A new international study carried out by the Institute of Environmental Science and Technology of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (ICTA-UAB) has examined the distribution of biomass across all life in the oceans, from bacteria to whales. Their quantification of human impact reveals a fundamental alteration to one of life’s largest scale patterns.
Credit: Ian Hatton, Eric Galbraith et al.
A new international study carried out by the Institute of Environmental Science and Technology of the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (ICTA-UAB) has examined the distribution of biomass across all life in the oceans, from bacteria to whales. Their quantification of human impact reveals a fundamental alteration to one of life’s largest scale patterns.
As policymakers assemble in Glasgow for the UN Climate Change Conference, there is growing recognition that human impacts on the environment are going global and growing urgent. However, gaining a quantitative perspective on these impacts has remained elusive.
Scientists from the ICTA-UAB in Spain, the Max Planck Institute for Mathematics in the Sciences in Germany, Queensland University of Technology in Australia, Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel, and McGill University in Canada have used advances in ocean observation and large meta-analyses to show that human impacts have already had major consequences for the larger oceanic species, and have dramatically changed one of life’s largest scale patterns – a pattern encompassing the entire ocean’s biodiversity, from bacteria to whales.
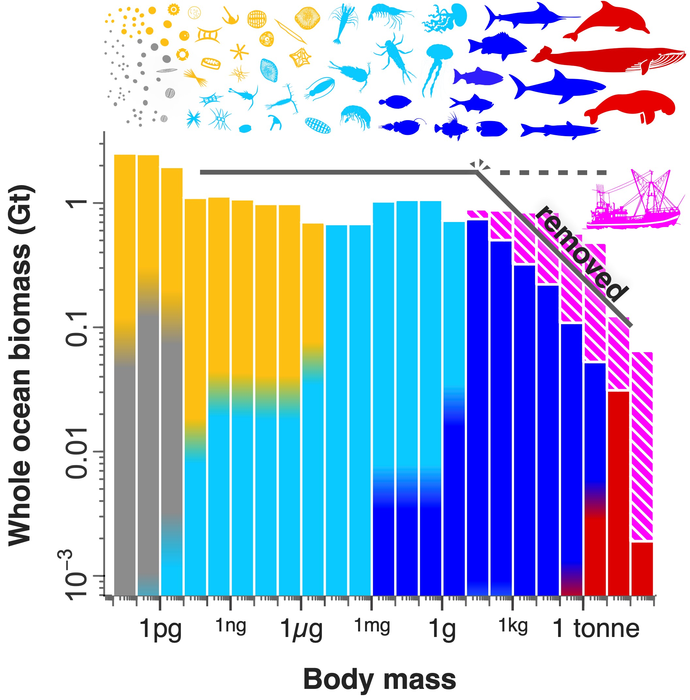
Early samples of marine plankton biomass from 50 years ago led researchers to hypothesize that roughly equal amounts of biomass occur at all sizes. For example, although bacteria are 23 orders of magnitude smaller than a blue whale, they are also 23 orders of magnitude more abundant. This size-spectrum hypothesis has since remained unchallenged, even though it was never verified globally from bacteria to whales. The authors of the study, published in the journal Science Advances, sought to test this hypothesis on a global scale for the first time. They used historical reconstructions and marine ecosystem models to estimate biomass before industrial scale fishing got underway (pre-1850) and compared this data to the present-day.
“One of the biggest challenges to comparing organisms spanning bacteria to whales is the enormous differences in scale”, recalls ICTA researcher and lead author Dr. Ian Hatton, currently based at the Max Planck Institute for Mathematics in the Sciences. “The ratio of their masses is equivalent to that between a human being and the entire Earth. We estimated organisms at the small end of the scale from more than 200,000 water samples collected globally, but larger marine life required completely different methods”.
Their approach focused on 12 major groups of aquatic life over roughly 33,000 grid points of the ocean. Evaluating the pre-industrial ocean conditions (pre-1850) largely confirmed the original hypothesis: there is a remarkably constant biomass across size classes.
“We were amazed to see that each order of magnitude size class contains approximately 1 gigaton of biomass globally”, remarks co-author Dr. Eric Galbraith of the ICTA-UAB and a current professor at McGill University. However, he was quick to point out exceptions at either extreme. While bacteria are over-represented in the cold, dark regions of the ocean, the largest whales are relatively rare, thus highlighting exceptions from the original hypothesis.
In contrast with an even biomass spectrum in the pre-1850 ocean, an investigation of the spectrum at present revealed human impacts on ocean biomass through a new lens. While fishing and whaling only account for less than 3 percent of human food consumption, their effect on the biomass spectrum is devastating: large fish and marine mammals such as dolphins have experienced a biomass loss of 2 Gt (60% reduction), with the largest whales suffering an unsettling almost 90% decimation. The authors estimate that these losses already outpace potential biomass losses even under extreme climate change scenarios.
“Humans have impacted the ocean in a more dramatic fashion than merely capturing fish. It seems that we have broken the size spectrum – one of the largest power law distributions known in nature”, reflects ICTA researcher and co-author Dr. Ryan Heneghan. These results provide a new quantitative perspective on the extent to which anthropogenic activities have altered life at the global scale.
###
Hatton, I.A., Heneghan, R. F., Bar-On, Y. M., Galbraith E. D. (2021) The global ocean size-spectrum from bacteria to whales. Science Advances. DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abh3732
Contact:
Dr. Ian Hatton – [email protected]
Professor Eric Galbraith – [email protected]
Media Contact
Isabel Lopera – [email protected]
Office: 34-935-868-652
Journal
Science Advances
DOI
10.1126/sciadv.abh3732
Method of Research
Data/statistical analysis
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
The global ocean size spectrum from bacteria to whales
Article Publication Date
10-Nov-2021




