Energy use in buildings contributes to over 40% of the world’s total energy consumption, of which lighting and space cooling make up a significant proportion. Traditional glass windows have been used for centuries, however, are not energy-efficient. In the summer, the near-infrared sunlight transmitted through windows produces into undesired heating, and the high reflection of mid-infrared limits heat rejection from the building. This “greenhouse effect” aggravates cooling energy consumption. How to manipulate the near- and mid-infrared light through the windows to reduce cooling consumption while maintaining the high visible transparence for lightning remains a very challenging problem for the design of glasses.
Credit: Jia Fu, Chunzao Feng, Yutian Liao, Mingran Mao, Huidong Liu & Kang Liu;
Energy use in buildings contributes to over 40% of the world’s total energy consumption, of which lighting and space cooling make up a significant proportion. Traditional glass windows have been used for centuries, however, are not energy-efficient. In the summer, the near-infrared sunlight transmitted through windows produces into undesired heating, and the high reflection of mid-infrared limits heat rejection from the building. This “greenhouse effect” aggravates cooling energy consumption. How to manipulate the near- and mid-infrared light through the windows to reduce cooling consumption while maintaining the high visible transparence for lightning remains a very challenging problem for the design of glasses.
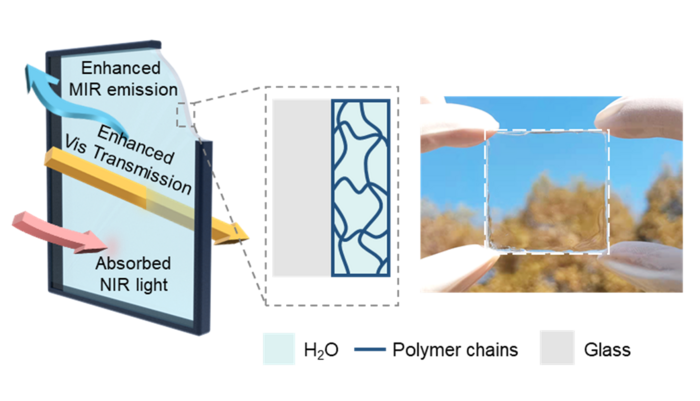
Researchers at Wuhan University in China, led by Prof. Kang Liu, propose a novel design of hydrogel-glass which consists of a layer of hydrogel and a layer of normal glass. Compared with traditional glass, the hydrogel-glass possesses a higher level of visible light transmission, stronger near-infrared light blocking, and higher mid-infrared thermal emittance. With these properties, the researchers demonstrate the hydrogel-glass windows can enhance indoor illumination and reduce the indoor temperature. Simulations show that the novel window can reduce the energy use of building lighting and cooling ranging from 2.37 to 10.45 MJ·m−2·year−1 for different cities around the world. The work entitled “Broadband light management in hydrogel glass for energy efficient windows” was published on the journal of Frontiers of Optoelectronics (August 5, 2022).
###
Reference: Fu, J., Feng, C., Liao, Y., Mao, M., Liu, H., Liu, K. Broadband light management in hydrogel glass for energy efficient windows. Front. Optoelectron. 15, 33 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12200-022-00033-4
About Higher Education Press
Founded in May 1954, Higher Education Press Limited Company (HEP), affiliated with the Ministry of Education, is one of the earliest institutions committed to educational publishing after the establishment of P. R. China in 1949. After striving for six decades, HEP has developed into a major comprehensive publisher, with products in various forms and at different levels. Both for import and export, HEP has been striving to fill in the gap of domestic and foreign markets and meet the demand of global customers by collaborating with more than 200 partners throughout the world and selling products and services in 32 languages globally. Now, HEP ranks among China’s top publishers in terms of copyright export volume and the world’s top 50 largest publishing enterprises in terms of comprehensive strength.
The Frontiers Journals series published by HEP includes 28 English academic journals, covering the largest academic fields in China at present. Among the series, 13 have been indexed by SCI, 6 by EI, 2 by MEDLINE, 1 by A&HCI. HEP’s academic monographs have won about 300 different kinds of publishing funds and awards both at home and abroad.
About Frontiers of Optoelectronics
Frontiers of Optoelectronics (FOE) aims at introducing the most recent research results and the cutting edge improvements in the area of photonics and optoelectronics. It is dedicated to be an important information platform for rapid communication and exchange between researchers in the related areas. The journal publishes review articles, research articles, letters, comments, special issues, and so on. The Editors-in-Chief are Academician Qihuang Gong from Peking University and Prof. Xinliang Zhang from Huazhong University of Science and Technology. FOE has been indexed by ESCI, Ei, SCOPUS, DOAJ, CSCD, Source Journals for Chinese Scientific and Technical Papers and Citations, etc. FOE is fully open access since 2022.
Journal
Frontiers of Optoelectronics
DOI
10.1007/s12200-022-00033-4
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Broadband light management in hydrogel glass for energy efficient windows
Article Publication Date
5-Aug-2022




