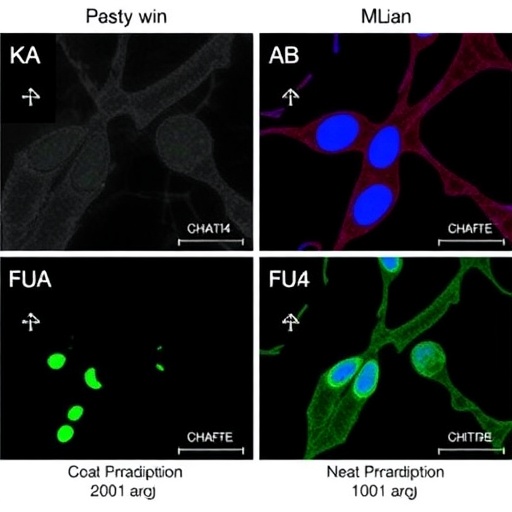
In the rapidly evolving landscape of cancer immunotherapy, glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) remains one of the most challenging tumors to treat. Characterized by its aggressive behavior and a profound capacity to evade the immune system, this malignant brain tumor has long puzzled researchers and clinicians alike. Recent advances shed light on the potential of interleukin-19 (IL-19) as a key player in modifying the tumor’s immunosuppressive microenvironment, offering a glimmer of hope for more effective therapeutic strategies. The intricate relationship between GBM and the immune system has opened up new avenues for exploration, particularly in the context of theranostic approaches.
IL-19, a member of the interleukin family, has emerged as a promising target for therapeutic intervention due to its dual role in modulating immune responses. The cytokine is predominantly produced by activated monocytes, macrophages, and other immune cells, reflecting its involvement in various inflammatory processes. However, its influence extends well beyond traditional immune responses, as it has been implicated in tumor progression and the development of immune tolerance within the tumor microenvironment. Researchers have recently turned their attention to IL-19, hypothesizing that targeting this cytokine could reset the balance between tumor progression and the host immune response in glioblastoma.
Preliminary studies suggest that elevated levels of IL-19 correlate with poor prognosis in glioblastoma patients. This correlation hints at an immune evasion mechanism employed by tumors, whereby they hijack IL-19 signaling to create an environment conducive to their survival. Specifically, IL-19 appears to foster a subset of immune cells that are less effective at mounting a robust anti-tumor response, further complicating the already intricate interplay between GBM and the immune system. As researchers delve deeper into the mechanistic pathways influenced by IL-19, they are beginning to uncover how this cytokine orchestrates immune cell behavior and modifies the tumor microenvironment.
The quest for effective immunotherapies in GBM has primarily focused on checkpoint inhibitors, vaccine strategies, and adoptive cell therapies. However, the immunosuppressive nature of glioblastoma poses significant challenges to these approaches. Tumors often recruit regulatory T cells (Tregs) and suppressive myeloid cells, both of which can dampen the efficacy of conventional immune therapies. By targeting IL-19, researchers hope to diminish the tumor’s ability to manipulate the immune response, thereby enhancing the overall effectiveness of existing therapeutic regimens.
Clinical models and trials investigating IL-19 as a potential therapeutic target are in their infancy, but early results are promising. The design of IL-19 antagonists aims not only to inhibit the cytokine’s activity but also to potentially reprogram the immune landscape surrounding the tumor cells. This could lead to the repolarization of suppressive immune cells into pro-inflammatory entities capable of mounting an effective anti-tumor response. Such an approach could synergize with conventional treatments, leading to a more favorable outcome for patients battling this formidable cancer.
Moreover, IL-19’s multifunctional nature may also lend itself well to theranostic applications—where therapeutic and diagnostic capabilities are combined. The identification of IL-19 as both a biomarker and a therapeutic target could revolutionize how clinicians approach treatment decisions in glioblastoma patients. Real-time monitoring of IL-19 levels may provide insights into the tumor’s behavior and responsiveness to treatment, thereby guiding personalized therapy. This transition from a one-size-fits-all model to a more tailored approach reflects the rapidly shifting paradigm in cancer treatment, one that prioritizes individual patient profiles and tumor characteristics.
The potential for IL-19-targeted therapies to reshape the glioblastoma treatment landscape extends beyond mere survival benefits. By understanding and manipulating the cytokine’s role within the tumor microenvironment, researchers may also address quality of life issues that arise during GBM treatment. Many conventional treatments carry debilitating side effects that can severely impact a patient’s well-being, leading to a pressing need for therapies that are not only effective but also minimize adverse effects. The exploration of IL-19 as a novel target may thus align treatment effectiveness with enhanced quality of life for patients.
Furthermore, the mechanistic insights gained from studying IL-19 can be extrapolated to other tumor types where immune evasion plays a critical role. As researchers establish the biological underpinnings of IL-19 in glioblastoma, it invites a broader examination of its effects across a spectrum of cancers. Understanding how IL-19 operates in different tumor microenvironments can lead to the identification of similar therapeutic targets and pave the way for innovative treatment strategies across the oncological landscape.
The interplay of IL-19 with other cytokines and immune mediators also warrants further investigation. The complexity of the immune system’s response to tumors underscores the importance of a holistic understanding of the tumor microenvironment. By elucidating the network of signals regulated by IL-19, researchers can potentially identify new combinatorial therapies that address multiple facets of the immune response in glioblastoma and beyond. Recent findings in other malignancies point toward promising synergies between cytokines, reinforcing the notion that a multifactorial approach may yield the most significant therapeutic gains.
As we stand on the precipice of breakthroughs in glioblastoma research, IL-19 represents more than just a singular target; it signifies a paradigm shift in the way we understand and treat this challenging form of cancer. The intricate dance between tumor cells and immune components inspires a renewed commitment to unraveling the complexities of the glioblastoma microenvironment. As new studies emerge detailing IL-19’s mechanisms, the excitement surrounding its therapeutic potential could soon translate into innovative treatment modalities, offering renewed hope for patients afflicted by this devastating disease.
In conclusion, the exploration of IL-19 as a theranostic target in glioblastoma epitomizes the ongoing quest for more refined and effective cancer therapies. With its dual role in both promoting and disrupting immune tolerance, IL-19 harbors the potential to not only expose the tumor to the immune system but also help carve a pathway towards a tumor-inhibitory environment. The coming years may very well see a revolution in how glioblastoma is approached, with IL-19 at the forefront of this transformative journey, fostering a future where immunotherapy can reclaim its rightful place as a cornerstone of cancer treatment.
Subject of Research: Interleukin-19 (IL-19) as a theranostic target in glioblastoma.
Article Title: IL-19 as a promising theranostic target to reprogram the glioblastoma immunosuppressive microenvironment.
Article References:
Lee, G.A., Hsu, J.BK., Chang, YW. et al. IL-19 as a promising theranostic target to reprogram the glioblastoma immunosuppressive microenvironment.
J Biomed Sci 32, 34 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-025-01126-w
Image Credits: AI Generated
DOI:
Keywords: IL-19, glioblastoma, immunotherapy, tumor microenvironment, theranostic target, cancer research.
Tags: cytokine modulation in cancer therapyglioblastoma and immune response dynamicsglioblastoma multiforme immunotherapy challengesIL-19 in glioblastoma treatmentimmune system evasion in glioblastomaimmune tolerance in glioblastomainflammatory processes in tumor progressioninterleukin-19 role in tumor microenvironmentpotential of IL-19 in cancer treatmenttargeting immune suppression in brain tumorstheranostic approaches for glioblastomatherapeutic strategies for challenging brain tumors