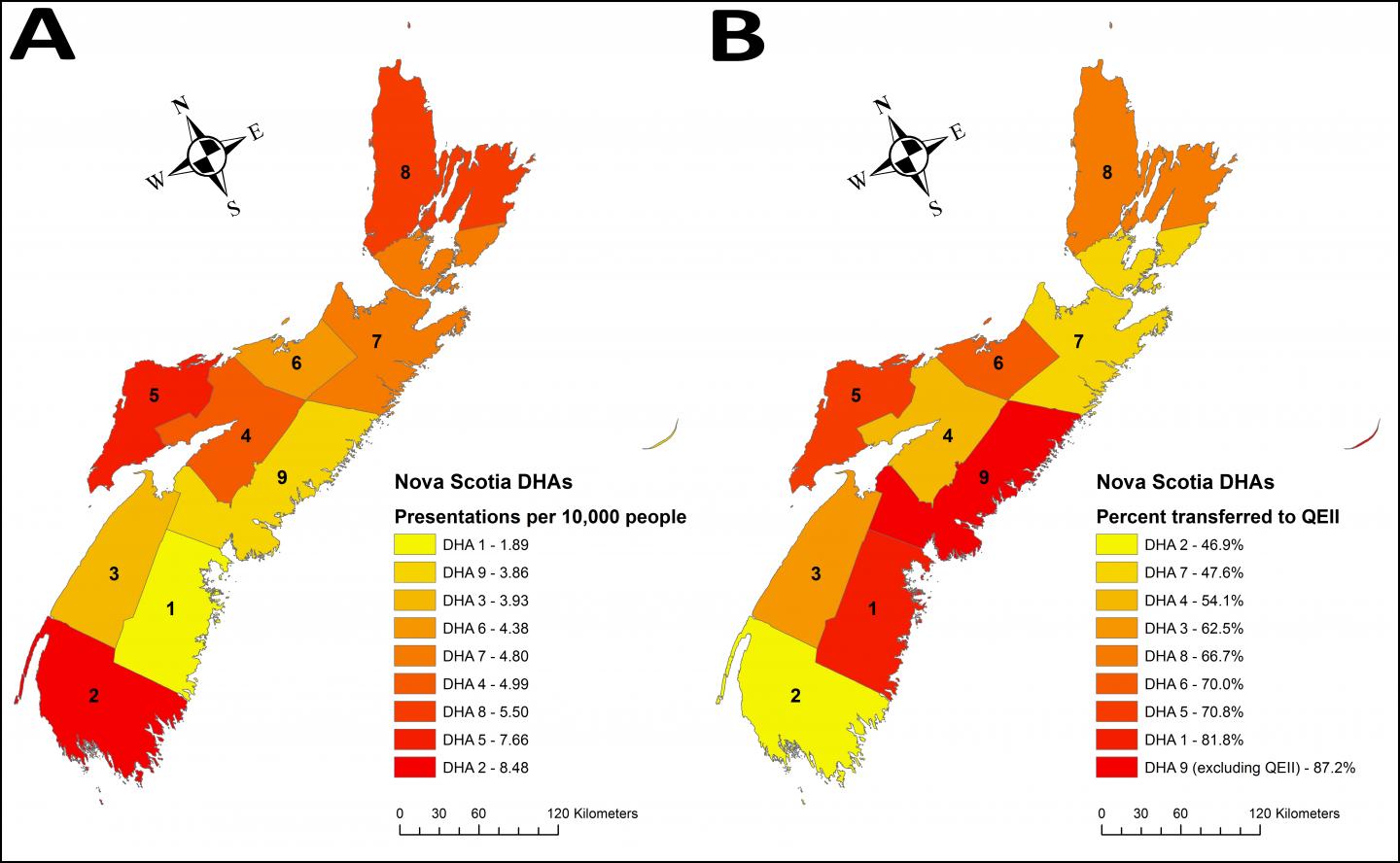
When comparing patients presenting with ACS + CS relative to the population in each of the nine separate District Health Authorities (DHA) in Nova Scotia, investigators identified regions with a greater than four-fold difference from the highest to lowest incidence, with the DHAs at the geographic extremes from Halifax having the highest incidence (see maps in Figure). They also determined that the percentage of cases resulting in transfer to QEII-HSC from each DHA ranged from about 47 percent (DHA 2) to about 87 percent (DHA 9, including QEII-HSC). This almost two-fold difference in transfer rates was congruent with the areas of highest incidence.
The investigators note that during the five-year study period, the incidence of ACS complicated by CS was 2.9 percent, which is lower than the 6.3 percent previously found in Nova Scotia, and which follows a global trend of decreasing incidence of CS. They also found that the overall mortality rate for ACS + CS patients decreased to 52.6 percent versus the previously reported 60.1 percent. Nevertheless, the marked disparities across the Province point to areas for improvement.
According to Dr. Légaré, "Our study suggests that patients living furthest from the only cardiac catheterization center in the Province have the highest rates of ACS + CS and lowest access to invasive care. Given that access to invasive care appears to provide the best chance of survival, continued public health efforts to increase access and gaining a better understanding of barriers to care are needed."
###
Media Contact
Eileen Leahy
[email protected]
732-238-3628
@elseviernews
http://www.elsevier.com
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cjca.2017.11.021