Credit: Polechová
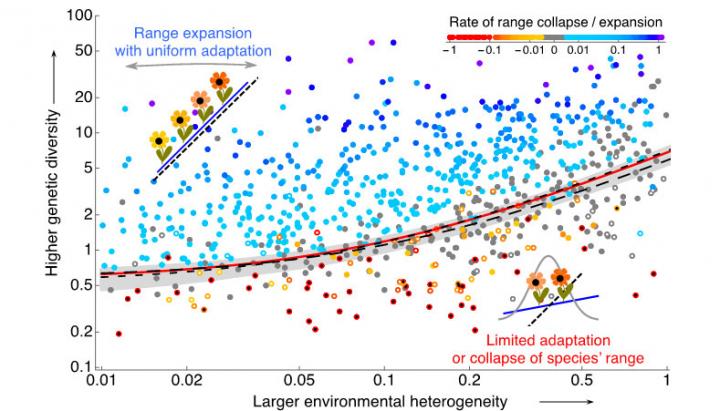
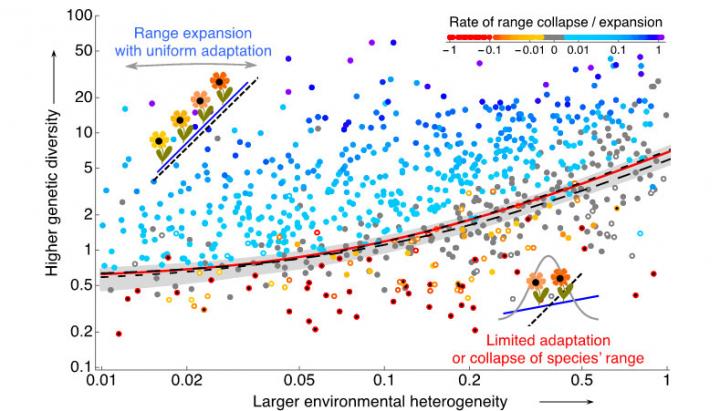
All species have restricted distributions. Yet a joint coherent theory explaining the span and borders of species' ranges has been missing both due to the complexity of the problem and the disparate traditions in ecology and evolution. Jitka Polechová provides a general, testable prediction for formation of species' range margins. The theory includes both population and evolutionary dynamics, and elucidates the role of dispersal for adaptation across a species' range. Dispersal has conflicting effects: on the beneficial side, it increases the genetic variation that is necessary for adaptation and counters the loss of genetic diversity due to genetic drift. However, dispersal also carries a cost: it may swamp adaptation to local conditions. This interplay is crucial for the evolution of a species' range.
The novel theory demonstrates that adaptation across a species' range depends on two dimensionless parameters: i) the fitness cost of dispersal – a measure of environmental heterogeneity, and ii) the strength of genetic drift – a measure of the reduction of genetic diversity. The more heterogeneous is an environment, the more challenging it is to expand into, and the lower the genetic diversity, the more limited is the scope for potential adaptation. Together, these two parameters define an expansion threshold: adaptation fails when the number of individuals accessible by dispersal within one generation is so small that genetic drift reduces genetic diversity below that required for adaptation to a heterogeneous environment. This threshold provides a testable prediction for the formation of a range margin and for the collapse of a species' range.
Interestingly, the parameters are independent of the genetic architecture, offering a wide scope for empirical tests of the theory across many species. Furthermore, the theory explains that the benefits of dispersal into marginal populations are likely to outweigh the costs, offering a theoretical base for management strategies of threatened populations.
###
Publication in "PLoS Biology"
Polechová J. (2018) Is the sky the limit? On the expansion threshold of a species' range. PLoS Biology.
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2005372
Scientific contact
Jitka Polechová, PhD.
Faculty of Mathematics
University of Vienna
Oskar-Morgenstern-Platz 1
1090 Vienna, Austria
M +43-664-374-1607
[email protected]
Press contact
Mag. Alexandra Frey
Press office of the University of Vienna
Research and Teaching
1010 Vienna, Universitätsring 1
T +43-1-4277-175 33
M +43-664-602 77-175 33
[email protected]
Media Contact
Jitka Polechová, PhD
[email protected]
43-664-374-1607
@univienna
http://www.univie.ac.at/en/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2005372