Researchers from Osaka University and the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology show that cancer cells cultured on Matrigel migrate to form a network structure as they do in vivo, and describe the forces responsible
Credit: Osaka University
Osaka, Japan – Cancer cells are known to migrate and collaborate to form networks that function as conduits providing access to nutrients and blood vessels. Now, researchers in Japan have generated similar large-scale structures from cancer cells in the laboratory and thus gained a better understanding of the underlying forces and their interactions.
Proliferating cells often cooperate in order to form self-beneficial large-scale structures; these include bacterial biofilms, protective epithelial monolayers or even more complex configurations such as endothelial capillaries. Malignant cells, in a process called vasculogenic mimicry, form structures that facilitate access to nutrients for tumor growth and to blood vessels for metastasis. The biochemical and biophysical mechanisms are not well understood, as this purposive behavior was difficult to reproduce experimentally until now.
In a study published in the Biophysical Journal in March 2020, researchers from Osaka University in collaboration with Advanced ICT Research Institute, the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT), have demonstrated migration and large-scale structure formation by cancer cells grown on Matrigel substrate, and have developed simple simulated models that reproduce their observations.
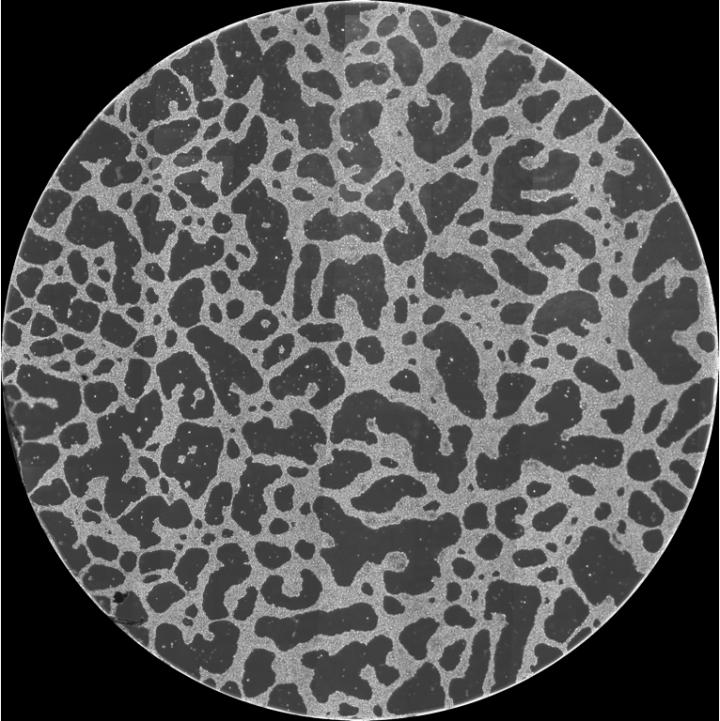
The research team first cultured HeLa cells, a strain of epithelial-like cervical cancer cells, on Matrigel, a gelatinous protein mixture resembling the extracellular environment of many tissues, and showed that the cells migrate aggressively and form large-scale structures. This was previously difficult to achieve in vitro as HeLa cells are relatively non-motile on glass. Using time-lapse imaging they analyzed the cell migration patterns and quantified the large-scale structures with a two-point correlation function.
“We observed that HeLa cells first exhibited increased motility on Matrigel, which later decreased after they integrated into a spatially distinct structure,” explains Dr. Tokuko Haraguchi, senior researcher at NICT. “We also noted that HeLa cells in close proximity formed bridges between cell aggregates, and that structures were formed in a cell-density dependent manner.”
To explain these results, the researchers developed a simulated model in which cells migrate and interact using two distinct forces: remote forces that act at a distance through substrate deformation, and contact forces between cells in physical proximity. By selectively enabling these forces, they modelled the three types of structures formed–islands, network-like structures and continents–according to cell density.
Tadashi Nakano, lead author, explains the potential implications of their findings. “Cancer cells may rely on vasculogenic mimicry for survival and proliferation,” he says. “A complete understanding of this process can, by manipulation of the relevant cell density and force parameters, inhibit these network-like structures. This may have great potential for combating cancer.”
###
The article, “Roles of remote and contact forces in epithelial cell structure formation” was published in the Biophysical Journal at DOI: https:/
About Osaka University
Osaka University was founded in 1931 as one of the seven imperial universities of Japan and now has expanded to one of Japan’s leading comprehensive universities. The University has now embarked on open research revolution from a position as Japan’s most innovative university and among the most innovative institutions in the world according to Reuters 2015 Top 100 Innovative Universities and the Nature Index Innovation 2017. The university’s ability to innovate from the stage of fundamental research through the creation of useful technology with economic impact stems from its broad disciplinary spectrum.
Website: https:/
About NICT (National Institute of Information and Communications Technology)
As the only public institution that specializes in Information and Communications Technology (ICT), NICT promotes research and development, comprehensively carries out collaboration with industry, academia, and government and business promotion, etc., and works toward the realization of an affluent, safe and secure society.
Website: https:/
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
[email protected]
81-661-055-886
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




