Light supplies the energy plants need to build up biomass. A research team from Bergen, Bochum, Düsseldorf, Münster and Potsdam headed by Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) is researching how plants adapt their photosynthesis to changing light. In the scientific journal Nature Communications, they describe a key molecular mechanism that synchronises the processes involved.
Credit: Uni Bergen/Tobias Rindfleisch
Light supplies the energy plants need to build up biomass. A research team from Bergen, Bochum, Düsseldorf, Münster and Potsdam headed by Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) is researching how plants adapt their photosynthesis to changing light. In the scientific journal Nature Communications, they describe a key molecular mechanism that synchronises the processes involved.
Photosynthesis is the central process by which plants build up biomass using light, water and the carbon dioxide from the air. Gaining a detailed understanding of this process makes it possible to modify and thus optimise it – for example with a view to increasing food production or stress tolerance.
The research group headed by Professor Dr Ute Armbruster from the Institute of Molecular Photosynthesis at HHU is examining this process from a range of perspectives. Together with an interdisciplinary research team, the group now presents its findings on the processes involved in plant reactions to different light conditions in a current publication in Nature Communications. The Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology in Golm and research groups from the universities in Bergen (Norway), Bochum, Münster and Potsdam were involved in the work.
Photosynthesis comprises two steps or “modules”. First of all, in the so-called light-driven reaction, light energy is converted into chemical energy that the plant can use in the form of the molecules ATP and NADPH. This energy is then used to fix carbon dioxide from the air into biomass by the “carbon-fixing reaction”.
Plants live in often rapidly changing light conditions. To make optimum use of this light, the modules must be closely synchronised. There has been little scientific research into this synchronisation in particular to date.
If it is too bright, the plant cannot convert all the light energy; this is a potentially harmful situation. To ensure that no damage is caused by the excess light energy – which can result in the formation of e.g. highly reactive oxygen species – the plant activates a protective mechanism: The so-called energy-dependent quenching (for short: “qE”) ensures that excess energy is discharged in the form of heat.
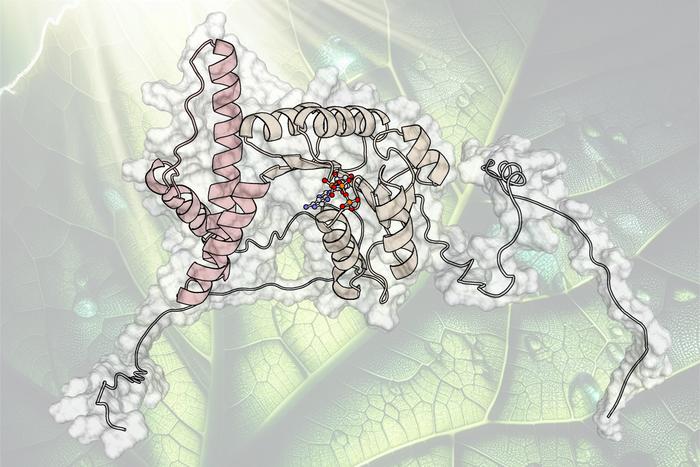
From earlier research, it is known that qE is switched off again more quickly by the “thylakoid K+-exchange antiporter 3” (KEA3) in the shade. However, the process is still so slow overall that usable light energy is lost when brightness decreases.
For the first time, the research team has now identified a molecular mechanism by means of which the two photosynthesis modules synchronise their activities via KEA3. To achieve this, the researchers used both computer simulations and various experimental approaches, including biosensors.
Firstly, the pH value of the medium surrounding the thylakoid membrane reacts highly dynamically to light changes. Secondly, the structure and thus the activity of KEA3 changes according to the pH value. However, this only occurs when KEA3 has also bound ATP and NADPH. In excess light, this leads to KEA3 being inactivated, thus allowing qE to be active. After a sudden transition to shade, KEA3 becomes activated, which upregulates the light-driven reactions of photosynthesis.
Professor Armbruster: “Through our work, we now understand for the first time how the two functional modules of photosynthesis communicate with each other via KEA3. It is important to know this with a view to developing strategies to improve photosynthesis in the field, in order to increase crop yields in the long term.”
Original publication:
Michał Uflewski, Tobias Rindfleisch, Kübra Korkmaz, Enrico Tietz, Sarah Mielke, Viviana Correa Galvis, Beatrix Dünschede, Marcin Luzarowski, Aleksandra Skirycz, Markus Schwarzländer, Deserah D. Strand, Alexander P. Hertle, Danja Schünemann, Dirk Walther, Anja Thalhammer, Martin Wolff and Ute Armbruster. The thylakoid proton antiporter KEA3 regulates photowsynthesis in response to the chloroplast energy status. Nature Communications 15, 2792 (2024)
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-47151-5
Journal
Nature Communications
DOI
10.1038/s41467-024-47151-5
Article Title
The thylakoid proton antiporter KEA3 regulates photowsynthesis in response to the chloroplast energy status
Article Publication Date
30-Mar-2024




