Vermont scientists create tool to explore billions of social media messages, potentially predict political and financial turmoil
Credit: UVM
For thousands of years, people looked into the night sky with their naked eyes — and told stories about the few visible stars. Then we invented telescopes. In 1840, the philosopher Thomas Carlyle claimed that “the history of the world is but the biography of great men.” Then we started posting on Twitter.
Now scientists have invented an instrument to peer deeply into the billions and billions of posts made on Twitter since 2008 — and have begun to uncover the vast galaxy of stories that they contain.
“We call it the Storywrangler,” says Thayer Alshaabi, a doctoral student at the University of Vermont who co-led the new research. “It’s like a telescope to look — in real time — at all this data that people share on social media. We hope people will use it themselves, in the same way you might look up at the stars and ask your own questions.”
The new tool can give an unprecedented, minute-by-minute view of popularity, from rising political movements to box office flops; from the staggering success of K-pop to signals of emerging new diseases.
The story of the Storywrangler — a curation and analysis of over 150 billion tweets–and some of its key findings were published on July 16 in the journal Science Advances.
EXPRESSIONS OF THE MANY
The team of eight scientists who invented Storywrangler — from the University of Vermont, Charles River Analytics, and MassMutual Data Science — gather about ten percent of all the tweets made every day, around the globe. For each day, they break these tweets into single bits, as well as pairs and triplets, generating frequencies from more than a trillion words, hashtags, handles, symbols and emoji, like “Super Bowl,” “Black Lives Matter,” “gravitational waves,” “#metoo,” “coronavirus,” and “keto diet.”
“This is the first visualization tool that allows you to look at one-, two-, and three-word phrases, across 150 different languages, from the inception of Twitter to the present,” says Jane Adams, a co-author on the new study who recently finished a three-year position as a data-visualization artist-in-residence at UVM’s Complex Systems Center.
The online tool, powered by UVM’s supercomputer at the Vermont Advanced Computing Core, provides a powerful lens for viewing and analyzing the rise and fall of words, ideas, and stories each day among people around the world. “It’s important because it shows major discourses as they’re happening,” Adams says. “It’s quantifying collective attention.” Though Twitter does not represent the whole of humanity, it is used by a very large and diverse group of people, which means that it “encodes popularity and spreading,” the scientists write, giving a novel view of discourse not just of famous people, like political figures and celebrities, but also the daily “expressions of the many,” the team notes.
In one striking test of the vast dataset on the Storywrangler, the team showed that it could be used to potentially predict political and financial turmoil. They examined the percent change in the use of the words “rebellion” and “crackdown” in various regions of the world. They found that the rise and fall of these terms was significantly associated with change in a well-established index of geopolitical risk for those same places.
WHAT’S HAPPENING?
The global story now being written on social media brings billions of voices — commenting and sharing, complaining and attacking — and, in all cases, recording — about world wars, weird cats, political movements, new music, what’s for dinner, deadly diseases, favorite soccer stars, religious hopes and dirty jokes.
“The Storywrangler gives us a data-driven way to index what regular people are talking about in everyday conversations, not just what reporters or authors have chosen; it’s not just the educated or the wealthy or cultural elites,” says applied mathematician Chris Danforth, a professor at the University of Vermont who co-led the creation of the StoryWrangler with his colleague Peter Dodds. Together, they run UVM’s Computational Story Lab.
“This is part of the evolution of science,” says Dodds, an expert on complex systems and professor in UVM’s Department of Computer Science. “This tool can enable new approaches in journalism, powerful ways to look at natural language processing, and the development of computational history.”
How much a few powerful people shape the course of events has been debated for centuries. But, certainly, if we knew what every peasant, soldier, shopkeeper, nurse, and teenager was saying during the French Revolution, we’d have a richly different set of stories about the rise and reign of Napoleon. “Here’s the deep question,” says Dodds, “what happened? Like, what actually happened?”
GLOBAL SENSOR
The UVM team, with support from the National Science Foundation, is using Twitter to demonstrate how chatter on distributed social media can act as a kind of global sensor system — of what happened, how people reacted, and what might come next. But other social media streams, from Reddit to 4chan to Weibo, could, in theory, also be used to feed Storywrangler or similar devices: tracing the reaction to major news events and natural disasters; following the fame and fate of political leaders and sports stars; and opening a view of casual conversation that can provide insights into dynamics ranging from racism to employment, emerging health threats to new memes.
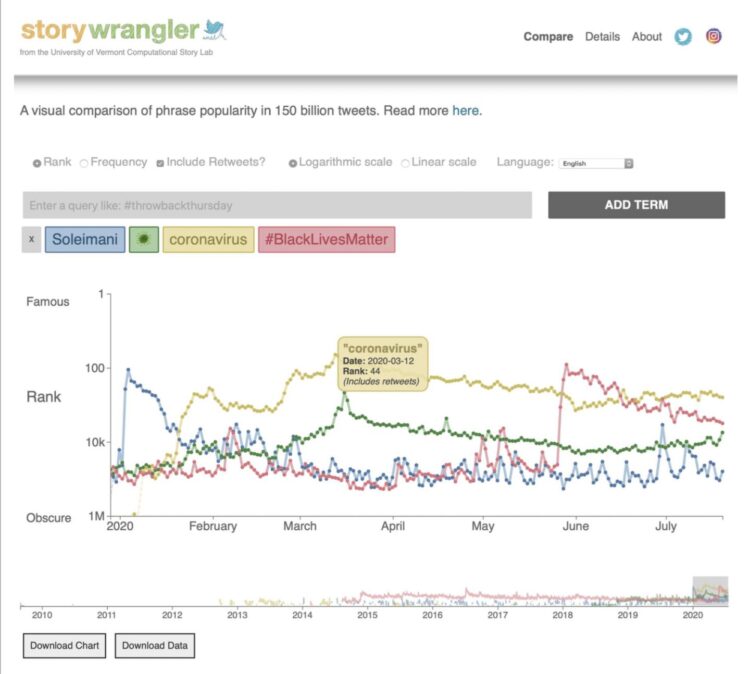
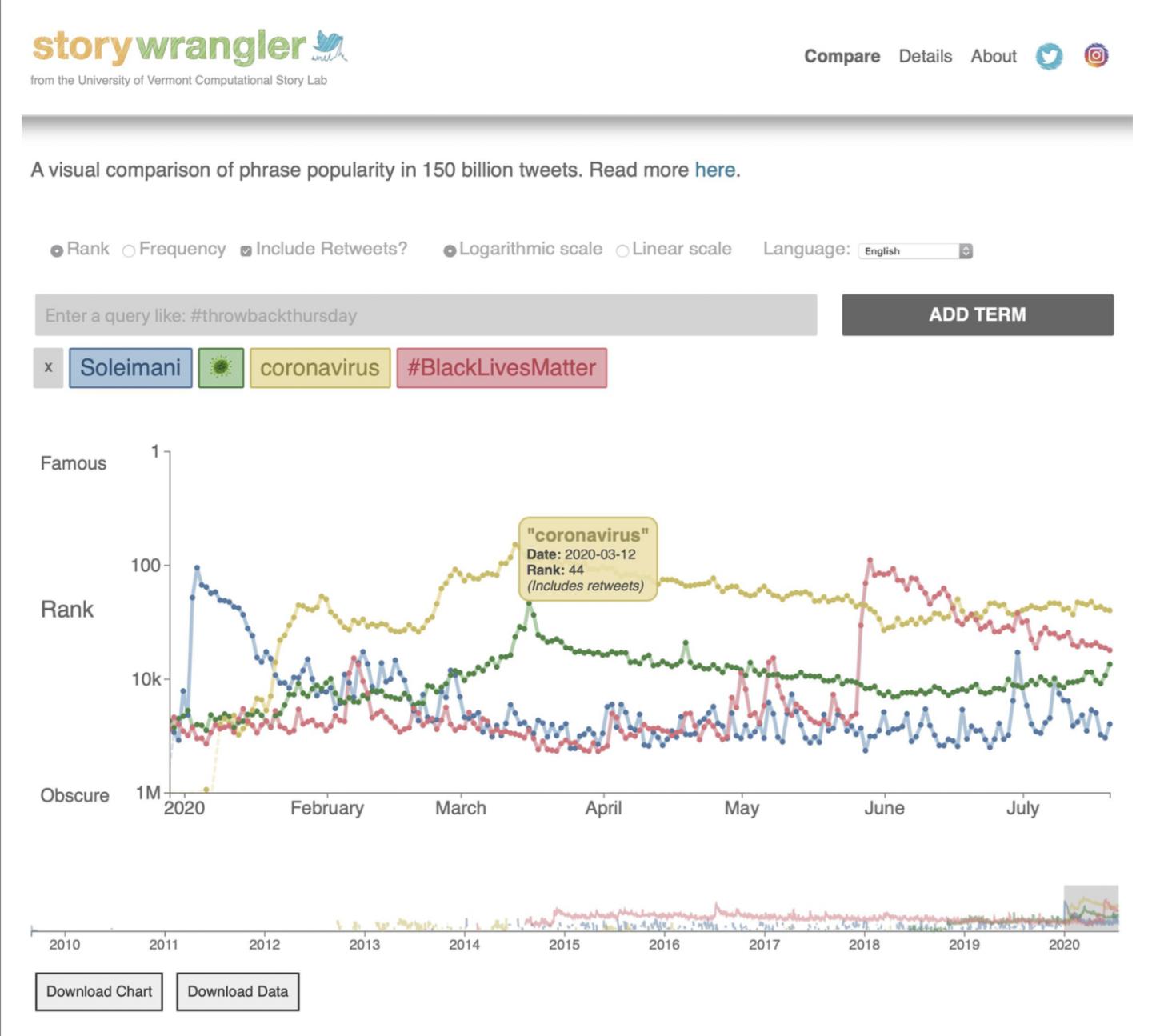
In the new Science Advances study, the team presents a sample from the Storywrangler’s online viewer, with three global events highlighted: the death of Iranian general Qasem Soleimani; the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic; and the Black Lives Matter protests following the murder of George Floyd by Minneapolis police. The Storywrangler dataset records a sudden spike of tweets and retweets using the term “Soleimani” on January 3, 2020, when the United States assassinated the general; the strong rise of “coronavirus” and the virus emoji over the spring of 2020 as the disease spread; and a burst of use of the hashtag “#BlackLivesMatter” on and after May 25, 2020, the day George Floyd was murdered.
“There’s a hashtag that’s being invented while I’m talking right now,” says UVM’s Chris Danforth. “We didn’t know to look for that yesterday, but it will show up in the data and become part of the story.”
###
Media Contact
JOSHUA E BROWN
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.