Credit: by Guoqing Pu, Lilin Yi, Li Zhang, Chao Luo, Zhaohui Li and Weisheng Hu
Because pulse trains achieve excellent performance with a simple laser setup, passively mode-locked fiber lasers (MLFLs) based on nonlinear polarization evolution (NPE) have numerous applications. However, NPE-based MLFLs are difficult to operate in the desired pulsation regime via manual polarization tuning and are prone to detaching from the desired regime due to polarization drift from environmental disturbances. To address these challenges, automatic or intelligent mode-locking techniques using adaptive algorithms and electric polarization controllers (EPCs) have emerged in recent years. Several automatic mode-locking lasers use temporal information to help identify the mode-locking regimes. Combined with automatic optimization algorithms, such lasers can successfully reach the mode-locking regimes, but their pulse width and spectral shape are unpredictable. Thus, automatic mode-locking techniques based on a temporal discrimination alone cannot achieve mode-locking with the possible shortest pulse width and desired spectral distribution. Even though optical spectral information can be utilized in automatic mode-locking using an optical spectrum analyser (OSA), such bulky and slow equipment only obtains integrated spectral information and therefore cannot be used for real-time mode-locking.
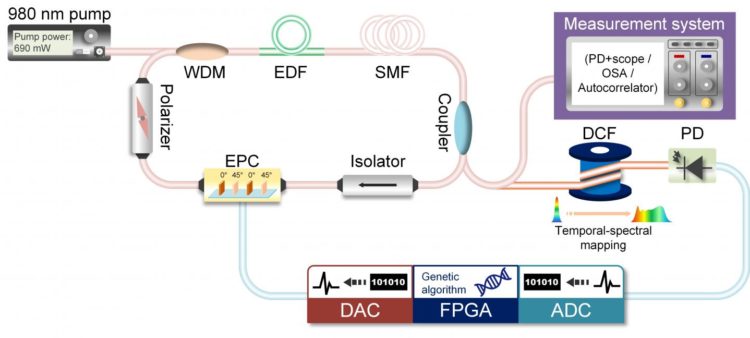
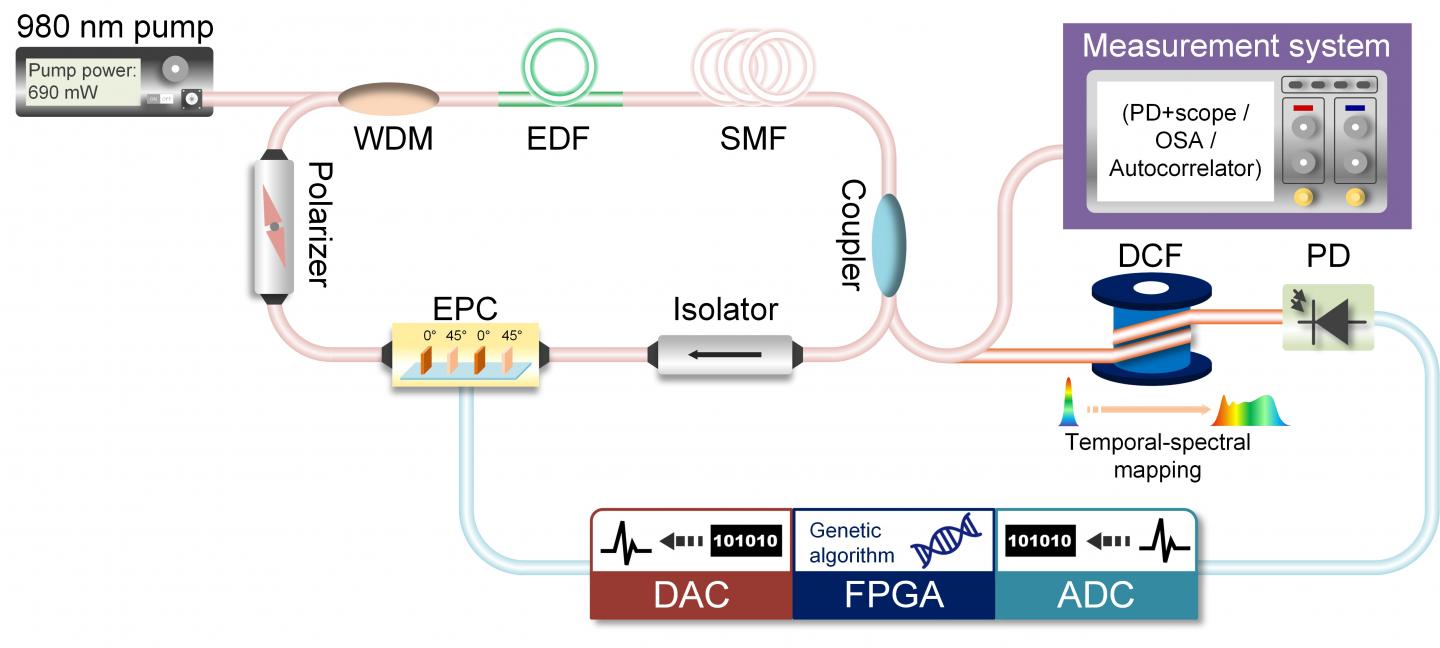
In a new paper published in Light: Science & Application, scientists from the State Key Lab of Advanced Communication Systems and Networks, Shanghai Institute for Advanced Communication and Data Science, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, for the first time, proposed using time stretch dispersive Fourier transformation (TS-DFT)-based fast spectral analysis as the discrimination criterion to achieve rich mode-locking regimes. By simply inserting a dispersion medium into the real-time feedback loop of an automatic mode-locking laser and combining this method with an intelligent polarization search using a genetic algorithm (GA), they can manipulate the spectral width and shape of the mode-locked femtosecond pulses in real time. The technique is termed as the time-stretch-assisted real-time pulse controller (TSRPC). With the TSRPC, the spectral width of the mode-locked femtosecond pulses can be tuned from 10 nm to 40 nm with a resolution of ~1.47 nm, and the spectral shape can be programmed to be hyperbolic secant or triangular. Benefitting from the TS-DFT and the real-time GA optimizer, the TSRPC overcomes the considerable slowness, cost, and bulkiness of traditional OSAs used in previous automatic mode-locking lasers. The TSRPC can be made even more portable by replacing the DCF with a small optical grating, and its spectral programming resolution can be improved by using an ADC with a higher sampling rate or a medium with large dispersion. Furthermore, with real-time control of the spectral width and shape of the mode-locking pulses, they revealed the complex and repeatable transition dynamics from the narrow-spectrum mode-locking regime to the wide-spectrum mode-locking regime, including five middle phases: a relaxation oscillation, single soliton state, multi-soliton state, triangle-spectrum transition, and chaotic transition, providing deep insight into the ultrashort pulse formation that cannot be observed with traditional mode-locked lasers.
###
Media Contact
Lilin Yi
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.