Credit: Aleksandra Krolik
Researchers from the Muñiz group have published a paper in Angewandte Chemie – International Edition presenting a new metal-free methodology for the photo-catalysed nucleophilic fluorination of aliphatic hydrocarbon bonds. Daniel Bafaluy, first author of the paper shares the story behind it:
What have you done?
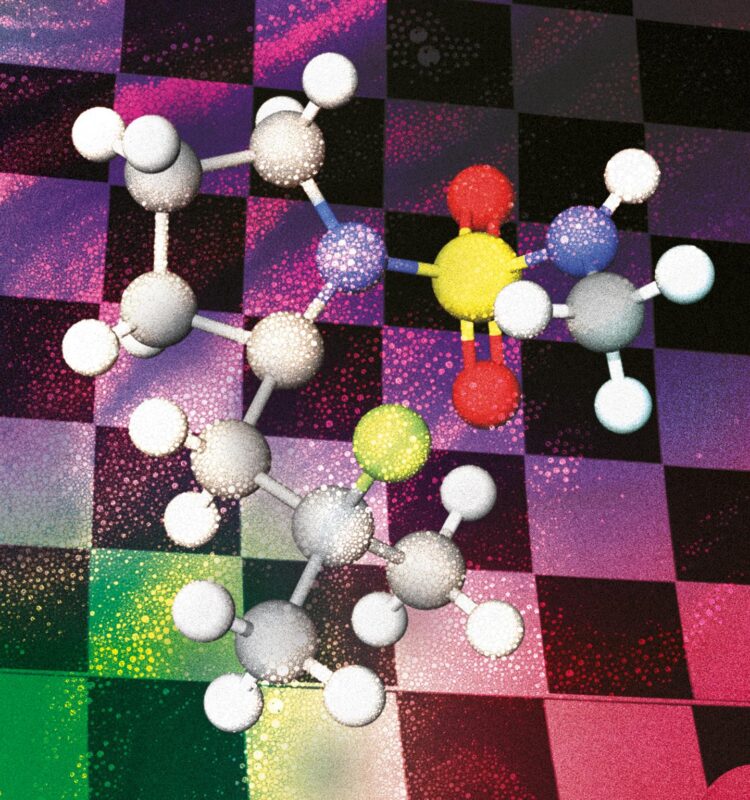
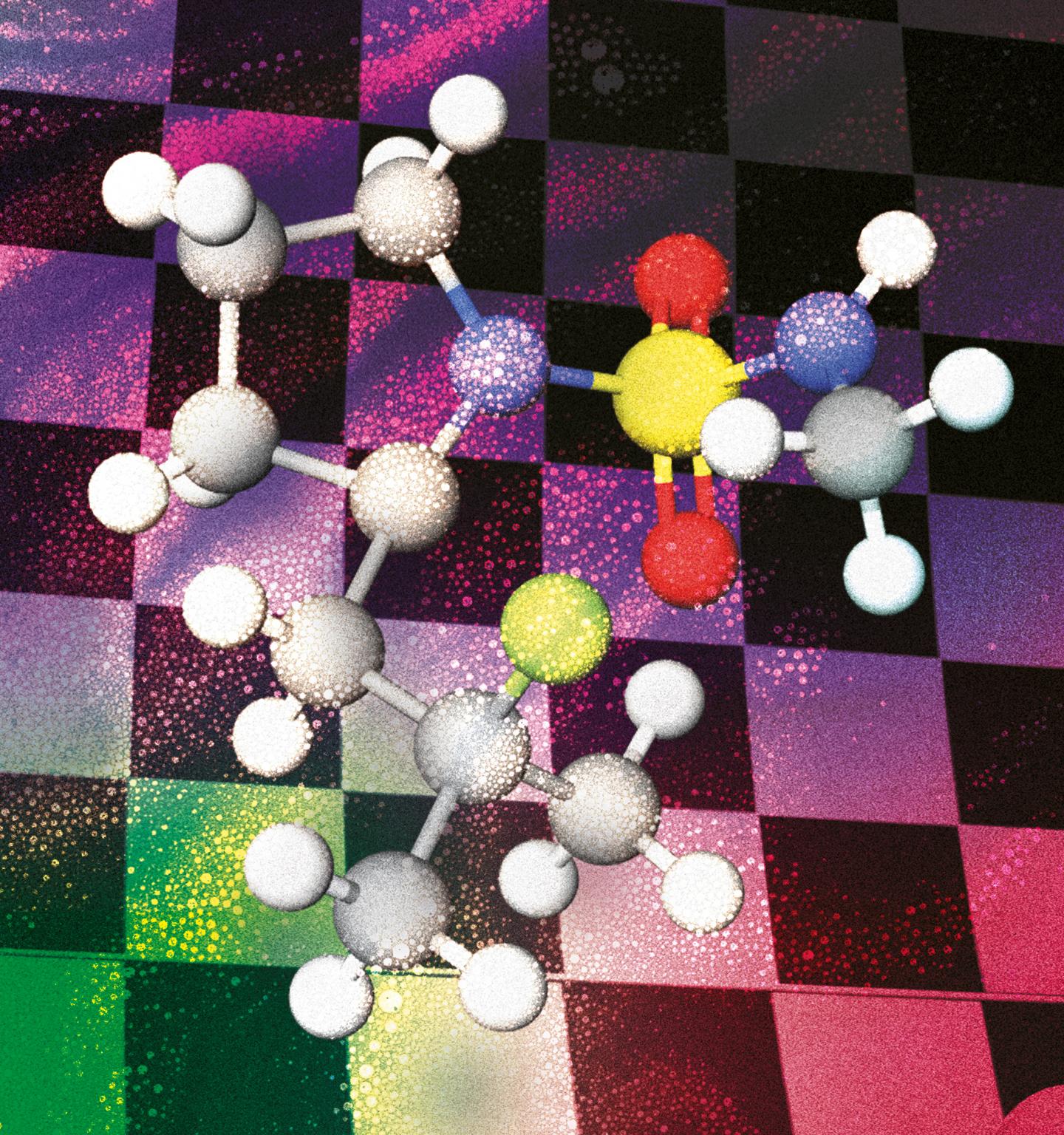
The paper describes a new metal-free method to selectively introduce Fluor in aliphatic C-H bonds that can be applied to late-stage functionalisation. The current methodologies used to this purpose employ electrophilic Fluor reagents, but they present economic as well as environmental drawbacks. So, we decided to take a page from the group’s strategies to carry out aminations using an iodine oxidant and applied the know-how to develop nucleophilic fluorinations.
By using an iodine oxidant, we create in situ a nitrogen-iodine bond which we then photochemically break to create the nitrogen radical. Breaking that bond is quite easy because it’s a very labile species and doesn’t require much energy – a regular lightbulb is enough for this. The new strategy works under mild conditions and uses a (nucleophilic) ammonium fluoride as fluorine source and molecular Iodine as a catalyst to address position-selectivity and produce fewer by-products than the current electrophilic Fluor methods.
Since we employed the nitrogen functionality as the directing group, the strategy can be used on different amine derivatives. In general, we can control the position selectivity by means of the directing group choice and specifically insert the Fluor atom on tertiary positions. This way we gain access to two different kinds of compounds: 1,3 or 1,4 fluoroamines with the same protocol. For example, the reaction works in the presence of benzylic positions, heteroatoms in phenyl groups, etc.
Why is this important?
From a basic-research viewpoint, this work demonstrates that Iodine catalysis has a big potential to be further explored. We present a novel nucleophilic Fluor and metal-free strategy that combines the power of an Iodonium III oxidiser and photochemistry, which is unprecedented in the literature. Also, with our strategy, we selectively control the position where we will introduce the Fluor.
Finally, fluorinated compounds are important from a biological and pharmacological point of view, the presence Fluor enhances the bio-utility of these compounds as drugs or pesticides, among other applications. Unfortunately, their synthesis is quite complex. So, our new method can be quite useful for the late-stage functionalisation of organic molecules.
What’s next?
Aside from its use for late-stage-functionalisation, we would have liked to further optimise the process and apply it to radio-labelling for medical applications, like PET scans for instance. Some of the most common compounds used as radiotracers are molecules containing Fluor-18 isotope, which is generated in synchrotrons and has a 20-minute half-life time. This means the isotope must be rapidly inserted into the radiotracers before injecting it to the patient and doing the scan. Therefore, that needs to be a fast-paced procedure. Current methods use electrophilic Fluor but synchrotrons generate nucleophilic Fluor-18, so our new methodology could be easily adapted to fulfil these medical applications.
###
Media Contact
Berta Carreño
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.