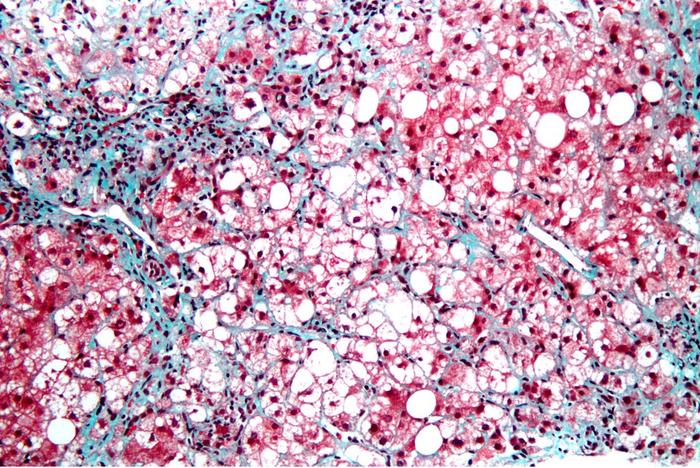
Hepatic fibrosis occurs when scar tissue replaces damaged cells in the liver. Over time, accumulating scarring distorts the liver, interferes with its blood supply and may progressively lead to worsening consequences, from cirrhosis to liver failure to liver cancer. In advanced cases, the only treatment is an organ transplant.
Credit: Copyright © 2011 Michael Bonert
Hepatic fibrosis occurs when scar tissue replaces damaged cells in the liver. Over time, accumulating scarring distorts the liver, interferes with its blood supply and may progressively lead to worsening consequences, from cirrhosis to liver failure to liver cancer. In advanced cases, the only treatment is an organ transplant.
In a new paper, published online in the journal Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology, a team of scientists led by corresponding authors David A. Brenner, M.D., president and CEO of Sanford Burnham Prebys, and Tatiana Kisseleva, M.D., Ph.D., professor of surgery at UC San Diego School of Medicine, describe the origin and fate of liver myofibroblasts — the cells that form liver scar tissue — and emerging evidence that liver fibrosis can be reversed if the causative agent is removed.
“Liver fibrosis is quite common, in part because it can be caused by a number of things that damage the organ but result in scarring rather than healthy repair,” said Brenner, a gastroenterologist and noted liver disease researcher. “Everything from viral hepatitis to excessive alcohol consumption to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), which is extremely common in the U.S.”
Indeed, it’s estimated that NAFLD affects approximately 1 billion people worldwide, or roughly one-quarter of the human population. Roughly 20 percent of patients with NAFLD progress to a more serious form called nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), characterized by inflammation of the liver, fibrosis and cirrhosis.
In their paper, Brenner, Kisseleva and co-authors explain that myofibroblasts are not present in normal, healthy livers, but activate in response to chronic liver injury, such as excessive alcohol consumption. An inflammatory response triggers activation of hepatic stellate cells (aHSC), which transition from relatively scarce, quiescent, vitamin A-storing cells into proliferative myofibroblasts that secrete the scar forming proteins.
These myofibroblasts begin forming a chicken wire of non-functional scar tissue that, over time, thickens and coalesces to clog and choke the liver, cascading to other, life-threatening conditions.
“There are many causes of liver fibrosis and thus, there are no effective therapies currently because most efforts have focused on single targets when the nature of chronic liver injury is incredibly complex,” Brenner said.
An emerging therapeutic approach, said the researchers, is to zero in on disrupting the creation of hepatic myofibroblasts while simultaneously addressing the underlying cause of the liver damage, such as a viral infection or excessive drinking. Do so, the thinking goes, and aHSCs revert to their dormant state and liver fibrosis disappears.
“That means zeroing in on the factors that activate hepatic stellate cells,” said Brenner, “the signaling pathways that turn them into scar tissue factories. Recent studies in mouse models and humans have begun to illuminate these cellular and molecular mechanisms. And new single cell technologies and tools like spatial transcriptomics (which can comprehensively characterize tissue organization and architecture at single cell or subcellular resolution) will further the cause.”
Additional authors on the study include Hyun Young Kim, Sadatsugu Sakane, Alvaro Eguileor, Raquel Carvalho Gontijo Weber, Wonseok Lee, Xiao Liu, Kevin Lam, Kei Ishizuka, Sara Brin Rosenthal and Karin Diggle, all at UC San Diego.
This study was also recently presented at the Japanese Society of Hepatology, where Brenner gave the state-of-the-science lecture.
The study was supported by funding from the National Institutes of Health (grants DK099205, AA028550, DK101737, AA011999, DK120515, AA029019, DK091183, P42ES010337 and R44DK115242).
The study’s DOI is https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmgh.2023.09.008.
Journal
Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology
DOI
10.1016/j.jcmgh.2023.09.008
Method of Research
Literature review
Subject of Research
Human tissue samples
Article Title
The origin and fate of liver myofibroblasts
Article Publication Date
22-Sep-2023




