All living cells harbor nuclei—key biological structures that play an important role in information storage, retrieval, and duplication of genetic information. In mammals, these nuclei possess the nuclear envelope (NE)—the biological shield that protect nuclei from environmental stimuli (e.g., mechanical stress) and the associated damage. However, certain external stimuli can cause damage to the NE. When this happens, various mechanisms kick in to initiate the process of NE repair. However, the precise mechanism of NE repair has remained elusive.
Credit: Tokyo Tech
All living cells harbor nuclei—key biological structures that play an important role in information storage, retrieval, and duplication of genetic information. In mammals, these nuclei possess the nuclear envelope (NE)—the biological shield that protect nuclei from environmental stimuli (e.g., mechanical stress) and the associated damage. However, certain external stimuli can cause damage to the NE. When this happens, various mechanisms kick in to initiate the process of NE repair. However, the precise mechanism of NE repair has remained elusive.
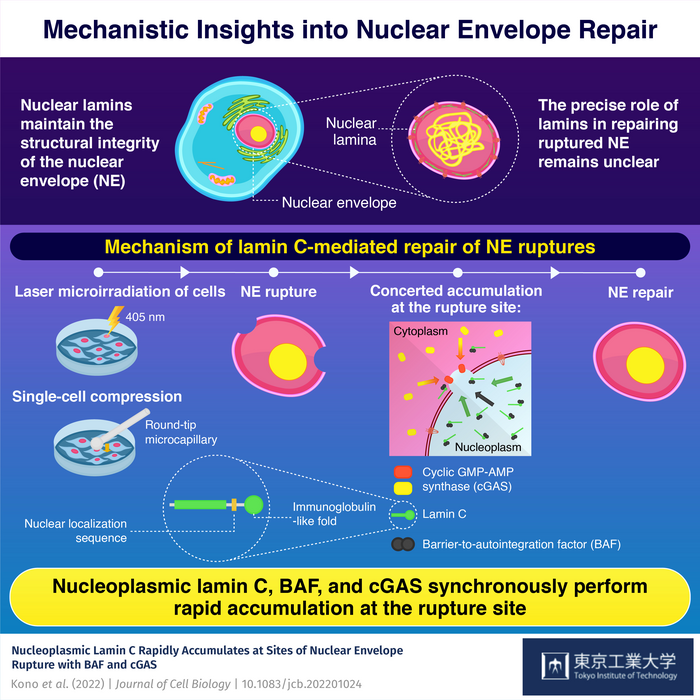
Quite recently, an international team of researchers led by Dr. Takeshi Shimi, Specially Appointed Associate Professor at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), was able to identify the precise role of the key components involved in this important physiological process. Using a high-power laser to induce NE rupture, the researchers demonstrated how a “repair army” comprising lamin C, Barrier-to-autointegration factor (BAF), and cytoplasmic cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS), important proteins with key biological functions, synergistically facilitated the process of NE repair in mouse embryonic fibroblasts. The findings of their study were published in Journal of Cell Biology.
“In mammalian cell nuclei, the nuclear lamina underlies the NE to maintain nuclear structure. The nuclear lamins is the major structural components of the nuclear lamina and is involved in the protection against NE rupture caused by mechanical stress. Our analyses using immunofluorescence and live-cell imaging revealed that a nucleoplasmic pool of lamin C rapidly accumulates at the sites of laser-microirradiation-induced NE rupture in mammalian cells,” explains Dr. Shimi, elaborating on their findings.
The process of NE repair is sometimes hampered owing to the presence of certain mutations. In their study, the research team successfully identified key lamin C mutations—structural and functional modifications that adversely affect the repair process. For instance, they found that rapid repair did not occur or was weakened in lamin C mutants, namely R435C, R471C, R527H, A529V, and K542N, compared to wild type (control) lamin C that did not have these mutations. Moreover, the two mutants are found in patients with laminopathies and are responsible for causing cardiac and skeletal muscle diseases, dysplasia, and progeroid syndrome.
Based on these findings, Dr. Shimi concludes, “The accumulation of nuclear BAF and cGAS at the rupture sites was in part dependent on lamin A/C. Our results suggest that nucleoplasmic lamin C, BAF, and cGAS concertedly accumulate at sites of NE rupture for rapid repair.”
Let us hope that the insights gained from this breakthrough will lead to a better understanding of various rare genetic disorders, such as laminopathies.
Journal
Journal of Cell Biology
DOI
10.1083/jcb.202201024
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Nucleoplasmic Lamin C Rapidly Accumulates at Sites of Nuclear Envelope Rupture with BAF and cGAS
Article Publication Date
27-Oct-2022




