WASHINGTON, May 30, 2023 — How do flying insects like important pollinators locate odor sources in the great outdoors, despite encountering highly variable wind conditions? They use odor plumes — which travel like smoke and form when the wind blows odor molecules from their source — to track down sources such as flowers or pheromones.
Credit: Credit: Jaleesa Houle and Floris Van Breugel
WASHINGTON, May 30, 2023 — How do flying insects like important pollinators locate odor sources in the great outdoors, despite encountering highly variable wind conditions? They use odor plumes — which travel like smoke and form when the wind blows odor molecules from their source — to track down sources such as flowers or pheromones.
But wind tunnels are typically unable to replicate realistic outdoor wind conditions. In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, University of Nevada at Reno researchers decided to explore microscale wind conditions in various outdoor environments to better understand what flying insects might experience while tracking odor plumes.
Authors Jaleesa Houle and Floris Van Breugel assessed the mechanical turbulence produced by ambient wind flowing over surface roughness elements such as buildings, trees, and fences and its role in odor plume tracking.
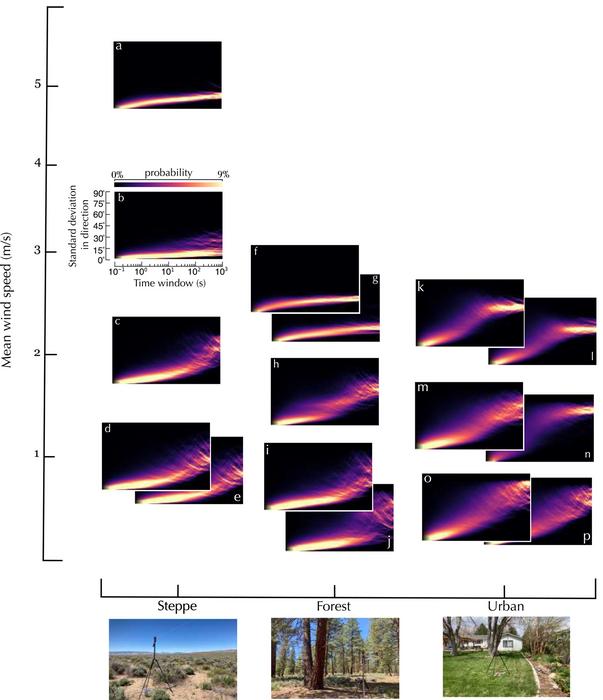
“Since we’re studying wind dynamics within the surface roughness sublayer, most known atmospheric similarity theories that describe properties of the wind profile are not applicable,” said Houle. “So, we use statistical analysis to find both spatial and temporally significant correlations between wind measurements for various sites where we collected data.”
They collected near-surface wind data from several sage steppe (shrub-filled grassland), forest, and urban areas in Northern Nevada and discovered near-surface wind direction is often highly variable over timescales of less than 10 minutes. They also found wind direction variability to be consistently higher in environments with greater surface complexity (urban areas) and lower at higher wind speeds.
“This is important because insects are typically tracking odor plumes in lower wind speeds, which indicates they are somehow making sense of the high directional variability they encounter,” said Houle. “Turbulence intensity is strongly correlated with standard deviations in wind direction, which might be useful for future wind tunnel experimental designs aimed at recreating more ‘natural’ winds.”
Based on their findings, Houle and van Breugel hypothesize an optimal range of wind speed and environmental surface complexity may exist to help insects locate an odor source.
“Further experiments will be needed to test our hypothesis and may help us better understand the implications of land fragmentation on the success of ecologically significant plume tracking insects, such as pollinators,” said Houle. “Beyond this, our results give a compelling reason for researchers to focus on increasing directional variability in wind tunnel studies if they want to uncover plume tracking behaviors that more closely resemble what we might see in nature.”
Next, the researchers will apply their findings to plume tracking wind tunnel experiments and a series of outdoor studies.
“During the summer, we plan to test our hypothesis regarding the types of wind conditions insects might prefer while tracking odor plumes,” said Houle. “In the lab, we’re actively looking for ways to create greater directional variability to better mimic natural wind.”
###
The article, “Near-surface wind variability over spatiotemporal scales relevant to plume tracking insects,” is authored by Jaleesa Houle and Floris Van Breugel. It will appear in Physics of Fluids on May 30, 2023 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0147945). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0147945.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
Physics of Fluids is devoted to the publication of original theoretical, computational, and experimental contributions to the dynamics of gases, liquids, and complex fluids. See https://aip.scitation.org/journal/phf.
Journal
Physics of Fluids
DOI
10.1063/5.0147945
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Near-surface wind variability over spatiotemporal scales relevant to plume tracking insects
Article Publication Date
30-May-2023




