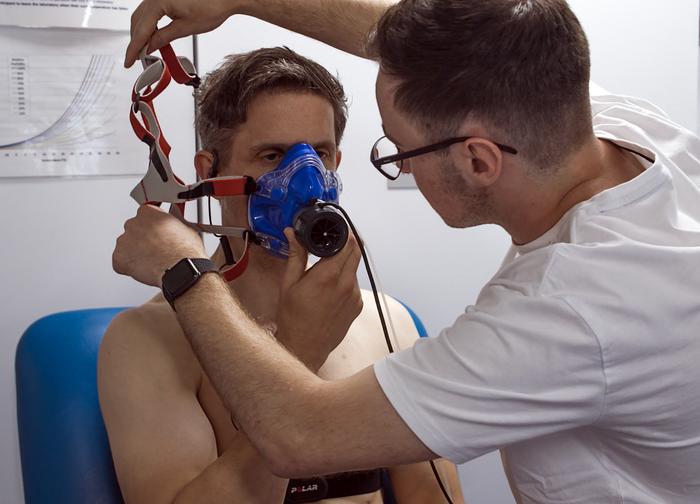
Ongoing research by Prof. Lewis Halsey and his team at the University of Roehampton, UK has identified that an upper critical temperature (UCT) exists for humans and is likely to be between 40°C and 50°C. Further research is now underway to explain this rise in metabolic energy costs at high temperatures.
Credit: Prof. Lewis Halsey, University of Roehampton.
Ongoing research by Prof. Lewis Halsey and his team at the University of Roehampton, UK has identified that an upper critical temperature (UCT) exists for humans and is likely to be between 40°C and 50°C. Further research is now underway to explain this rise in metabolic energy costs at high temperatures.
Prof. Halsey and his team have found that resting metabolic rate, a measure of how much energy the human body consumes to keep ticking over, can be higher when people are exposed to hot and humid conditions. “Quite a lot of work has been done on the range of temperatures that different animal species prefer to live at in terms of their metabolic rates being minimal and thus their energy expenditure being low, but, weirdly, information is much less available for humans when considering the upper limits of our thermal neutral zone,” says Prof. Halsey.
Understanding the temperatures at which human metabolic rates start to rise, and how this varies between people, can have implications for working conditions, sport, medicine and international travel. “This research provides fundamental knowledge about how we react to suboptimal environments, and how ‘optimal’ differs between people with different characteristics,” adds Prof. Halsey.
Prof. Halsey and his team are also investigating how heart function is affected by temperatures above the UCT, and how effects on the heart vary between people with different characteristics such as age and physical fitness. “We found some considerable changes in heart function responses to the heat between categories of people, the most novel being between the sexes,” adds Prof. Halsey. “That is, on the average, men and women display some key differences in their cardiovascular responses to the heat”.
Prof. Halsey’s team measured detailed heart function using a state-of-the-art echocardiograph. “It was not easy to operate this kit in the heat!”, he adds. “The sort of equipment you’d see in hospitals but rarely in research laboratories”.
These experiments are ongoing and Prof. Halsey’s talk at the SEB conference will highlight their most recent findings. “We are steadily building a picture about how the body responds to heat stress, how adaptable it can be, the limits to those adaptations, and – crucially – how varied responses are between individuals. In a warming world, this knowledge becomes ever more valuable,” he adds.




