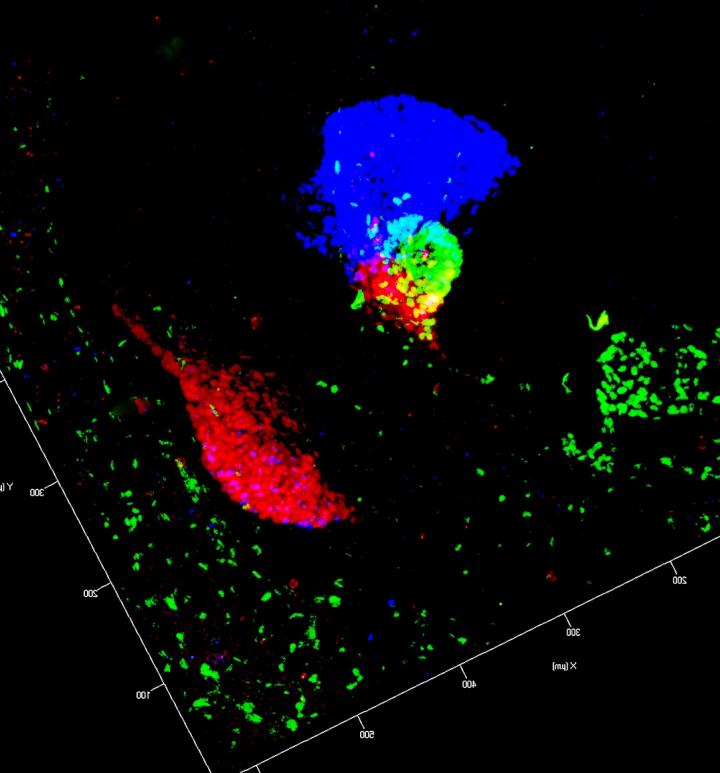
Credit: Image: Francesca Spagnoli, MDC
It is now possible to reprogram cells from the liver into the precursor cells that give rise to the pancreas by altering the activity of a single gene. A team of researchers at the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine in the Helmholtz Association (MDC) has now accomplished this feat in mice. Their results should make it feasible to help diabetic patients through cell therapy.
In patients suffering from type I diabetes, their immune system turns against their own bodies and destroys a type of pancreatic cell called islet cells. Without these cells, the pancreas is unable to produce the hormone insulin and blood glucose rises, which leads to diabetic disease. At that point, such patients need to inject insulin for the rest of their lives.
A way to provide a lasting help to the afflicted may be to grow new pancreatic cells outside of the body. MDC group leader and researcher Dr. Francesca has been pursuing the idea of reprogramming liver cells to become pancreatic cells. Dr. Spagnoli's team has now succeeded in thrusting liver cells into an "identity crisis" — in other words, to reprogram them to take on a less specialized state — and then stimulate their development into cells with pancreatic properties.
Promising success in animal experiments
A gene called TGIF2 plays a crucial role in the process. TGIF2 is active in the tissue of the pancreas but not in the liver. For the current study Dr. Nuria Cerda Esteban, at the time a PhD student in Dr. Spagnoli's lab, tested how cells from mouse liver behave when they are given additional copies of the TGIF2 gene.
In the experiment, cells first lost their hepatic (liver) properties, then acquired properties of the pancreas. The researchers transplanted the modified cells into diabetic mice. Soon after this intervention, the animals' blood glucose levels improved, indicating that the cells indeed were replacing the functions of the lost islet cells. The results bring cell therapies for human diabetic patients one step closer to reality.
The obvious next step is to translate the findings from the mouse to humans. The Spagnoli lab is currently testing the strategy on human liver cells in a project funded in 2015 by the European Research Council. "There are differences between mice and humans, which we still have to overcome," Spagnoli says. "But we are well on the path to developing a 'proof of concept' for future therapies."
###
Nuria Cerdá-Esteban et al. (2017): "Stepwise reprogramming of liver cells to a pancreas progenitor state by the transcriptional regulator Tgif2." Nature Communications. doi:10.1038/ncomms14127
Media Contact
Vera Glaßer
[email protected]
49-309-406-2120
http://www.mdc-berlin.de