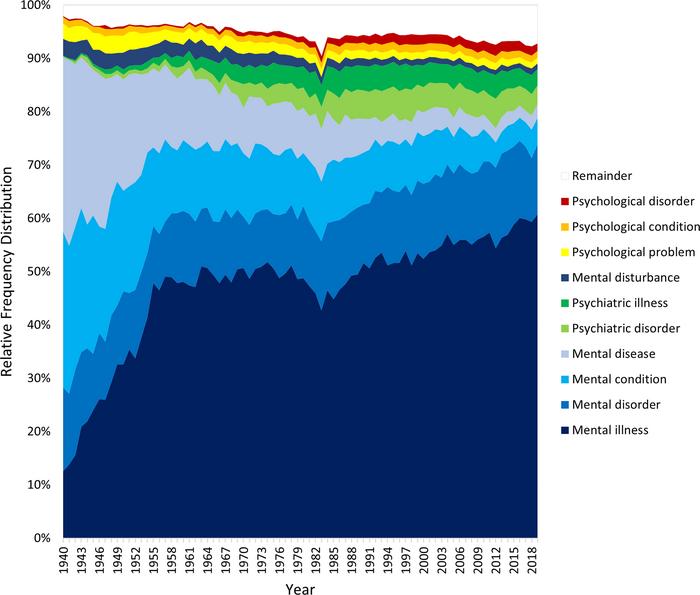
A new survey of nearly 340,000 texts spanning 79 years shows that generic terms in mental health have shifted away from words like “disease” and “disturbance” and toward “psychiatric” and “mental health,” with “mental illness” becoming the most-used term. Nick Haslam and Naomi Baes at the University of Melbourne in Australia present these findings in the new open-access journal PLOS Mental Health on June 4.
Credit: Haslam et al., 2024, PLOS Mental Health, CC-BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
A new survey of nearly 340,000 texts spanning 79 years shows that generic terms in mental health have shifted away from words like “disease” and “disturbance” and toward “psychiatric” and “mental health,” with “mental illness” becoming the most-used term. Nick Haslam and Naomi Baes at the University of Melbourne in Australia present these findings in the new open-access journal PLOS Mental Health on June 4.
The authors state that while words such as “crazy” and “lunatic” are clearly stigmatizing to modern ears, mental health professionals and communities continue to wrestle with other words for mental ill health. But while experts and patients debate “depressed person” or “person with depression,” larger umbrella terms, such as “mental illness” itself, have not been studied. To examine how these overarching terms have changed over time, Haslam and Baes analyzed two large collections of texts—Google Books, and a combination of the Corpus of Historical American English, and the Corpus of Contemporary American English. The first collection contained over 1 trillion words drawn from English language books, and the second included over 700 million words from fiction and non-fiction books, magazines, newspapers, spoken language, and TV shows. For the period from 1940-2019, the scientists looked at the popularity of 24 different generic terms for mental ill health. The terms were two- or three-word phrases that combined four adjectives—“mental,” “mental health,” “psychiatric,” and “psychological”—with six nouns “condition,” “disease,” “disorder,” “disturbance,” “illness,” and “problem.”
Generic terms for mental ill health appeared more than twice as often in 2019 as in 1940, as psychiatry, clinical psychology and other mental health professions grew, and the wider public began to recognize the importance of mental health. Phrases which included “disease,” and “disturbance” grew less common over time. Phrases that included words like “mental health,” “psychiatric,” and “illness” we used more commonly. In particular, “mental illness,” after a spike in popularity between the 1940s and 1960s, reigned as the most-used term. It’s important to note that the authors here have specifically looked at numerical frequency of word usage in written culture, rather than community word preferences over time. Based on these results, the scientists suggest further studies should focus on how mental health language is used by scientists and by the general public, and how that language affects people experiencing mental ill health.
The authors add: “Our study shows that the terms people use to refer to mental ill health have evolved over the past 80 years, but “mental illness” has steadily risen to become the most popular expression.”
PLOS Mental Health recognizes that terminology can be sensitive, regardless of the choice of words, and interpreted differently between individuals and communities. In this paper, although the frequency of the use of certain terminology is closely assessed, it does not necessarily reflect preferences of all communities. At PLOS Mental Health, we recognize that it is important to strike a balance between not over-medicalizing but also not trivializing mental health conditions and experiences and this balance will be unique to different contexts.
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Mental Health: https://journals.plos.org/mentalhealth/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmen.0000032
Citation: Haslam N, Baes N (2024) What should we call mental ill health? Historical shifts in the popularity of generic terms. PLOS Ment Health 1(1): e0000032. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000032
Author Countries: Australia
Funding: This work was supported by Australian Research Council Discovery Project DP210103984 to NH. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Journal
PLOS Mental Health
DOI
10.1371/journal.pmen.0000032
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
People
Article Publication Date
4-Jun-2024
COI Statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.