Credit: (c) S.Jolles, University Hospital of Wales
A new proof of concept study has shown that an imaging technique more commonly used to assess cancer patients may also be of help in assessing disease and treatment effects in patients with inflammatory diseases. The study is published in Clinical & Experimental Immunology.
Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is the commonest serious primary immunodeficiency of adults. Patients are not only unable to manufacture antibodies to protect them from infections but also suffer from inflammatory and autoimmune complications. CVID affects approximately 1 in 25,000 adults. While treatment with antibody replacement and antibiotics has significantly improved infections, the non-infectious inflammatory, autoimmune and malignant complications have emerged as major therapeutic challenges. One complication of CVID is called granulomatous lymphocytic interstitial lung disease (GLILD). This is a complex condition to diagnose and monitor as onset may be insidious leading to lung involvement, enlarged lymph-nodes and spleen. Currently, a combination of clinical features, laboratory markers, lung function measures and radiological investigations are used to diagnose and make treatment decisions about GLILD though there remains a lack of information to help clinicians determine the optimal frequency of testing and timing of treatment.
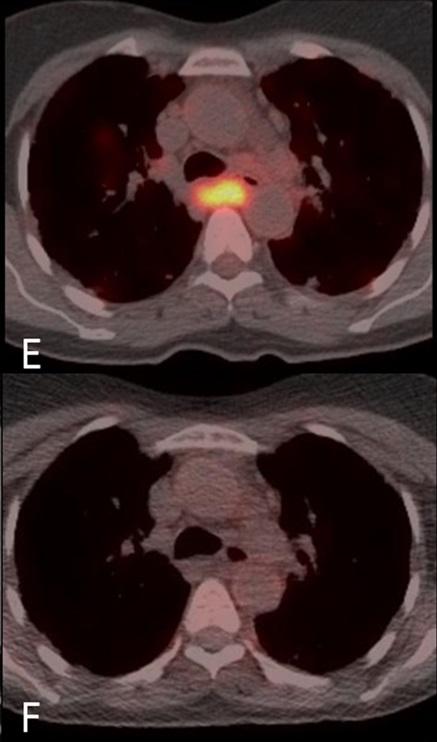
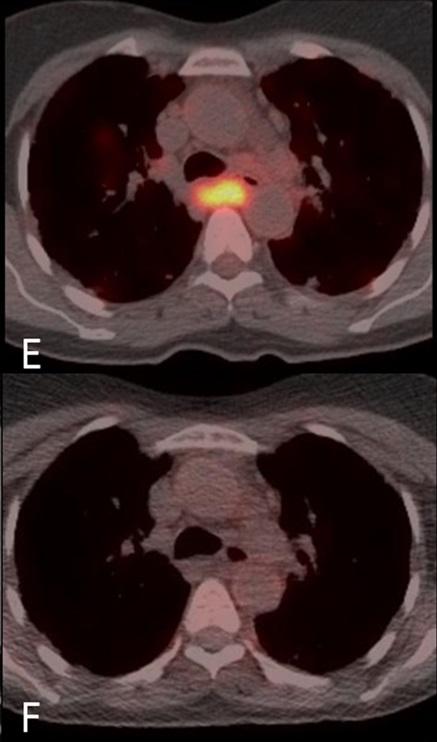
In this proof of concept study, Dr Stephen Jolles and colleagues from the University Hospital of Wales used an imaging technique called FDG PET-CT to simultaneously assess anatomical structure and metabolic activity in a patient with GLILD. FDG PET-CT imaging allows the detailed anatomical structure obtained by a CT scan to be overlaid and combined with PET images of rates of labelled glucose uptake into cells within the tissues; the clinical utility of which has already been proven in oncological imaging. However, FDG PET-CT's use to assess inflammatory disease is an emerging field and this paper is the first time that this technique has been employed to assess both anatomical and metabolic extent of the disease and to assess treatment response in the setting of GLILD.
The images (supplied) show that FDG PET-CT provides new insights into GLILD, showing widespread, high levels of metabolic activity not restricted to the lungs but affecting lymph nodes (even when these are normal in size) throughout the body before treatment. After treatment, clear improvements in both anatomical and functional activity can be observed. The combined FDG PET-CT demonstrates that GLILD is only the pulmonary facet of a highly metabolically active multisystem disease. The very high levels of metabolic activity may have implications for the development of autoimmunity and malignancy, both of which occur at higher frequency in patients with GLILD.
Larger studies are now needed to assess the potential role of this technology in the ongoing care of patients with GLILD and it is likely that it will be increasingly used in a wider range of inflammatory disorders.
Lead researcher Dr Stephen Jolles from the University Hospital of Wales said:
"Patients who develop granulomatous lymphocytic interstitial lung disease (GLILD) as a complication of common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) often have poorer outcomes. Given the multi-systemic nature of this disease, it is currently difficult for clinicians to accurately monitor and assess the optimal timing of treatment as well as the effect of treatment and its duration.
This study is the first time that the imaging technique, FDG PET-CT, has been used to assess the combined lung structure and metabolic activity in a patient with GLILD before and after treatment. The images are striking and enlightening in that they reveal the highly metabolically active multi-systemic nature of the disease. It remains to me amazing the ability of this technique to overlay structure with metabolic functional activity in this way."
###
Media Contact
Jennie Evans
[email protected]
44-020-301-95912
http://immunology.org