Nanocubes automatically connect, disassemble at different temperatures
Credit: Zhan et al. 2019 DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-09495-1
Researchers have designed two types of nano-sized building blocks that can automatically connect into cubes and scramble back into individual components based on the temperature of their environment. This accomplishment is another step towards chemical systems that more realistically mimic life.
“Imagine mixing two liquids together, like ink and water. They will automatically do the simple chemical process of dispersing until they are perfectly mixed,” said Professor Shuichi Hiraoka of the University of Tokyo Graduate School of Arts and Sciences.
“However, there’s no chemical process to automatically separate water and ink – you need to boil the water into a gas to separate it from the ink,” he added.
The new building blocks designed by Hiroka’s team can connect or scramble themselves automatically because of the different temperature stabilities of the cubes that they form.
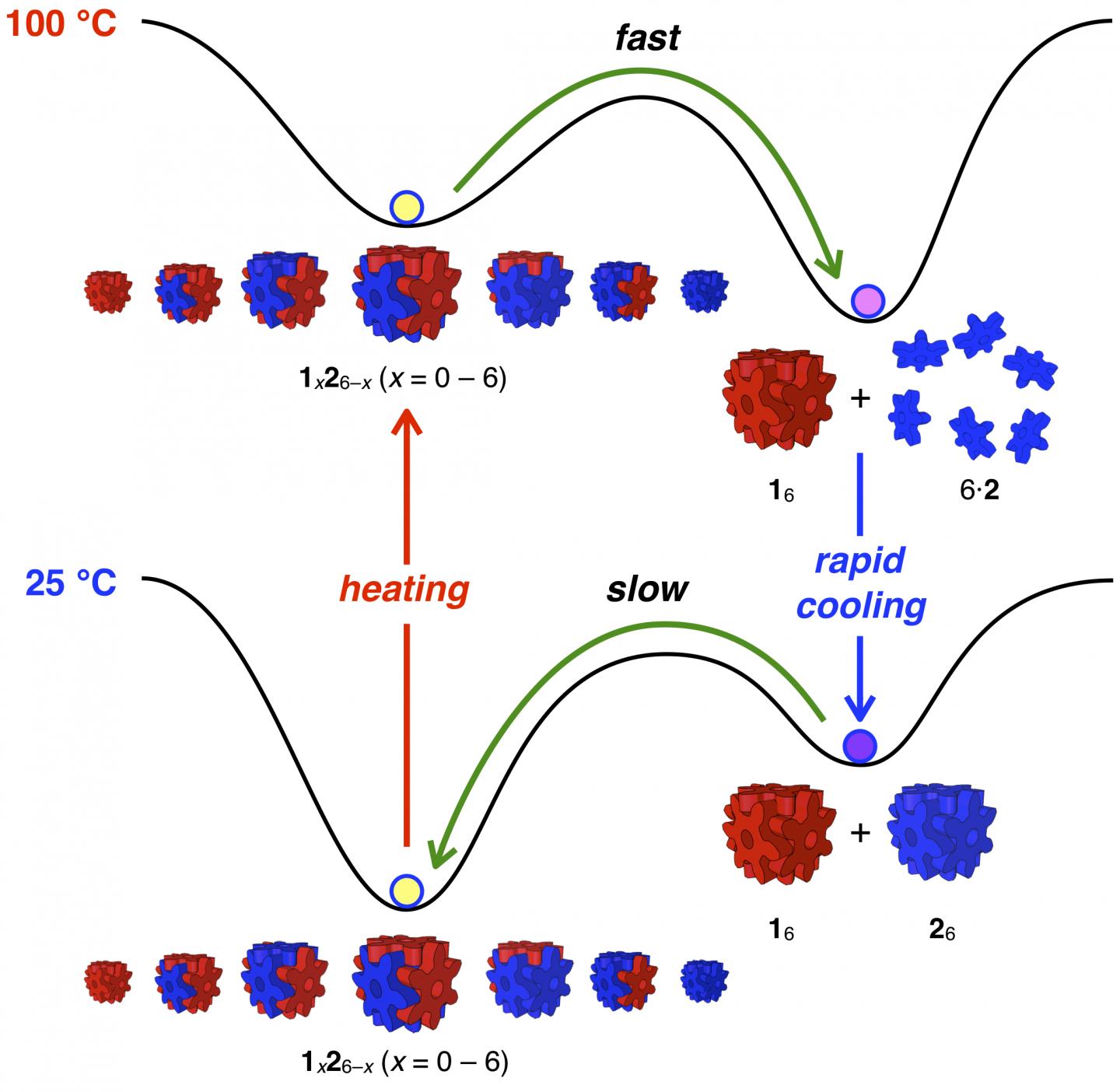
The two types of building blocks are nearly identical and are shaped like snowflakes. Researchers color them red or blue in schematic diagrams. A cube assembled from red blocks is stable below 130 degrees Celsius (266 degrees Fahrenheit), while a cube assembled from blue blocks is stable only below 65 degrees Celsius (149 degrees Fahrenheit).
When kept apart, the building blocks connect into entirely red or entirely blue uniform cubes.
When the two types of cubes are mixed together at room temperature (25 degrees Celsius, 77 degrees Fahrenheit), the red and blue building blocks automatically recombine into the most stable type of cubes, which are made of any combination of three red and three blue blocks. This mixture of red-blue cubes is analogous to well-mixed ink and water.
When researchers want to scramble the red-blue cubes to reform entirely red and entirely blue cubes, they do a simple two-step temperature change. This ability represents a chemical accomplishment not possible with a mixture of ink and water.
First, they heat the mixture up to boiling (100 degrees Celsius, 212 degrees Fahrenheit). The blue cubes become unstable and float off as individual molecules, while the red building blocks recombine into entirely red cubes.
Then, researchers rapidly cool the mixture (0 degrees Celsius, 32 degrees Fahrenheit) so that the red cubes stay together while the blue building blocks automatically assemble into entirely blue cubes.
Researchers can also prevent a mixture of entirely red and entirely blue cubes from scrambling into the more stable red-blue blended cubes by filling the cubes with something, for example other molecules like hydrocarbons. The guest molecules effectively lock the cubes closed from the inside so that the building blocks cannot scramble into other, more stable cube combinations.
“In the future, we plan to develop an even more complicated chemical system based on molecular cubes, using the unique self-assembly ability and a variety of energy sources beyond just heat,” said Hiraoka.
###
The nanocubes in the present research have the same basic structure as the design reported in October 2018. (https:/
Journal Article
Zhan YY, Tatsuo K, Ishii K, Takahashi S, Haketa Y, Maeda H, Uchiyama S, Hiraoka S. 29 March 2019. Temperature-controlled repeatable scrambling and induced-sorting of building blocks between cubic assemblies. Nature Communications. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-09495-1
https:/
Related Links
Graduate School of Arts and Sciences: http://www.
Department of Basic Science (Japanese only): http://www.
Hiraoka Group laboratory website (Japanese only): http://hiraoka.
Hiraoka Group Facebook page (Japanese only): https:/
Research Contact
Professor Shuichi Hiraoka
Department of Basic Science, Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 3-8-1 Komaba, Meguro-ku, Tokyo 153-8902, Japan
Tel: +81-3-5465-7659
Email: [email protected]
Press Contacts
Ms. Caitlin Devor
Division for Strategic Public Relations, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8654, JAPAN
Tel: +81-3-5841-0876
Email: [email protected]
Public Relations Office
Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, The University of Tokyo, 3-8-1 Komaba, Meguro-ku, Tokyo 153-8902, Japan
Tel: +81-3-5454-4920
Email: [email protected]
About the University of Tokyo
The University of Tokyo is Japan’s leading university and one of the world’s top research universities. The vast research output of some 6,000 researchers is published in the world’s top journals across the arts and sciences. Our vibrant student body of around 15,000 undergraduate and 15,000 graduate students includes over 2,000 international students. Find out more at http://www.
Media Contact
Shuichi Hiraoka
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.



