Credit: by Ying Jiang, Shula Chen, Weihao Zheng, Biyuan Zheng and Anlian Pan
TMDs vdW heterostructures generally possess a type-II band alignment which facilitates the formation of interlayer excitons between the constituent monolayers. Manipulation of the interlayer excitons in TMDs vdW heterostructures hold great promise for developing excitonic integrated circuits that serve as the counterpart of electronic integrated circuits, which allows the photons and excitons transforming between each other and thus bridges the optical communication and signal processing at the integrated circuit. Consequently, numerous researches have been carried out in order to get a deep insight of the physical properties of interlayer excitons, including the revealing of their ultrafast formation, long population recombination lifetimes, and the intriguing spin-valley dynamics. These outstanding properties ensure the interlayer excitons with good transport characteristics and may pave the way for their potential applications in efficient excitonic devices. At present, a systematical and all-round overview of these fascinating physics as well as the exciting applications of interlayer excitons in TMDs vdW heterostructures is still lacking and highly desirable for the scientific community.
In a new review paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professor Anlian Pan from Key Laboratory for Micro-Nano Physics and Technology of Hunan Province, School of Physics and Electronics, and College of Materials Science and Engineering, Hunan University, China, and co-workers have given a comprehensive description and discussion of the interlayer exciton formation, relaxation, transport, and the potential applications in excitonic optoelectronic devices, based on TMDs vdW heterostructures. An outlook of the future opportunities for interlayer excitons in TMDs based heterostructures was also presented in this review.
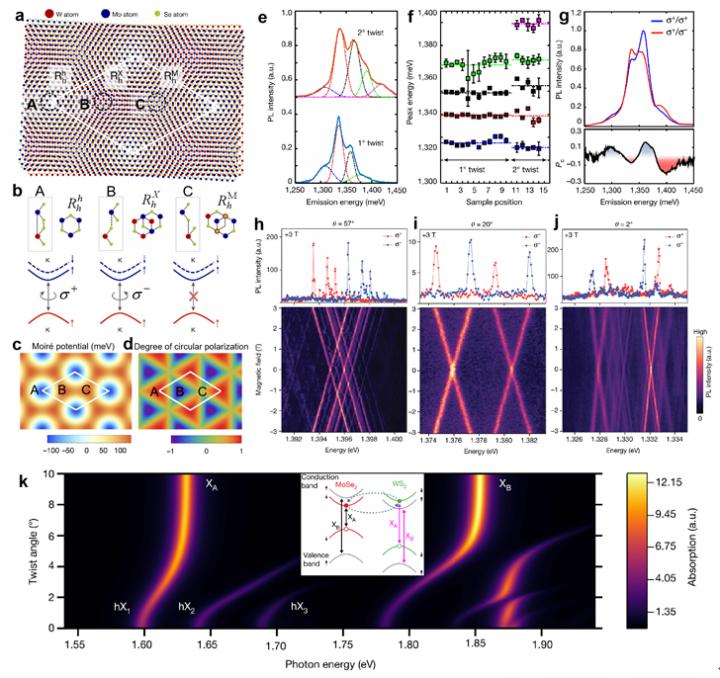
Specifically, the content of this review includes four sections. The first section discussed the band alignment, ultrafast charge transfer, and the interlayer exciton formation as well as its fundamental properties in TMDs vdW heterostructures. Moiré interlayer excitons, as a newly emerged research hotspot, were also detailed in this section.
The second section discussed the interlayer exciton relaxation processes including the population recombination dynamics, the intervalley scattering process, and the valley-polarized dynamics in TMDs vdW heterostructures. The recombination lifetimes of interlayer excitons in various TMDs vdW heterostructural systems were summarized, and the role of moiré superlattice on interlayer exciton lifetimes was also discussed in this part.
The third section reviewed the transport behaviors of interlayer excitons in TMDs vdW heterostructures, including the interlayer exciton diffusion without external electric field, the (valley-polarized) interlayer exciton transport with external electric field, and the manipulation of the interlayer exciton transport under various potential landscapes such as potential wells or barriers. Moreover, the influences of the moiré potential and the atomic reconstructions on the interlayer exciton transport were also detailed in this section. These related works offer a novel way to control the exciton transport behavior in potential excitonic devices.
After a detailed description of the interlayer exciton formation, relaxation and transport properties in TMDs vdW heterostructures, the final section of this review gave a brief introduction of the potential applications of interlayer excitons in various excitonic devices such as excitonic switches, lasers, and photodetectors. Quantum light based on moiré-trapped interlayer excitons was also discussed in this part. Nevertheless, the researches on excitonic devices based on interlayer excitons in TMDs vdW heterostructures are still at the early stages. Improving the performance of the already developed excitonic devices for practical applications and exploring more functional excitonic devices like waveguides and modulators are expected in further works. Moreover, the integration of individual excitonic devices such as light sources, switches, modulators, and detectors on a single chip is very likely and highly desirable in future to realize the on-chip integrated optoelectronics based on two-dimensional vdW heterostructures.
###
Media Contact
Anlian Pan
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




