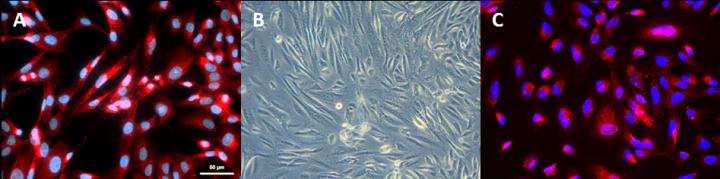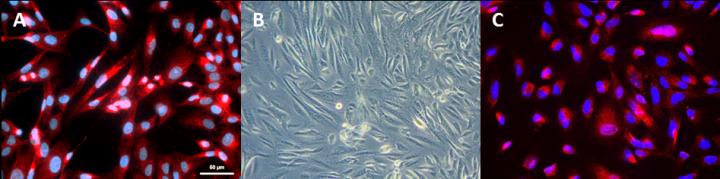
Credit: Rahman MS, Spitzhorn LS, Wruck W, Hagenbeck C, Balan P, Graffmann N, Bohndorf M, Ncube A, Guillot PV, Fehm T, Adjaye J. The presence of human mesenchymal stem cells of…
Amniotic fluid, the liquid surrounding the fetus, can be routinely obtained without harming the mother or the baby. Previously, Prof. Dr. Adjaye's team and others demonstrated that amniotic fluid contains mesenchymal stem cells with great differentiation and regenerative potential. Importantly, amniotic fluid stem cells are immune privileged, non-carcinogenic and their potential clinical applications such as cell-replacement therapies to treat bone defects, ischemic stroke, bladder dysfunction and pulmonary disease have been described. However, the origin of amniotic fluid stem cells has been enigmatic.
A collaborative study between the Institute for Stem Cell Research and Regenerative Medicine (Prof. Dr. James Adjaye), the Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology (Prof. Dr. med. Tanja Fehm) from the Medical Faculty of Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf-Germany and the Institute for Women's Health, Maternal and Fetal Medicine Department (Dr. Pascale V. Guillot)- University College London, published in the journal- Stem Cell Research and Therapy shows for the first time that human amniotic fluid contains mesenchymal stem cells of kidney origin.
The numbers of these cells increased with gestational time- meaning amniotic fluid obtained during delivery had the highest number simply because of the increased volume of amniotic fluid (composed of fetal urine) bathing the fetus at this stage.
Lead authors- Md Shaifur Rahman and Lucas-Sebastian Spitzhorn state-"the kidney-related features of amniotic fluid stem cells are of high interest as a promising cell source for research on nephrogenesis, modelling kidney-related diseases, nephrotoxicity testing and drug screening".
The derivation of 3D-kidney organoids directly from these cells without the need of induced pluripotent stem cells or renal cells cultured from kidney biopsies will add valuable insights into how the kidney develops.
Prof. Dr. Adjaye senior author, concludes: "Our ongoing research on renal stem cells isolated directly from urine, combined with molecular biology and bioinformatic analysis of the genes expressed in these cells enabled us to define these cells as originating from the kidney. At present kidney dialysis and kidney transplantation for managing kidney diseases are limited due to the shortage of compatible donated organs and high associated costs. In view of this, amniotic fluid should be regarded comparably with cordblood as valuable sources of fetal stem cells with regenerative potential and useful for therapeutic applications."
###
Rahman MS, Spitzhorn LS, Wruck W, Hagenbeck C, Balan P, Graffmann N, Bohndorf M, Ncube A, Guillot PV, Fehm T, Adjaye J. The presence of human mesenchymal stem cells of renal origin in amniotic fluid increases with gestational time. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Apr 25;9(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s13287-018-0864-7. PubMed PMID: 29695308.
Media Contact
James Adjaye
[email protected]
49 211 8108191
http://www.uni-duesseldorf.de/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13287-018-0864-7