Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University(TMDU) find that a periodontal pathogen, Porphyromonas gingivalis, inhibits autophagosome–lysosome fusion, and can therefore worsen cardiac remodeling and cause cardiac rupture after myocardial infarction
Credit: Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, TMDU
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University(TMDU) find that a periodontal pathogen, Porphyromonas gingivalis, inhibits autophagosome–lysosome fusion, and can therefore worsen cardiac remodeling and cause cardiac rupture after myocardial infarction
Tokyo, Japan – Brushing and flossing regularly can keep your smile shining as brightly as ever, but did you know that it could also help protect your heart? Now, researchers in Japan report that an infected mouth could lead to a broken heart.
In a study published last month in the International Journal of Oral Science, researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University(TMDU) have revealed that a common oral pathogen can stop cardiac myocytes from repairing themselves after a heart attack caused by coronary heart disease.
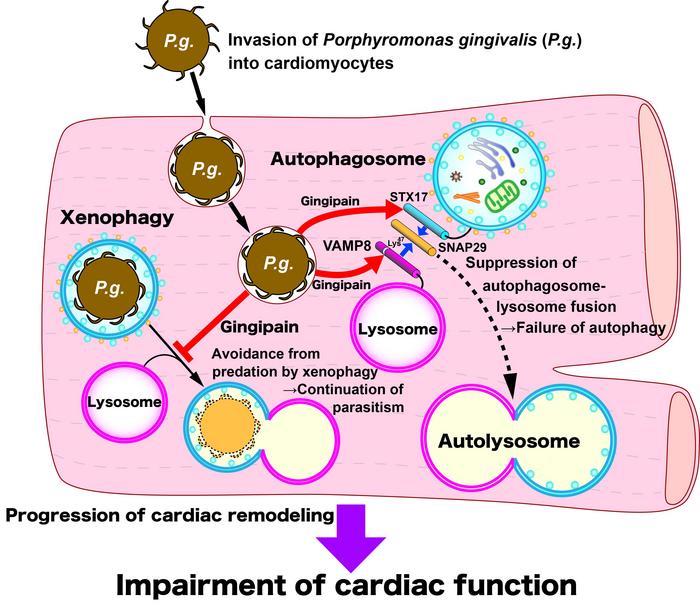
Heart attacks occur when blood flow in the coronary arteries is blocked, resulting in an inadequate supply of nutrients and oxygen to the heart muscle, and ultimately death of cardiac myocytes. To prevent this, cardiac myocytes use a process known as autophagy to dispose of damaged cellular components, keeping them from causing cardiac dysfunction.
“Previous studies have shown that the periodontal pathogen Porphyromonas gingivalis, which has been detected at the site of occlusion in myocardial infarction, can exacerbate post-infarction myocardial fragility,” says lead author of the study Yuka Shiheido-Watanabe. “However, the mechanisms underlying this effect remained unknown.”
To investigate this, the researchers created a version of P. gingivalis that does not express gingipain, its most potent virulence factor, which an earlier study showed can inhibit cells from undergoing programmed cell death in response to injury. They then used this bacterium to infect cardiac myocytes or mice.
“The results were very clear,” explains Yasuhiro Maejima, corresponding author. “The viability of cells infected with the mutant bacterium lacking gingipain was much higher than that of cells infected with the wild-type bacterium. In addition, the effects of myocardial infarction were significantly more severe in mice infected with wild-type P. gingivalis than in those infected with the mutant P. gingivalis lacking gingipain.”
More detailed investigation of this effect showed that gingipain interferes with fusion of two cell components known as autophagosomes and lysosomes, a process that is crucial to autophagy. In mice, this resulted in an increase in the size of cardiac myocytes and accumulation of proteins that would normally be cleared out of the cells to protect the cardiac muscle.
“Our findings suggest that infection with P. gingivalis producing gingipain results in excessive autophagosome accumulation, which can lead to cellular dysfunction, cell death, and ultimately cardiac rupture,” says Shiheido-Watanabe.
Given that P. gingivalis appears to have a substantial impact on the cardiac muscle’s ability to health itself after a heart attack, treating this common oral infection could help reduce the risk of fatal heart attack.
###
The article, “Porphyromonas gingivalis, a periodontal pathogen, impairs post-infarcted myocardium by inhibiting autophagosome–lysosome fusion,” was published in International Journal of Oral Science at DOI: 10.1038/s41368-023-00251-2.
Journal
International Journal of Oral Science
DOI
10.1038/s41368-023-00251-2
Article Title
Porphyromonas gingivalis, a periodontal pathogen, impairs post-infarcted myocardium by inhibiting autophagosome–lysosome fusion




