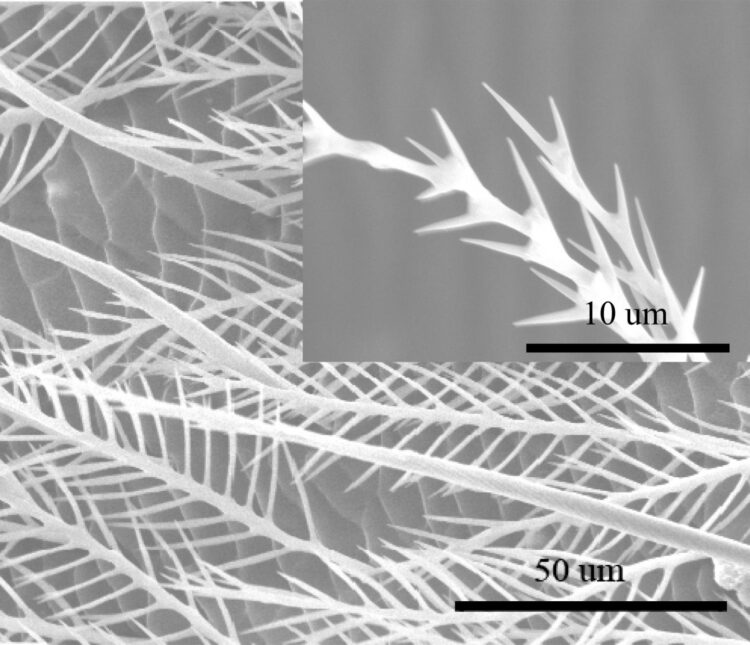
Credit: Adapted from ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2021, DOI: 10.1021/acsami.1c05500
Watching honeybees buzz among flowers, it’s easy to see how the expression “busy as a bee” arose. One of many movements a bee’s body makes is the repetitive curving and straightening of its abdomen. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces have found that tiny hairs reduce friction from these motions, saving energy for the industrious insects’ daily activities while reducing wear and tear. This knowledge could help researchers design longer-lasting moving parts.
A bee’s abdomen is divided into several tough outer plates that make up its exoskeleton. When the abdomen flexes and extends, these segments slide over each other, creating friction. However, the overlapping portions of the segments show very little wear and tear, a finding that has puzzled scientists. Jieliang Zhao, Shaoze Yan and colleagues wanted to investigate the anti-friction mechanism of the honeybee abdomen, which could someday be used to extend the lifetime of engineered soft devices, such as actuators and hinges.
The researchers observed honeybee abdomens under a scanning electron microscope, finding numerous branched hairs on the outer surface. Then, using atomic force microscopy, they measured the friction caused by moving an exoskeletal segment across either a hairy or hairless surface. Under the same load, the friction for the hairy surface was lower than that for a smooth surface. As the load increased, friction for the hairless surface rose, whereas no obvious rise in friction was observed for the hairy surface. The researchers calculated that the hairy surface reduced abrasion during abdominal contraction by about 60% and also saved energy with each contraction. This adds up to a large amount of conserved energy that is essential for conducting bees’ daily activities, the researchers say.
###
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission and the Beijing Institute of Technology Research Fund Program for Young Scholars.
The abstract that accompanies this paper can be viewed here.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook
Media Contact
Katie Cottingham
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.