Ever since its discovery in 2004, graphene has been revolutionizing the field of materials science and beyond. Graphene comprises two-dimensional sheets of carbon atoms, bonded into a thin hexagonal shape with a thickness of one atom layer. This gives it remarkable physical and chemical properties. Despite its thinness, graphene is incredibly strong, lightweight, flexible, and transparent. It also exhibits extraordinary electrical and thermal conductivity, high surface area, and impermeability to gasses. From high-speed transistors to biosensors, it boasts an unrivaled versatility in applications.
Credit: S.H. Joo & H. Kato.
Ever since its discovery in 2004, graphene has been revolutionizing the field of materials science and beyond. Graphene comprises two-dimensional sheets of carbon atoms, bonded into a thin hexagonal shape with a thickness of one atom layer. This gives it remarkable physical and chemical properties. Despite its thinness, graphene is incredibly strong, lightweight, flexible, and transparent. It also exhibits extraordinary electrical and thermal conductivity, high surface area, and impermeability to gasses. From high-speed transistors to biosensors, it boasts an unrivaled versatility in applications.
Nanocellular graphene (NCG) is a specialized form of graphene that achieves a large specific surface area by stacking multiple layers of graphene and controlling its internal structure with a nanoscale cellular morphology.
NCG is coveted for its potential to improve the performance of electronic devices, energy devices and sensors. But its development has been stymied by defects that occur during the manufacturing process. Cracks often appear when forming NCG, and scientists are looking for new processing technologies that can fabricate homogeneous, crack-free and seamless NCGs at appropriate scales.
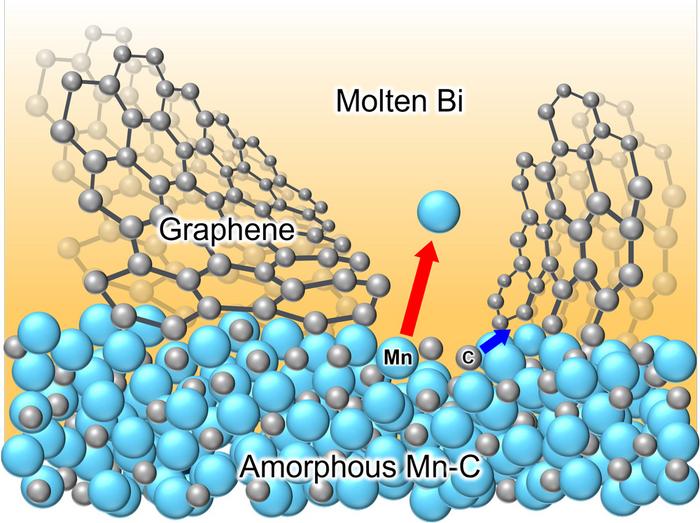
“We discovered that carbon atoms rapidly self-assemble into crack-free NCG during liquid metal dealloying of an amorphous Mn-C precursor in a molten bismuth,” says Won-Young Park, a graduate student at Tohoku University.
Dealloying is a processing technique that exploits the varying miscibility of alloy components in a molten metal bath. This process selectively corrodes certain components of the alloy while preserving others.
Park and his colleagues demonstrated that NCGs developed by this method exhibited high tensile strength and high conductivity after graphitization. Moreover, they put the material to the test in a sodium-ion battery (SIB).
“We used the developed NCG as an active material and current collector in a SIB, where it demonstrated a high rate, long life and excellent deformation resistance. Ultimately, our method of making crack-free NCG will make it possible to raise the performance and flexibility of SIBs – an alternative technology to lithium-ion batteries for certain applications, particularly in large-scale energy storage and stationary power systems where cost, safety, and sustainability considerations are paramount.”
Working alongside Park was Soo-Hyun Joo from the Institute of Materials Research (currently based at Dankook University) along with Hidemi Kato from the same institute. Details of their research were published in the journal Advanced Materials on February 23, 2024.
Their endeavors were made possible through collaboration with researchers from the Tohoku University’s Frontier Research Institute for Interdisciplinary Sciences and the Fracture and Reliability Research Institute; Pohang University of Science and Technology; and Johns Hopkins University.
Journal
Advanced Materials
DOI
10.1002/adma.202311792
Article Title
Mechanically Robust Self-Organized Crack-Free Nanocellular Graphene with Outstanding Electrochemical Properties in Sodium Ion Bat
Article Publication Date
23-Feb-2024




