Over the course of hundreds of millions of years, Earth has lived through a series of climatic shifts, shaping the planet as we know it today. Past changes in CO2 levels and temperature can help us understand the planet‘s response to global warming today.
Credit: Rogger J et al. Science Advances 2024
Over the course of hundreds of millions of years, Earth has lived through a series of climatic shifts, shaping the planet as we know it today. Past changes in CO2 levels and temperature can help us understand the planet‘s response to global warming today.
As part of a growing field called biogeodynamics, researchers are racing to understand how such changes have impacted life on the planet in the past. “We’re trying to understand processes relevant to the present using the geological past,” says Julian Rogger, who focuses on biogeodynamics at the Institute of Geophysics at ETH Zurich.
Rogger is fascinated by the interplay of plant life and climate. So far our planet is the only one we know of in the universe suited to support living organisms. Its climatic conditions allow for the presence of enough liquid water to enable plants and other complex organisms to thrive, or at least survive. When the planet’s climate shifts, it impacts plant life, forcing ecosystems to evolve and adapt to changing conditions. “I’m interested in the role of life itself in the whole system,” Rogger says. “I find it really fascinating to reconstruct the world as it was millions of years ago.”
Plants actively shape the climate cycle
In a paper published recently in the journal Science Advances, Rogger and colleagues from ETH and the University of Leeds argue that those plants aren’t just passive participants in Earth’s climate cycle – they can play an important role in shaping it. “We could assume life is just reacting to changes, but it’s also possible it’s interacting with the system and regulates it,” Rogger says.
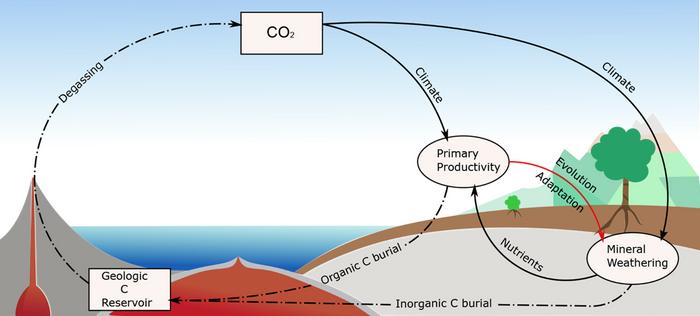
To show how, Rogger used computer models that simulate the interplay between climate change, movement of the continents and plant life in the deep past. The models indicate plants probably help regulate the makeup of the planet’s atmosphere by trapping carbon and emitting oxygen, helping control CO2 levels. They also accelerate the process of mineral weathering in soils, a process that consumes CO2. Rogger’s models suggest the planet’s climate and atmosphere are part of a feedback loop: Life itself plays a role in regulating or accelerating climatic changes.
390 million years of Earth’s history reconstructed
When change is slow – slow enough for plants to evolve or spread to new niches over millions of years – plant activity can act as a buffer, preventing temperatures from shifting too rapidly. But geology and the fossil record show there were also changes that took place too fast, and resulted in major disruptions of vegetation and even mass extinctions. “What we want to know is how fast vegetation is able to change its characteristics when the world suddenly gets 5 or 6 degrees warmer,” Rogger says. “The overall goal is to understand the co-evolution of climate, vegetation and tectonics.”
Rogger and his co-authors – an interdisciplinary team of geologists, computer scientists and earth scientists– created a computer model of the last 390 million years that took into account the shifting of the continents and climate and the vegetation’s response to these changes. Running simulations on powerful supercomputers can still take up to a month, given the complexity of the problem and the length of time they are supposed to represent.
Whenever possible, the team uses geological data to make the models as realistic as possible: Chemical analysis of sediments, for example, can be an indicator for carbon dioxide levels in the past. Fossils can show when dramatic shifts in climate led to mass extinctions, or the evolution of new ecosystems in response to changing conditions.
The models show that long periods of stability make it possible for vegetation to flourish, absorbing CO2 and stabilizing the Earth’s climate over time. In their models, the team saw that plants were able to evolve fast enough to adjust to gradual shifts in climate and landscapes due to continental drift, for example.
But when the climate system is disrupted and changes too rapidly for vegetation to adapt, the opposite happens: Plants are wiped out and can’t act as a buffer to slow down shifts in climate. Without plants to act as a brake, environmental changes happen even faster and push further towards the extreme. “It’s like a feedback effect,” Rogger explains. “Because regulation falls away, you could have a stronger increase in CO2 and more climate change than was previously expected.”
Resilience put to the test
In the geological record, abrupt climate changes are often accompanied by mass extinction events. “There are strong vegetation changes where it took thousands to millions of years for vegetation to adapt and recover,” Rogger says, “and what recovers can be very different than what was there before.”
That’s not good news. “The rate of change we have at the moment is thought to be unprecedented over the past 400 million years,” Rogger says. “There could be a reduction in the capacity of vegetation to regulate climate if there is a strong change, like we’re experiencing now.”
At a time when the Earth’s climate is changing faster than ever before, Rogger’s research has practical implications: Information from the past can help people today understand how resilient the Earth’s interlocking systems are. “How fast are ecosystems able to respond to changes in the climate and landscape? That’s one of the major unknowns,” he says. “It’s an acute question – how resilient is the Earth?”
Journal
Science Advances
DOI
10.1126/sciadv.adj4408
Method of Research
Computational simulation/modeling
Article Title
Speed of thermal adaption of terrestrial vegetation alters Earth’s long-term climate
Article Publication Date
1-Mar-2024