Animals instinctively find and consume water when feeling thirsty in order to restore body fluid osmolality and plasma volume to their set points. The feeling of thirst is strongly influenced by the subfornical organ (SFO), a forebrain structure that integrates circulating signals, such as osmotic pressure and sodium contents, to stimulate thirst. While Secretin (SCT), a classical gastrointestinal hormone, has been implicated as a humoral factor regulating body-fluid homeostasis. As known that the mundane behavior of drinking water is actually governed by the complex neural mechanisms of SCT in the central nervous system, but how the signalling is involved in this process was unclear.
Credit: Dr Fengwei ZHANG
Animals instinctively find and consume water when feeling thirsty in order to restore body fluid osmolality and plasma volume to their set points. The feeling of thirst is strongly influenced by the subfornical organ (SFO), a forebrain structure that integrates circulating signals, such as osmotic pressure and sodium contents, to stimulate thirst. While Secretin (SCT), a classical gastrointestinal hormone, has been implicated as a humoral factor regulating body-fluid homeostasis. As known that the mundane behavior of drinking water is actually governed by the complex neural mechanisms of SCT in the central nervous system, but how the signalling is involved in this process was unclear.
Recently, a research team from the School of Biological Sciences (SBS) at The University of Hong Kong (HKU) collaborated with Jinan University and the Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) to adopt a projection-specific gene deletion approach, demonstrating the neural mechanism for the first time, which reveals the important role of SCT Recepter (SCTR) in regulating drinking behaviour under thirst. This study not only expands the functional boundary of SCT, but also puts forward new insights into the regulation of the gut-brain axis in maintaining body fluid homeostasis, which provides new ideas for solving hydromineral imbalance symptoms (e.g., fatigue, headaches, arrhythmia, nausea, and vomiting etc.). Their findings have been published in the top journal Current Biology.
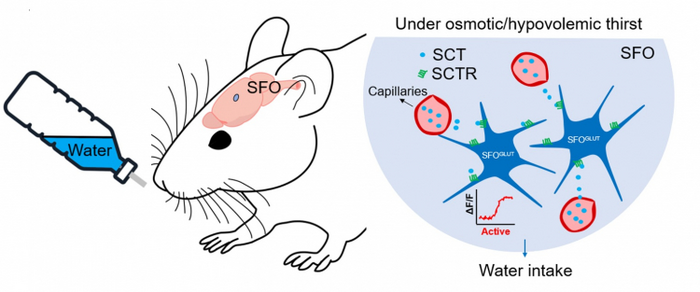
The SFO located in the mammalian forebrain is the key site that regulates internal water balance, while SFO neurons are poised to receive signals about plasma osmolality, blood pressure, and hormones, which integrates these information to regulate thirst. Excitatory neurons in SFO are strongly activated under dehydration, and activation of such neurons can promote voracious water intake even under hydrated conditions. Previous studies focused on dissecting the neural circuits underlying thirst, but how peptide signalling is involved in this process still needs to be better understood.
SCT was recently identified as a key factor that regulates body fluid homeostasis. Central and peripheral administration of SCT triggered water intake in rodents. Notably, the SCTR was also expressed in the SFO and is activated by SCT from blood circulation, suggesting that they may directly involve in body fluid balance dominated by SFO.
To better understand the neural basis of how SCTR regulates thirst, the research team led by Professor Billy CHOW from HKU SBS, Dr Li ZHANG from Jinan University and Professor YUNG Wingho from CUHK jointly demonstrated that SCTR deletion in the SFO significantly reduces water intake in dehydrated mice.
The team used electrophysiology and fibre photometry to show the SCT-SCTR axis participants in the activation of SFO excitatory neurons under dehydration. Moreover, they adopted a projection-specific gene deletion approach to demonstrate that SCTR participates in SFO to the median preoptic nucleus (MnPO) neurons pathway to regulate thirst.
In short, this study reveals the important role of SCTR in regulating drinking behavior under thirst. SCTR may maintain normal drinking behaviour after thirst by regulating the membrane current changes of SFO excitatory neurons and mediating the neural excitability of the SFO to the MnPO pathway. This study provides a new perspective for understanding the role of gastrointestinal peptides in human body fluid homeostatic regulation.
‘Discovering the role of SCT in the central nervous system is exciting, but this is just the beginning, and our research is gradually expanding the role of SCT in the brain,’ says Professor Chow. ‘We will continue to follow the traces of SCT signals in the brain to descript a clearer neural mechanism.’
The journal paper can be accessed here: https://www.cell.com/current-biology/fulltext/S0960-9822(22)01537-8
More information about Dr Billy Chow and his research group can be found from their group’s webpage: http://www.biosch.hku.hk/staff/bc/bc.html
Images download and captions: https://www.scifac.hku.hk/press
For media enquiries, please contact Ms Casey To, External Relations Officer (Tel: 3917-4948; email: [email protected]) and Ms Cindy Chan, Assistant Communications Director of Faculty of Science (Tel: 3917-5286; email: [email protected]).
Journal
Current Biology
DOI
10.1016/j.cub.2022.09.037
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Cells
Article Title
Secretin receptor deletion in the subfornical organ attenuates the activation of excitatory neurons under dehydration
Article Publication Date
21-Nov-2022




