Credit: Michigan Medicine
Strokes and heart attacks often strike without warning. But, a unique application of a medical camera could one day help physicians know who is at risk for a cardiovascular event by providing a better view of potential problem areas.
A new paper in Nature Biomedical Engineering reports proof-of-concept results for this new imaging platform for atherosclerosis.
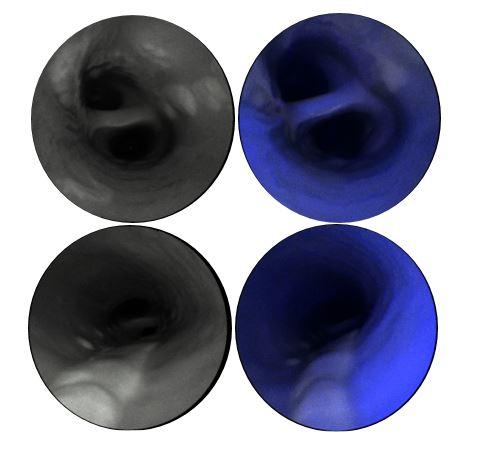
"The camera actually goes inside the vessels," says first author Luis Savastano, M.D., a Michigan Medicine resident neurosurgeon. "We can see with very high resolution the surface of the vessels and any lesions, such as a ruptured plaque, that could cause a stroke. This technology could possibly find the 'smoking gun' lesion in patients with strokes of unknown cause, and may even be able to show which silent, but at-risk, plaques may cause a cardiovascular event in the future."
The scanning fiber endoscope, or SFE, used in the study was invented and developed by co-author and University of Washington mechanical engineering research professor Eric Seibel, Ph.D. He originally designed it for early cancer detection by clearly imaging cancer cells that are currently invisible with clinical endoscopes.
The Michigan Medicine team used the instrument for a new application: acquiring high-quality images of possible stroke-causing regions of the carotid artery that may not be detected with conventional radiological techniques.
Researchers generated images of human arteries using the SFE, which illuminates tissues with multiple laser beams, and digitally reconstructs high-definition images to determine the severity of atherosclerosis and other qualities of the vessel wall.
"In addition to discovering the cause of the stroke, the endoscope can also assist neurosurgeons with therapeutic interventions by guiding stent placement, releasing drugs and biomaterials and helping with surgeries," Seibel says.
In addition, the SFE uses fluorescence indicators to show key biological features associated with increased risk of stroke and heart attacks in the future.
"The ability to identify and monitor the biological markers that render a plaque unstable and at risk for rupture could enable the detection of individuals within high-risk populations who are most likely to suffer from cardiovascular events, and therefore benefit the most from preventive treatment during the asymptomatic stage," says B. Gregory Thompson, M.D., professor of neurosurgery at the University of Michigan Medical School and a senior author on the new paper.
"In addition, plaque-specific data could help physicians modulate treatment intensity of atherosclerosis, which is currently based on systemic surrogates such us cholesterol and blood sugar levels and occurrence of cardiovascular events such as stroke or myocardial infarction."
All research is in the pre-clinical phase.
###
Additional authors: Quan Zhou, Arlene Smith, Karla Vega, Carlos Murga-Zamalloa, David Gordon, Jon McHugh, Lili Zhao, Michael M. Wang, Aditya Pandey, Jie Xu, Jifeng Zhang, Y. Eugene Chen and Thomas D. Wang.
Funding: Cerebrovascular Research Award, Joint Section on Cerebrovascular Surgery of the American Association of Neurological Surgeons and Congress of Neurological Surgeons, and National Institutes of Health (U54 CA163059, R01 706 EB016457, R01 HL129778, R01 HL117491 and R01CA200007).
Disclosure: Seibel participates in royalty sharing with his employer, the University of Washington, which has ownership of patents that may gain or lose financially through this publication.
Media Contact
Haley Otman
[email protected]
734-764-2220
@UMHealthSystem
http://www.med.umich.edu