Credit: Pierre Fabre and Lucille Lopez-Delisle/EPFL
The genes that are involved in the development of the fetus are activated in different tissues and at different times. Their expression is carefully regulated by so-called "enhancer sequences", which are often located far from their target genes, and requires the DNA molecule to loop around and bring them in close proximity to their target genes. Such 3D changes of the DNA are in turn controlled by other sequences called topologically associating domains (TADs). EPFL scientists have now studied the TADs involved in digit development in the fetus and have gained insights in some of the big questions surrounding them. The work is published in Genome Biology.
Boundaries and tape
TADs are portion of the DNA molecule that divides the entire genome of an organism into manageable chunks, like districts in a city. Inside the cell, the vast amount of DNA is packaged into chromatin and chromatin is packaged into the familiar chromosomes. Inside every TAD there exist genes as well as the elements that regulate them, all packaged together and insulated from genes and regulators in neighboring TADs, like channels or walls that separate city districts. Breaking down the boundaries set by TADs leads to a number of disorders such as colon, esophagus, brain, and blood cancers.
But despite their importance, we know little about these boundaries, which confer to a TAD its structure. This raises the question: Is the information coming from the inner parts of a TAD or due to boundaries. The latter are DNA sequences that are often associated with the proteins cohesin and CTCF, which stick to the TAD extremities like tape, seemingly helping them divide and loop DNA around. CTCF, found at the boundaries of TAD domains, has been of special interest, recently, as it was shown to insulate TAD domains from each other rather than the genetic elements within a single TAD domain.
Digit insights
Now, a study by the lab of Denis Duboule at EPFL, with their colleagues at the University of Geneva, provides significant insights about TADs and how they organize DNA. "We were looking at DNA architecture and function," says researcher Pierre Fabre, who led the project.
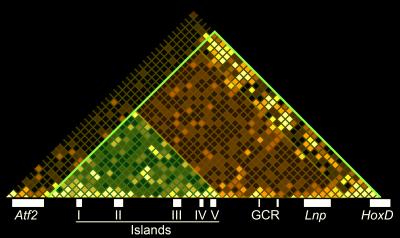
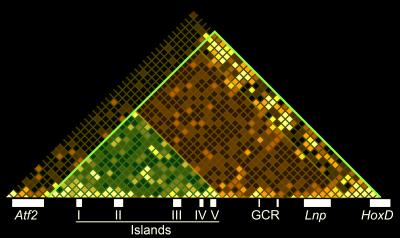
Specifically, the scientists looked at a set of genes that Duboule's lab has longstanding expertise, the HoxD gene cluster, which controls digit development in mammalian embryos. The researchers used it as a model to learn about the interplay between multiple enhancer sequences within TADs, as well as "constitutive contacts", which refer to constant interactions between TADs and proteins that organize the packaging of HoxD genes into DNA chromatin, even without gene transcription going on.
The researchers combined chromosome conformation capture (4C-seq) and DNA fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) to measure compaction levels and TAD discreteness. They also made serial genomic deletions and inversions that impact the integrity of the HoxD chromatin domain and also cause remodeling of long-range regulatory elements. This allowed them to assess the robustness of the TAD architecture in this domain.
The data indicates that these TADs can host multiple associations between Hoxd genes and up to three of their enhancers, and that disrupting the 3D structure of chromatin leads to the remodeling of TAD structure. Additionally, CTCF seems to mediate the gating of long-range DNA contacts in a boundary-selection mechanism. "The building of the recomposed TAD depends on both distinct functional and intrinsic parameters such as the genomic distance," says Fabre.
###
Funding
EPFL
University of Geneva
Swiss National Research Fund
European Research Council (SystemHox and RegulHox)
Reference
Pierre J. Fabre, Marion Leleu, Benjamin H. Mormann, Lucille Lopez-Delisle, Daan Noordermeer, Leonardo Beccari, Denis Duboule. Large scale genomic reorganization of topological domains at the HoxD locus. Genome Biology 18:149, 7 August 2017. DOI: 10.1186/s13059-017-1278-z
Media Contact
Nik Papageorgiou
[email protected]
41-216-932-105
@EPFL_en
http://www.epfl.ch/index.en.html
Original Source
https://actu.epfl.ch/news/how-the-genome-sets-its-functional-micro-architect/ http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13059-017-1278-z