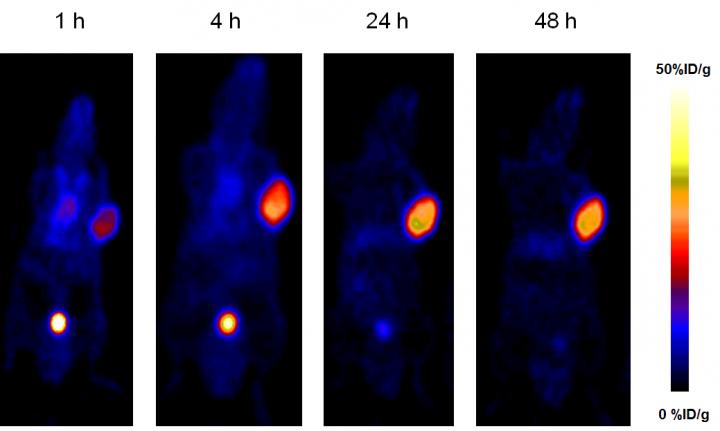
Credit: Z Wang et al., National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD
PHILADELPHIA – Research presented at the 2018 Annual Meeting of the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) demonstrates a potentially more effective method of imaging and treating prostate cancer that modifies a prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-targeted radioligand by adding an albumin-binding Evans blue (an azo dye) derivative.
Several radioligands that target PSMA have been clinically introduced as a new class of theranostics for prostate cancer diagnosis and therapy. One of them, methyl cysteine-glutamate urea (MCG), has been labeled successfully with both fluorescent dyes and radioisotopes for prostate cancer imaging.
For this study using a mouse model, MCG was conjugated with an albumin-binding Evans blue (EB) derivative to further improve tumor delivery and increase the therapeutic effect. Albumin, the most abundant plasma protein in human blood, is a natural transport protein and has a long circulatory half-life.
"Albumin-based drug delivery systems play a very important role in the treatment of diabetes and are also expanding to the field of oncology," explains Zhantong Wang, corresponding author and a researcher at the U.S. National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering.
The study used yttrium-86 (86Y)-DOTA-EB-MCG for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging performed at 1, 4, 24 and 48 hours post injection to evaluate biodistribution and tumor uptake. DOTA-EB-MCG was then labeled with yttrium-90 (90Y) for the radioligand therapy.
Administration of a 3.7 MBq dose of 90Y-DOTA-EB-MCG resulted in significant tumor growth inhibition, and when a single 7.4 MBq dose of 90Y-DOTA-EB-MCG was used, the tumors were completely eradicated, with no apparent associated toxicity or weight loss. In comparison, a 7.4 MBq dose of 90Y-DOTA-MCG only showed a marginal delay of tumor growth. Modification of MCG with the EB derivative therefore resulted in a highly efficient prostate cancer-targeting agent in mice.
Wang notes, "With the incorporation of EB, binding with albumin will usually extend the circulation time of the radioligands, resulting in an increased time frame for them to interact with the PSMA receptors. Additionally, the relatively large size of the albumin-radioligand complex will facilitate tumor accumulation via enhanced permeability and retention. Furthermore, additional internalization of the radioligand may be mediated by albumin-binding proteins, such as the gp60 receptor, which are overexpressed in tumor cells." He concludes, "All these findings strongly suggest radioligand therapy using albumin-binding moieties is a promising strategy in cancer management. Additional study is required to determine its effectiveness in humans."
###
Abstract 2: "An Improved Prostate Specific Membrane Antigen Targeting Agent for Prostate Cancer Imaging and Therapy," Zhantong Wang; Orit Jacobson; Rui Tian; Dale O. Kiesewetter, PhD; Gang Niu, MD, and and Xiaoyuan Chen, PhD, National Institutes of Health (NIH), Bethesda, MD; Ronnie C. Mease, PhD, Johns Hopkins University, Fairfax, VA; Martin G. Pomper, MD, PhD, Johns Hopkins Medical Institutions, Baltimore, MD, SNMMI's 65th Annual Meeting, June 23-26, Philadelphia, PA.
Link to Abstract
NOTE: See Abstract 118 of the SNMMI 2018 Annual Meeting on long-lasting radiolabeled somatostatin analogue 177Lu-DOTA-EB-TATE for neuroendocrine tumors, also an NIH study using Evans blue platform technology.
Please visit the SNMMI Media Center for more information about molecular imaging and personalized medicine. To schedule an interview with the researchers, please contact Laurie Callahan at (703) 652-6773 or [email protected]. Current and past issues of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine can be found online at http://jnm.snmjournals.org. The SNMMI 2018 Annual Meeting abstracts are available at http://jnm.snmjournals.org/content/59/supplement_1.
ABOUT THE SOCIETY OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE AND MOLECULAR IMAGING
The Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) is an international scientific and medical organization dedicated to advancing nuclear medicine and molecular imaging, vital elements of precision medicine that allow diagnosis and treatment to be tailored to individual patients in order to achieve the best possible outcomes.
SNMMI's more than 16,000 members set the standard for molecular imaging and nuclear medicine practice by creating guidelines, sharing information through journals and meetings and leading advocacy on key issues that affect molecular imaging and therapy research and practice. For more information, visit http://www.snmmi.org.
Media Contact
Laurie F Callahan
[email protected]
@SNM_MI
http://www.snm.org
Original Source
http://www.snmmi.org/NewsPublications/NewsDetail.aspx?ItemNumber=29422