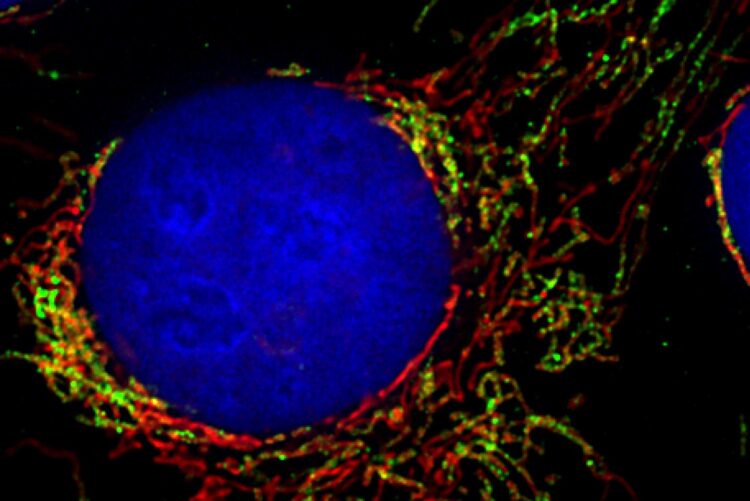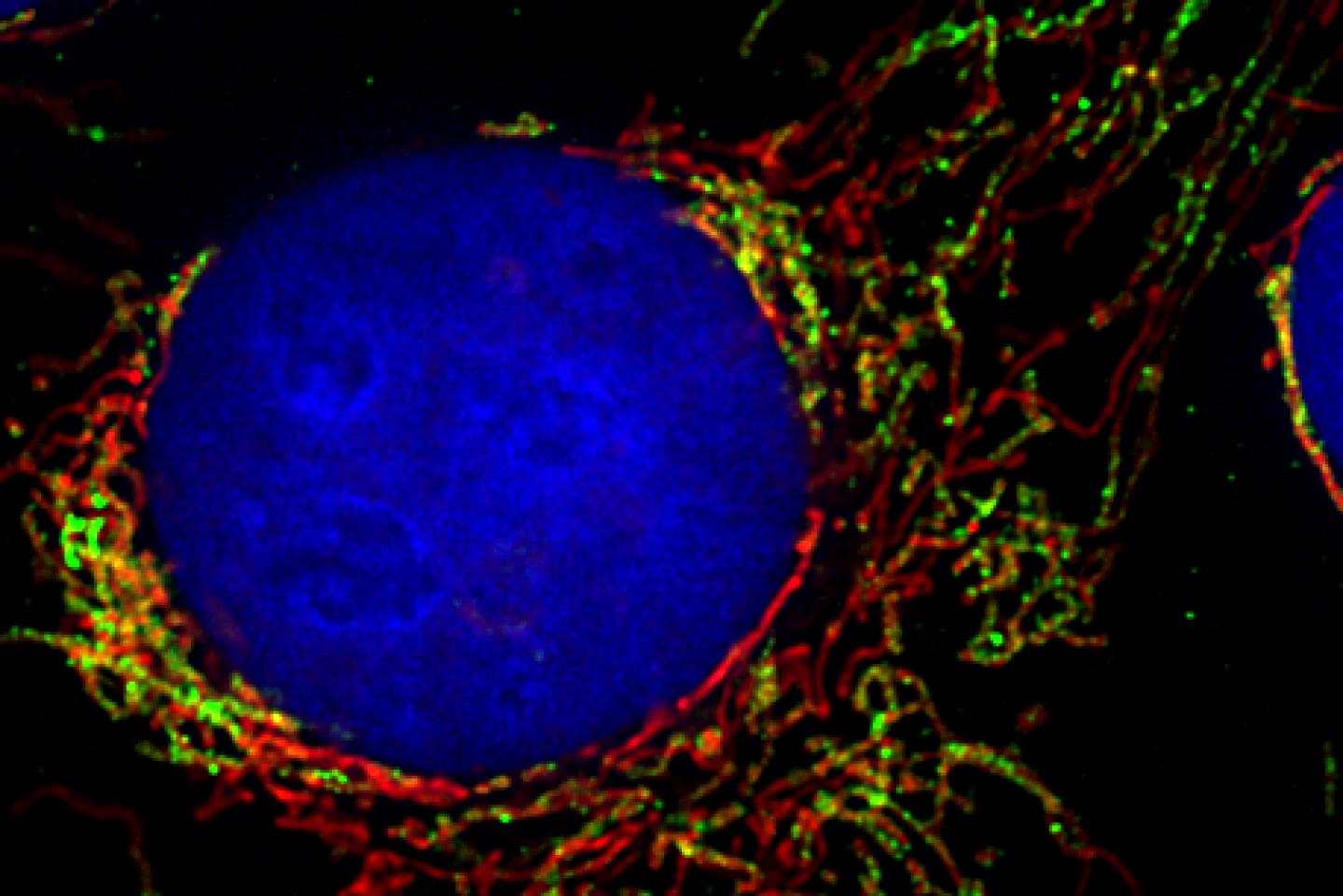
Credit: Pablo Sánchez-Martín/University of Freiburg
Errors in the metabolic processes of mitochondria are responsible for a variety of diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. Scientists needed to find out just how the necessary building blocks are imported into the complex biochemical apparatus of these cell areas. The TOM complex (translocase of the outer mitochondrial membrane) is considered the gateway to the mitochondrion, the proverbial powerhouse of the cell. The working group headed by Professor Chris Meisinger at the Institute of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at the University of Freiburg has now demonstrated – in human cells – how signaling molecules control this gate. A signaling protein called DYRK1A modifies the molecular machinery of TOM and makes it more permeable for enzymes that are important for the cell metabolism. The group has thus discovered the first signaling protein that directly influences this import process in humans. Their work has been published in the journal Nature Communications.
Developmental disorders in a new light
In neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism, microcephaly and Down’s syndrome, DYRK1A is defective. “The connection with mitochondria is new. These results allow us to better understand these disorders and develop treatment strategies,” says Dr. Adinarayana Marada, a member of Meisinger’s team.
“For a long time, researchers thought that the TOM complex was a rigid structure in the mitochondrial membrane whose doors were always open,” Meisinger explains. His team recently demonstrated signaling mechanisms in baker’s yeast that alter the subunits of the TOM complex depending on the metabolic state of the cell, or in response to sudden stress. In this way, the cell can specifically control the influx of precursor proteins for building elements of the metabolism, and it can adapt the function of the mitochondria to an altered cellular state. Whether such mechanisms also exist in humans was previously unknown.
DYRK1A acts upon the TOM complex
The first authors of the study, Dr. Corvin Walter and Dr. Adinarayana Marada of Meisinger’s research group, developed a systematic approach to track down signaling mechanisms such as those triggered by protein kinases, in humans. Over several years, they tested candidates using cell biological and bioinformatic methods and found what they were looking for – DYRK1A, one such protein kinase, acts on the TOM complex. “With this, we actually found the needle in the haystack,” says Walter.
###
The work was done in collaboration with Professor Nora Vögtle, Professor Tilman Brummer and Professor Claudine Kraft from the University of Freiburg as well as researchers at the Universities of Göttingen, Dortmund and Fribourg, Switzerland. Meisinger is speaker of the Collaborative Research Center “Dynamic Organization of Cellular Protein Mechanisms” at the University of Freiburg. In addition, he is a member of the Freiburg Cluster of Excellence CIBSS – Centre for Integrative Biological Signalling Studies, the research training group 2202 Transport across and into Membranes, and 2606 ProtPath.
Publication:
Walter, C., Marada, A., Suhm, T., Ernsberger, R., Muders, V., Kücükköse, C., Sánchez-Martín, P., Hu, Z., Aich, A., Loroch, S., Solari, F.A., Poveda-Huertes, D., Schwierzok, A., Pommerening, H., Matic, S., Brix, J., Sickmann, A., Kraft, C., Dengjel, J., Dennerlein, S., Brummer, T., Vögtle, F.N., and Meisinger, C. (2021): Global kinome profiling reveals DYRK1A as critical activator of the human mitochondrial import machinery. In: Nat. Commun. 12:4284. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-24426-9
Media Contact
Professor Dr. Chris Meisinger
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.