Credit: Maki Takagishi
Nagoya, Japan – Some cells in the body contain long thin structures called cilia on their surface, which exhibit a whip-like motion that promotes the flow of fluid past the cell. Although these cilia are known to play vital roles in the body, much remains to be understood about their molecular components and the mechanisms by which they work. This is especially true for the cilia on cells that line the ventricles of the brain, which contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that has various functions including cushioning the brain against potentially damaging impacts.
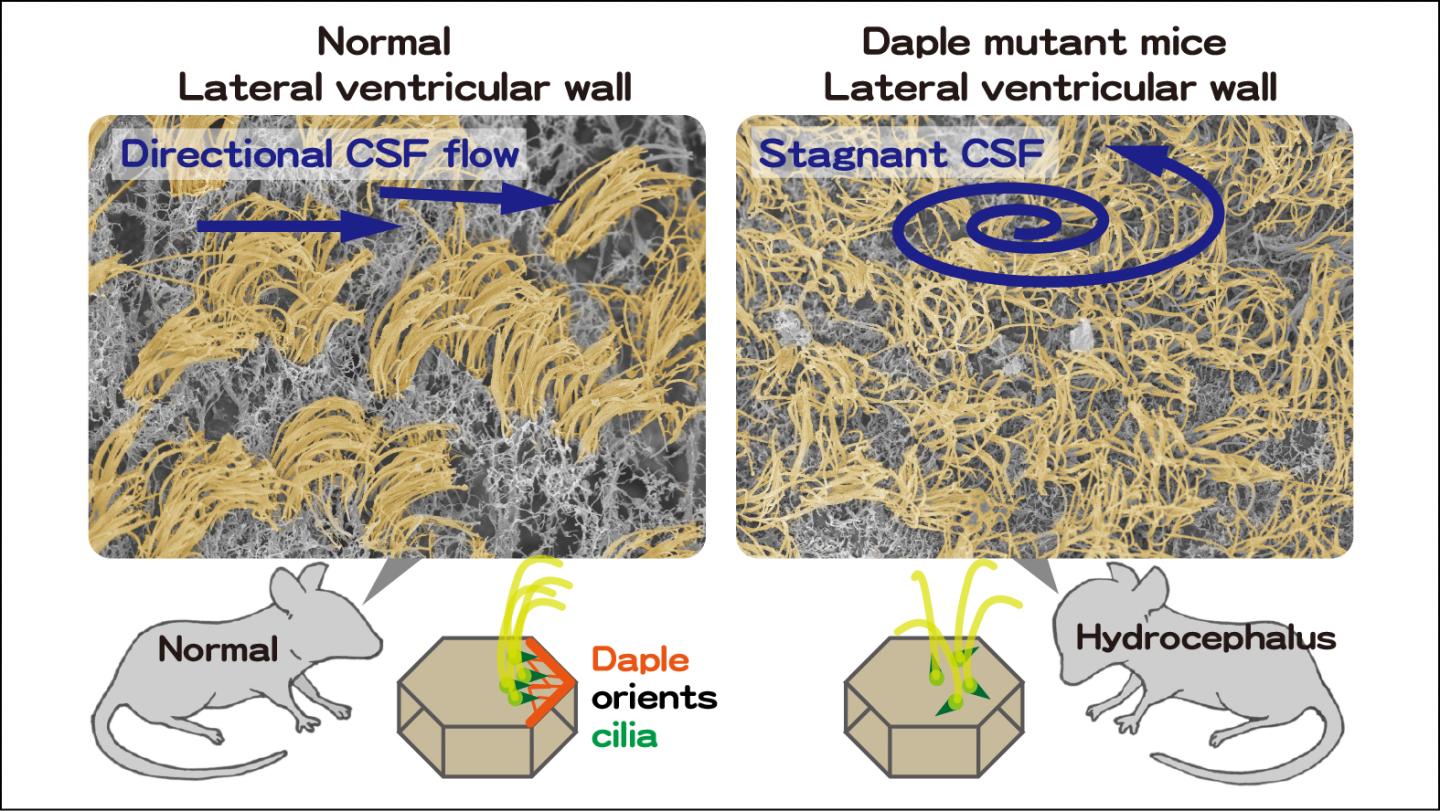
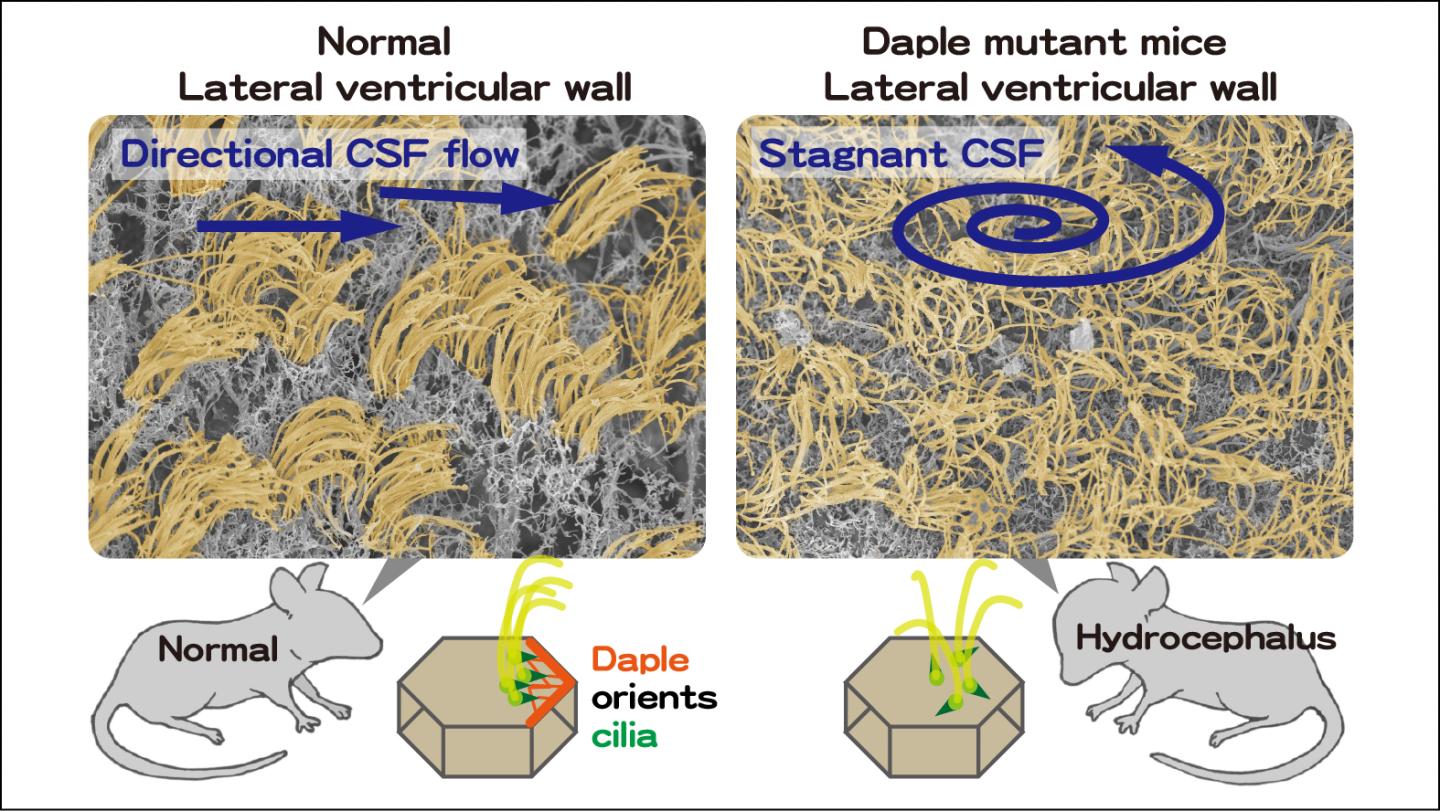
A team at Nagoya University has shed light on this issue by revealing that a molecule called Daple is essential for cilia to adopt an arrangement by which they can beat in one direction at the same time, thereby creating a flow of fluid past the cell exterior. This arrangement on cell surfaces all along the lining of ventricles in the brain ensures the correct flow of CSF, which in turn prevents its accumulation associated with brain swelling known as hydrocephalus.
The team revealed the importance of Daple by creating mutant mice that did not express the Daple protein. By around 20 days after birth, these mice had enlarged heads, similar to that in human hydrocephalus cases. Further studies showed that this was due to the flow of CSF being disrupted.
"We cut out part of the wall of the brain's lateral ventricle and investigated whether fluorescent beads would be propelled along its surface in a particular direction," says Maki Takagishi. "For mice with normal Daple expression, there was consistent movement in one direction, but this was absent in the Daple-knockout mice."
The findings also showed that the lack of Daple stopped cilia all adopting the same orientation on the same side of cells. Without the cilia all beating in the same direction, there would be no directional flow of CSF, leading to its accumulation and subsequent swelling.
According to Masahide Takahashi, "Daple functions through a cytoplasmic structure called microtubules, which are protein filaments involved in various functions including maintaining the overall structure of cells. When Daple is absent, the microtubules are unable to accurately specify the arrangement of structures called basal bodies, from which the cilia develop."
The team's findings should lead to a deeper understanding of diseases caused by the dysfunction of cilia. These include not only hydrocephalus, but also asthma and even female infertility, given the structural and functional similarities of cilia in the trachea and oviduct.
The article "Daple Coordinates Planar Polarized Microtubule Dynamics in Ependymal Cells and Contributes to Hydrocephalus" was published in Cell Reports at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.06.089.
###
Media Contact
Koomi Sung
[email protected]
@NU__Research
http://www.nagoya-u.ac.jp/en/
Original Source
http://en.nagoya-u.ac.jp/research/activities/news/2017/08/how-whip-like-cell-appendages-promote-bodily-fluid-flow.html http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.06.089