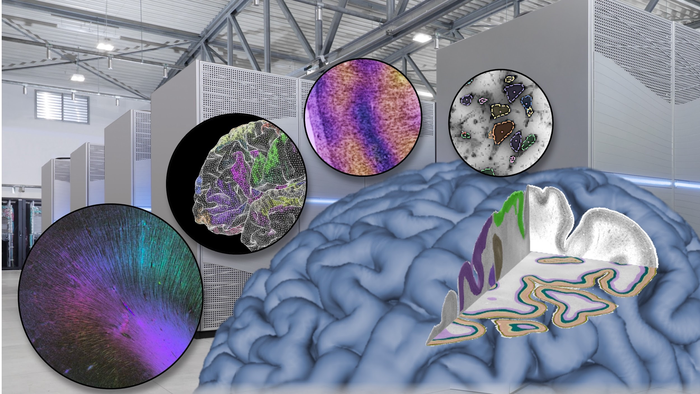
“Understanding the brain in all its complexity requires insights from multiple scales – from genomics, cells and synapses to the whole-organ level. This means working with large amounts of data, and supercomputing is becoming an indispensable tool to tackle the brain,” says Katrin Amunts, Scientific Director of the Human Brain Project (HBP), Director of the C. and O. Vogt-Institute of Brain Research, Universitätsklinikum Düsseldorf and Director of the Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine (INM-1) at Research Centre Jülich.
Credit: Timo Dickscheid, Sascha Kreklau / Forschungszentrum Juelich
“Understanding the brain in all its complexity requires insights from multiple scales – from genomics, cells and synapses to the whole-organ level. This means working with large amounts of data, and supercomputing is becoming an indispensable tool to tackle the brain,” says Katrin Amunts, Scientific Director of the Human Brain Project (HBP), Director of the C. and O. Vogt-Institute of Brain Research, Universitätsklinikum Düsseldorf and Director of the Institute of Neuroscience and Medicine (INM-1) at Research Centre Jülich.
“It’s an exciting time in supercomputing,” says Thomas Lippert, Director of the Jülich Supercomputing Centre and leader of supercomputing in the Human Brain Project. “We get a lot of new requests from researchers of the neuroscience community that need powerful computing to tackle the brain’s complexity. In response, we are developing new tools tailored to investigating the brain.”
The human brain contains around 86 billion neurons that form trillions of contact points. Imaging an entire brain at cellular resolutions produces data in the range of several Petabytes; electron microscopy of a whole brain would amount to more than one Exabyte of data. “Brain research, medicine and information technologies face challenges that can only be addressed by joining the forces of all three domains,” says Amunts.
In Europe, the big data challenge of neuroscience is addressed by the Human Brain Project’s research infrastructure EBRAINS. It provides a range of tools, data-, and compute-services to brain researchers. This includes access to supercomputing systems via the Fenix federated Infrastructure, which has been set up by Europe’s leading Supercomputing Centres as part of the Human Brain Project and will serve communities beyond brain research.
Within the next five years, Europe is aiming to deploy its first two exascale supercomputers. They will be acquired by the European High Performance Computing Joint Undertaking (EuroHPC JU), a joint initiative between the EU, European countries and private partners. “The brain research community stands ready to use these exascale systems,” says Amunts.
Journal
Science
Method of Research
Commentary/editorial
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Brain research challenges supercomputing
Article Publication Date
25-Nov-2021




