An interdisciplinary research team from the University of Göttingen and Hannover Medical School (MHH) has detected significant changes in the heart muscle tissue of people who died from Covid-19. Damage to lung tissue has been the research focus in this area for some time and has now been thoroughly investigated. The current study underpins the involvement of the heart in Covid-19 at the microscopic level for the first time by imaging and analysing the affected tissue in the three dimensions. The results were published in the journal eLife.
Credit: M. Reichardt, P. Møller Jensen, T. Salditt
An interdisciplinary research team from the University of Göttingen and Hannover Medical School (MHH) has detected significant changes in the heart muscle tissue of people who died from Covid-19. Damage to lung tissue has been the research focus in this area for some time and has now been thoroughly investigated. The current study underpins the involvement of the heart in Covid-19 at the microscopic level for the first time by imaging and analysing the affected tissue in the three dimensions. The results were published in the journal eLife.
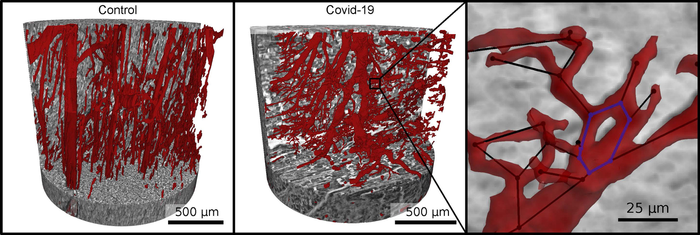
The scientists imaged the tissue architecture to a high resolution using synchrotron radiation – a particularly bright X-ray radiation – and displayed it three-dimensionally. To do this, they used a special X-ray microscope that the University of Göttingen set up and operates at the German Electron Synchrotron DESY in Hamburg. They observed clear changes at the level of the capillaries (the tiny blood vessels) in the heart muscle tissue when they examined the effects there of the severe form of Covid-19 disease.
In comparison with a healthy heart, X-ray imaging of tissues affected by severe disease, revealed a network full of splits, branches and loops which had been chaotically remodelled by the formation and splitting of new vessels. These changes are the first direct visual evidence of one of the main drivers of lung damage in Covid-19: a special kind of “intussusceptive angiogenes” (meaning new vessel formation) in the tissue.
In order to visualise the capillary network, the vessels in the three-dimensional volume first had to be identified using machine learning methods. This initially required researchers to painstakingly, manually label the image data. “To speed up image processing, we therefore also automatically broke the tissue architecture down into its local symmetrical features and then compared them,” explains Marius Reichardt, at the University of Göttingen and first author of the paper. “The parameters obtained from this then showed a completely different quality compared to healthy tissue, or even to diseases such as severe influenza or common myocarditis,” explain the leaders of the study, Professor Tim Salditt from the University of Göttingen and Professor Danny Jonigk from the MHH.
There is a very special feature of this study: in contrast to the vascular architecture, the required data quality could be achieved using a small X-ray source in the laboratory of the University of Göttingen. In principle, this means it could also be done in any clinic to support pathologists with routine diagnostics. In the future, the researchers want to further expand the approach of converting the characteristic tissue patterns into abstract mathematical values in order to develop automated tools for diagnostics, again by further developing laboratory X-ray imaging and validating it with data from synchrotron radiation. The collaboration with DESY will be further expanded in the coming years.
Original publication: Marius Reichardt et al. 3D virtual histopathology of cardiac tissue from Covid-19 patients on phase-contrast x-ray tomography. eLife 2021. Doi: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.71359
Contact:
Professor Tim Salditt
University of Göttingen
Institute for X-ray Physics
Friedrich-Hund-Platz 1, 37077 Göttingen, Germany
Tel: (0551) 39-25556
Email: [email protected]
www.roentgen.physik.uni-goettingen.de
Journal
eLife
DOI
10.7554/eLife.71359
Method of Research
Imaging analysis
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Innovative X-ray imaging shows Covid-19 can cause vascular damage to the heart
Article Publication Date
21-Dec-2021




