Credit: ©Science China Press
The novel coronavirus outbreak is a global pandemic that has spread to more than 200 countries and territories around the world. Currently, countries and territories are fighting the spread of the disease using social distancing such as quarantine, testing or isolation which can be regarded as immunization.
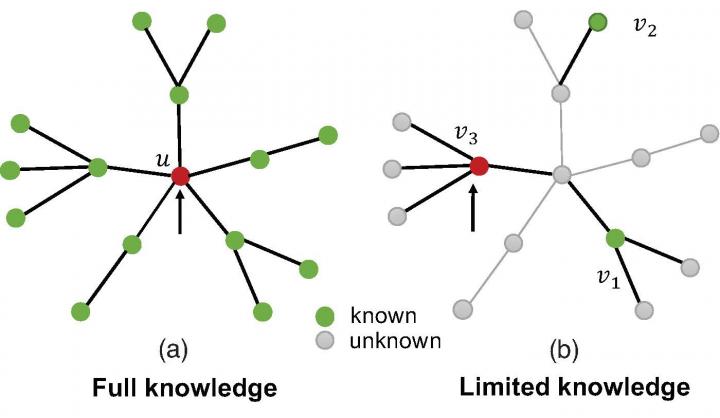
Given the important role that networks play in disease spreading, much effort has been made to understand and develop efficient methods such as targeted immunization. Previous models have typically assumed full knowledge of the network structure and immunized the most central nodes (see left panel of the below figure). However, in real-world scenarios, knowledge and observations of the full social network is usually limited thereby precluding a full assessment of the optimal (most central) nodes to test or quarantine or immunize that will efficiently stop the spread of pandemic.
Here, they present and study a novel and efficient immunization strategy incorporating the realistic case that we have only limited observability of the network (see right panel of the above figure). One can assume that only n nodes can be observed at a given time and that the most central of these n is immunized. This could represent a case where separate teams are sent to immunize or quarantine individuals. Each team examines n individuals and immunizes or quarantines the most connected of these n nodes.
The authors find, both analytically and via simulations, that as n increases, to even moderate numbers (approximately 10), the percolation threshold increases significantly towards its optimal value for i.e., towards percolation with full information. Larger values of percolation thresholds imply greater efficiency since a lower fraction of nodes can be immunized to stop the epidemic. They develop a general analytical framework for this approach of information on only n nodes, and determine the critical percolation threshold and the size of the giant component for networks with arbitrary degree distributions, for any given n. They also test our limited knowledge immunization on real-world networks and confirm that in these real networks, the critical threshold increases significantly even for small n.
The findings highlight that even for low n around 10 (local knowledge i.e., degrees of only 10 nodes) it is possible to obtain a significant reduction in the spreading as represented by the lower size of the giant component and the higher critical point of transition. These findings could help in applying efficient methods for immunizing individuals.
###
See the article:
Yangyang Liu, Hillel Sanhedrai, GaoGao Dong, Louis M. Shekhtman, Fan Wang, Sergey V. Buldyrev, Shlomo Havlin
Efficient network immunization under limited knowledge
Natl Sci Rev; doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwaa229
https:/
The National Science Review is the first comprehensive scholarly journal released in English in China that is aimed at linking the country’s rapidly advancing community of scientists with the global frontiers of science and technology. The journal also aims to shine a worldwide spotlight on scientific research advances across China.
Media Contact
Gaogao Dong
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




