Credit: Yared B. Yohannes et al., Environmental Research, June 5, 2020
Scientists have unveiled a correlation between high blood lead levels in children and methylation of genes involved in haem synthesis and carcinogenesis, indicating a previously unknown mechanism for lead poisoning.
Lead poisoning is a well-documented disease, the incidence of which has drastically reduced since the use of lead has been curtailed. Nevertheless, many areas across the world still have unsafe levels of lead in the environment. Lead poisoning causes symptoms such as abdominal pain, kidney failure and infertility, among others, but the most damaging effects are seen in children, where it causes neurological and developmental deterioration; however, a number of mechanisms behind it have been elusive.
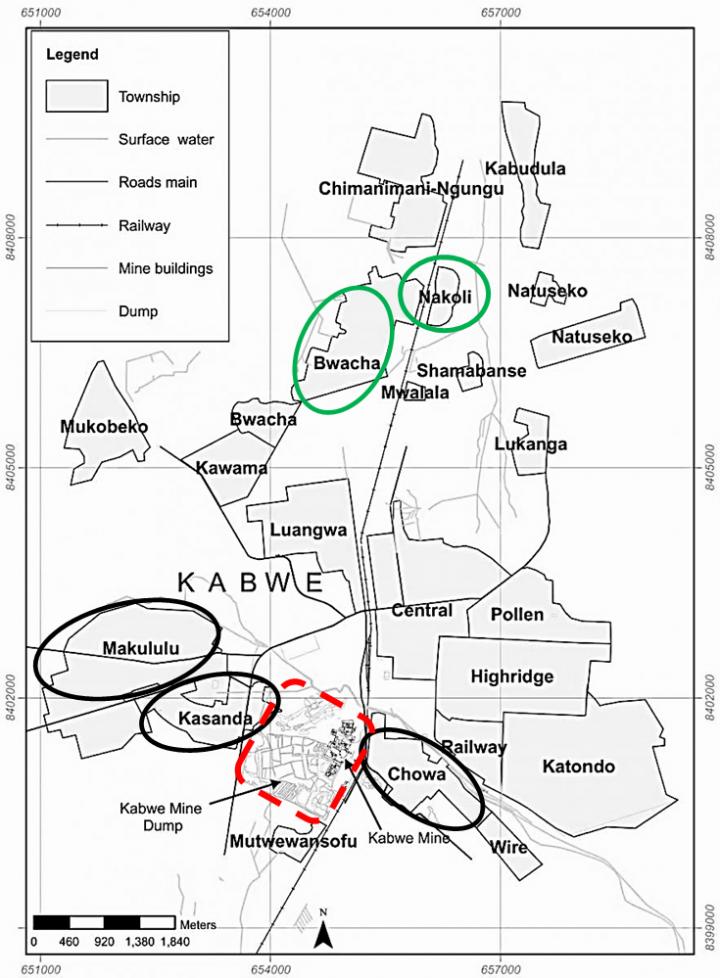
In the current work, published in the journal Environmental Research, scientists at Hokkaido University collaborated with colleagues at the University of Zambia to investigate blood lead levels in 140 children aged 2 to 10 years in Kabwe, Zambia. Children were chosen from townships close to and distant from an old, highly polluted lead-zinc mine. According to a survey conducted by the Blacksmith Institute (now, Pure Earth), due to this mine, Kabwe was considered one of the 10 most polluted places on Earth in 2013.
Blood lead levels were measured in all children. The scientists discovered that children living closer to the mine had blood levels that were three times higher than that of children living further away. They then used a technique called methylation-specific polymerase chain reaction (MSP) to determine the methylation of the DNA sequences. Methylation is a process by which methyl (CH3) groups are added to DNA; this modification generally causes the activity of genes to reduce.
Increased blood lead levels correlated positively with aberrant, increased methylation of DNA responsible for the expression of genes. The genes affected were ALAD, which synthesizes a key compound in the development of red blood cells; and p16, a tumour suppressor gene, which is frequently inactivated in different types of cancer.
This study has established the correlation between blood lead levels and aberrant methylation of DNA. It has also revealed a major healthcare issue in children in the region. Future work in this area would involve large-scale studies to determine the true extent of lead poisoning, as well as setting up an effort to provide children in the region with the necessary care and treatment. “The ultimate goal is,” Dr. Yohannes says, “to achieve a lead-free population to ensure a healthy future.”
Dr. Yared B. Yohannes, Assistant Professor Shouta Nakayama, and Professor Mayumi Ishizuka from the Laboratory of Toxicology were the key contributors to this research. The laboratory has been studying lead poisoning in Kabwe for over half a decade. Their research is part of ongoing collaborations with eight African countries on the project Clarification of the Effect of Continued Environmental Contamination in Africa on Humans and Animals.
###
Media Contact
Sohail Keegan Pinto
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




