This study is conducted by the Jiangsu Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention, National Institute of Diagnostics and Vaccine Development in Infectious Diseases, State Key Laboratory of Vaccines for Infectious Diseases of Xiamen University, China National Institutes for Food and Drug Control, and Xiamen Innovax Biotech Company.
Credit: ©Science China Press
This study is conducted by the Jiangsu Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention, National Institute of Diagnostics and Vaccine Development in Infectious Diseases, State Key Laboratory of Vaccines for Infectious Diseases of Xiamen University, China National Institutes for Food and Drug Control, and Xiamen Innovax Biotech Company.
Premalignant and malignant lesions of the cervix and other sites related to the human papillomavirus (HPV) infection pose a significant health burden worldwide, especially in developing countries. Although prophylactic HPV vaccination is considered one of the most effective measures to prevent cervical cancer and other related diseases, accessibility to HPV vaccines, particularly the 9-valent HPV vaccine, remains a considerable challenge. Among the six available prophylactic HPV vaccines worldwide, the E. coli-produced HPV 16/18 bivalent vaccine (Cecolin, Xiamen Innovax) has been approved by the National Medical Products Administration of China (NMPA) and received prequalification by the World Health Organization (WHO) based on its high efficacy and good safety profile. Using the same E. coli expression system as the first-generation HPV vaccine, a second-generation 9-valent HPV vaccine (Cecolin 9, Xiamen Innovax), covers seven high-risk types (HPV 16/18/31/33/45/52/58) and two low-risk types (HPV 6/11), was developed. To further evaluate the immunogenicity and safety of this 9vHPV vaccine candidate, a single-center, double-blind, randomized, and placebo-controlled phase 2 clinical trial was conducted in an expanded female population aged 18–45 years old.
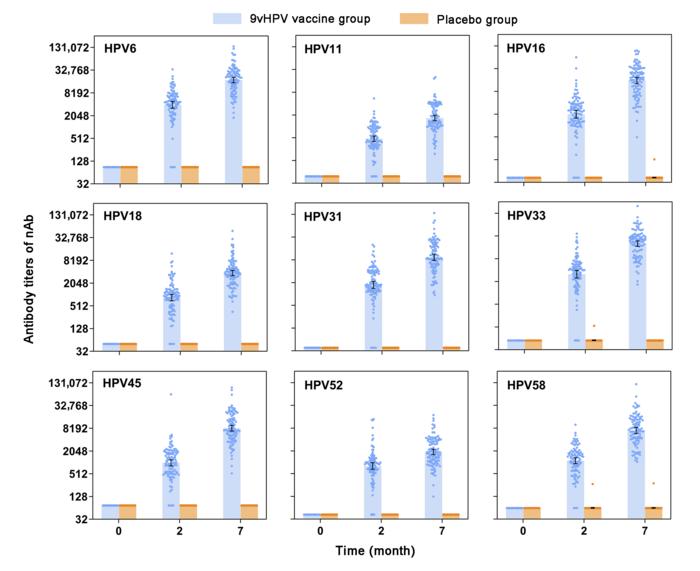
In total, 627 eligible healthy female volunteers from Dongtai, Jiangsu Province of China, were randomly allocated (1:1) to receive three doses of 1.0 mL (270 µg) of Cecolin 9 or a placebo on a 0-1-6-month schedule. All adverse events (AEs) were monitored after each vaccination, and serial serum samples were collected from all participants to evaluate the seroconversion rate and level of antibodies against nine HPV types. All participants in the per-protocol set for immunogenicity (PPS-I) seroconverted for nAbs or IgG antibodies against all the nine HPV types at month 7. For safety assessment, the incidence rates of total AEs in the Cecolin 9 and placebo groups were comparable, with the majority of them being mild and recovering shortly. None of the SAEs were considered related to vaccination. In conclusion, the E. coli-produced 9-valent HPV vaccine candidate was well tolerated and immunogenic, which warrants further efficacy studies in larger populations.
The insufficient supply and uneven distribution of HPV vaccines are one of the important barriers to the implementation of the WHO’s strategy to accelerate the elimination of cervical cancer, which was proposed in 2018. Given the robustness and low cost of the E. coli system, Cecolin 9 is believed to be an important addition to the national immunization program, especially in countries with limited resources.
Journal
Science Bulletin
DOI
10.1016/j.scib.2023.09.020




