The research was published in Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering
Credit: Kazan Federal University
KFU’s In-Situ Combustion Lab has been in charge of the project since 2016. Senior Research Associate Irek Mukhamatdinov is the project head. The team also includes Lab Head Alexey Vakhin and Junior Research Associate Firdavs Aliev. A number of publications, including a master thesis (“Study of the rheological and wetting properties of polymer solutions based on polyacrylamides” by Anabel Sosa Acosta), have appeared since then.
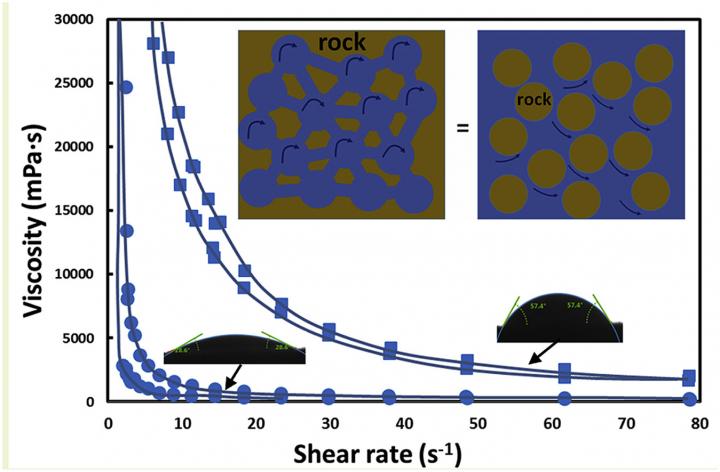
The development and implementation of innovative integrated methods to increase oil recovery is one of the key approaches to solving existing problems in the oil industry. Residual oil in the water-filled formations is kept stationary by surface capillary forces on the scale of individual pores and low permeability inclusions, as well as viscous forces on the scale of low-permeability differences and layers of the formation. One of the reasons for the low coefficient of displacement and formation coverage by the water-flooding process in fields containing high viscosity oil is the large ratio of oil and water viscosities, which leads to a decrease in the coverage of the formation with a displacing agent. The addition of a high molecular weight polymer to water makes it possible to increase the viscosity of water and improve the ratio of the mobility of oil and water, thus increasing oil recovery. The nature of the wettability of the pore surface of a reservoir rock determines filtration processes. The displacement coefficient is determined by the consolidated action of a number of factors, such as porosity, permeability, heterogeneity of the pore space structure, and pore size distribution.
One of the most important and fundamental characteristics of the microstructure of porous media in oil-bearing formations is the wettability of their surface. The specificity of the displacement of oil by polymer solutions, the state and distribution of residual oil saturation in the formation, and the dominant goal of stimulating the formation to reduce residual oil reserves depend on the wettability of the porous medium.
The study established the properties of reservoir rocks of various types to determine the optimal operating conditions of the field. The physico-chemical properties of the interfaces of various phases and the laws of their interaction are characterized by a number of indicators – surface tension at the interface, phenomena of wettability and spreading, adhesion and cohesion, and heat of wetting. The properties of the contacting phases and the patterns of their interaction along the surface tension of formation fluids on various surfaces were also studied. The surface tension at the rock-liquid, rock-gas interface is practically inaccessible for measurement, and indirect methods are used, in particular, wettability is studied.
The results obtained for the studied polymer solutions confirm the significant influence of the chemical nature of the mineral skeleton of the reservoir rock on their viscosity, and hence on the efficiency of application to increase oil recovery. Laboratory selection of an effective polymer and its optimal concentration can be carried out according to the proposed methodological approach. This technique complements the use of filtration experiments, which are much longer and more expensive. Therefore, preliminary screening on a large number of polymer variants and their concentrations is important.
This work contributes to the development of an understanding of phenomena at interfaces in oil and gas reservoirs at the micro level, and gives a clearer picture of the physics of the wetting process.
Based on the results of laboratory tests, field trials of various polymer compositions of the established concentration will be recommended.
Further development of the topic will be carried out in the direction of studying wetting and rheological properties at various temperatures and pressures close to reservoir conditions, as well as on real oil-saturated rocks.
###
Media Contact
Yury Nurmeev
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




