A smart quantum technology for identification of light sources with fewer measurements
Credit: Elsa Hahne
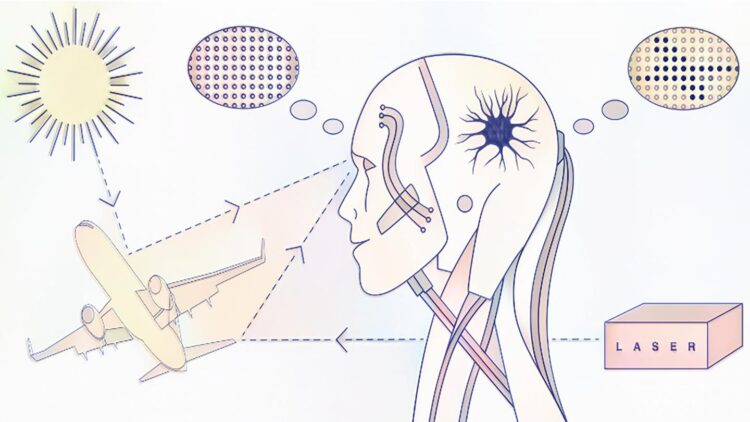
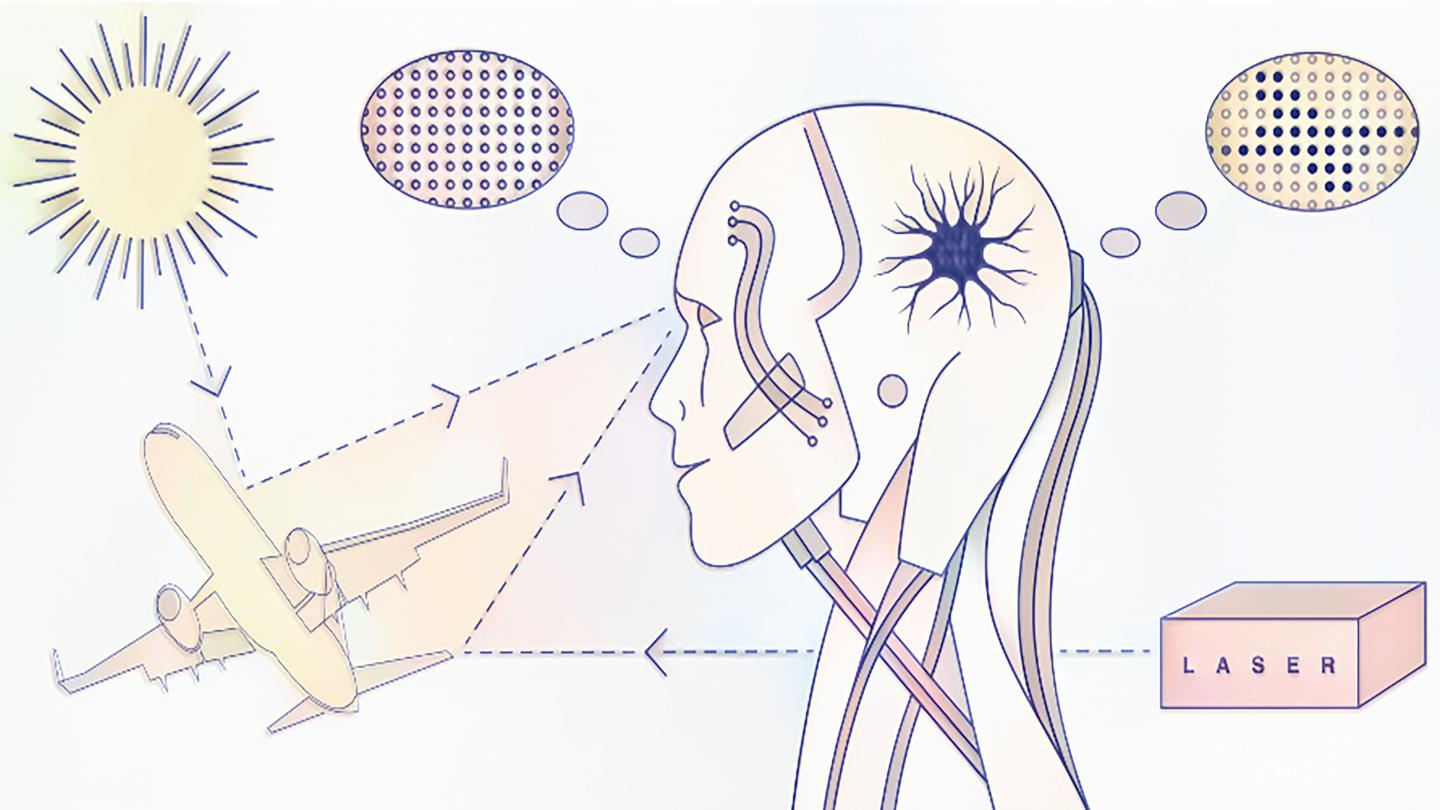
WASHINGTON, May 5, 2020 — Identifying sources of light plays an important role in the development of many photonic technologies, such as lidar, remote sensing, and microscopy. Traditionally, identifying light sources as diverse as sunlight, laser radiation, or molecule fluorescence has required millions of measurements, particularly in low-light environments, which limits the realistic implementation of quantum photonic technologies.
In Applied Physics Reviews, from AIP Publishing, researchers demonstrated a smart quantum technology that enables a dramatic reduction in the number of measurements required to identify light sources.
“We trained an artificial neuron with the statistical fluctuations that characterize coherent and thermal light,” said Omar Magana-Loaiza, an author of the paper.
After researchers trained the artificial neuron with light sources, the neuron could identify underlying features associated with specific types of light.
“A single neuron is enough to dramatically reduce the number of measurements needed to identify a light source from millions to less than hundred,” said Chenglong You, a fellow researcher and co-author on the paper.
With fewer measurements, researchers can identify light sources much more quickly, and in certain applications, such as microscopy, they can limit light damage since they don’t have to illuminate the sample nearly as many times when taking measurements.
“If you were doing an imaging experiment with delicate fluorescent molecular complexes, for example, you could reduce the time the sample is exposed to light and minimize any photodamage,” said Roberto de J. León-Montiel, another co-author.
Cryptography is another application where these findings could prove valuable. Typically to generate a key to encrypt an email or message, researchers need to take millions of measurements. “We could speed up the generation of quantum keys for encryption using a similar neuron,” said Magana-Loaiza.
As laser light plays an important role in remote sensing, this work could also enable development of a new family of smart lidar systems with the capability to identify intercepted or modified information reflected from a remote object. Lidar is a remote sensing method that measures distance to a target by illuminating the target with laser light and measuring the reflected light with a sensor.
“The probability of jamming a smart quantum lidar system will be dramatically reduced with our technology,” he said. In addition, the possibility to discriminate lidar photons from environmental light such as sunlight will have important implications for remote sensing at low-light levels.
###
The article, “Identification of light sources using machine learning,” is authored by Chenglong You, Mario Alan Quiroz Juarez, Aidan Lambert, Narayan Bhusal, Chao Dong, Armando Perez-Leija, Amir Javaid, Roberto de J. León Montiel and Omar S. Magana-Loaiza. The article will appear in Applied Physics Reviews on May 5, 2020 (DOI: 10.1063/1.5133846). After that date, it can be accessed at https:/
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Applied Physics Reviews features articles on significant and current topics in experimental or theoretical research in applied physics, or in applications of physics to other branches of science and engineering. The journal publishes both original research on pioneering studies of broad interest to the applied physics community, and reviews on established or emerging areas of applied physics. See https:/
Media Contact
Larry Frum
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.