Credit: Deepak Bhandari & Dmitry Lapin
Plant defense against invading pathogens relies upon effective recognition of non-self organisms and a subsequent signaling response characterized by reprogramming of host gene expression and localized cell death to combat infection and provide resistance. At a molecular level, plant responses are initiated by the recognition of so-called effectors by intracellular receptors in a process known as effector-triggered immunity (ETI). While the importance of the recognition itself and the transcriptional reprogramming are well accepted, less is known about how the two are linked, i.e., how recognition is translated into resistance?
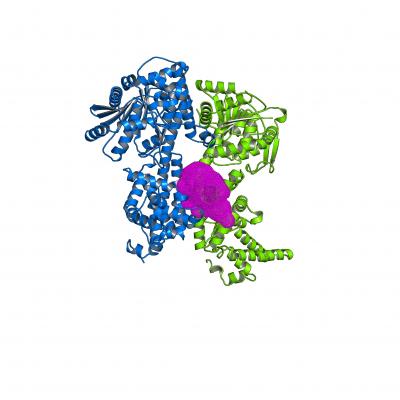
Jane Parker and her group at the MPIPZ study a protein called enhanced disease susceptibility 1 (EDS1), a key player in the plant’s immune arsenal. By promoting reprogramming of gene expression, cell death and resistance upon effector recognition, EDS1 acts as a link between the recognition and signaling modules of plant immunity. It carries out this function, at least in part, by partnering up with two other proteins, phytoalexin deficient 4 (PAD4) and senescence-associated gene 101 (SAG101) and by promoting accumulation of the defense hormone salicylic acid (SA) as well as blocking the detrimental actions of a bacterial virulence molecule. In work just published in the journal Nature Communications, Deepak Bhandari, Parker, and her group have identified a key surface in the EDS1 protein that enables it to carry out its functions in plant immunity.
To better characterize the role of EDS1 in immune signaling, the authors focused on a previously uncharacterized portion of the EDS1 protein at the surface of a cavity formed between EDS1 and its partners. When the authors switched one of the positively charged amino acids lining this cavity to a neutral one, they found that plants were as susceptible to infection as those lacking EDS1 completely. These plants failed to accumulate SA in a timely manner, and transcriptional reprogramming was also sluggish. EDS1 still provided some resistance in experiments where both the effects of SA and transcriptional reprogramming were abrogated, indicating that EDS1, and specifically the positively charged cavity, promotes an as yet uncharacterized third branch of ETI.
In protein-protein interaction experiments, the authors observed that the mutant EDS1 could still bind its partner PAD4 but was defective even if expressed at high levels in plant cells. What then is the importance of the positive charge if it is not crucial for EDS1 to bind its partners? “Most likely the positive charge in the cavity is important for the binding of EDS1 and its partners to yet other molecules”, says Jane Parker. In the future, the authors plan to discover the identity of these molecules and to better characterize the newly uncovered third branch of EDS1 immune signaling.
###
Media Contact
Prof. Jane E. Parker
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




