Credit: UTA
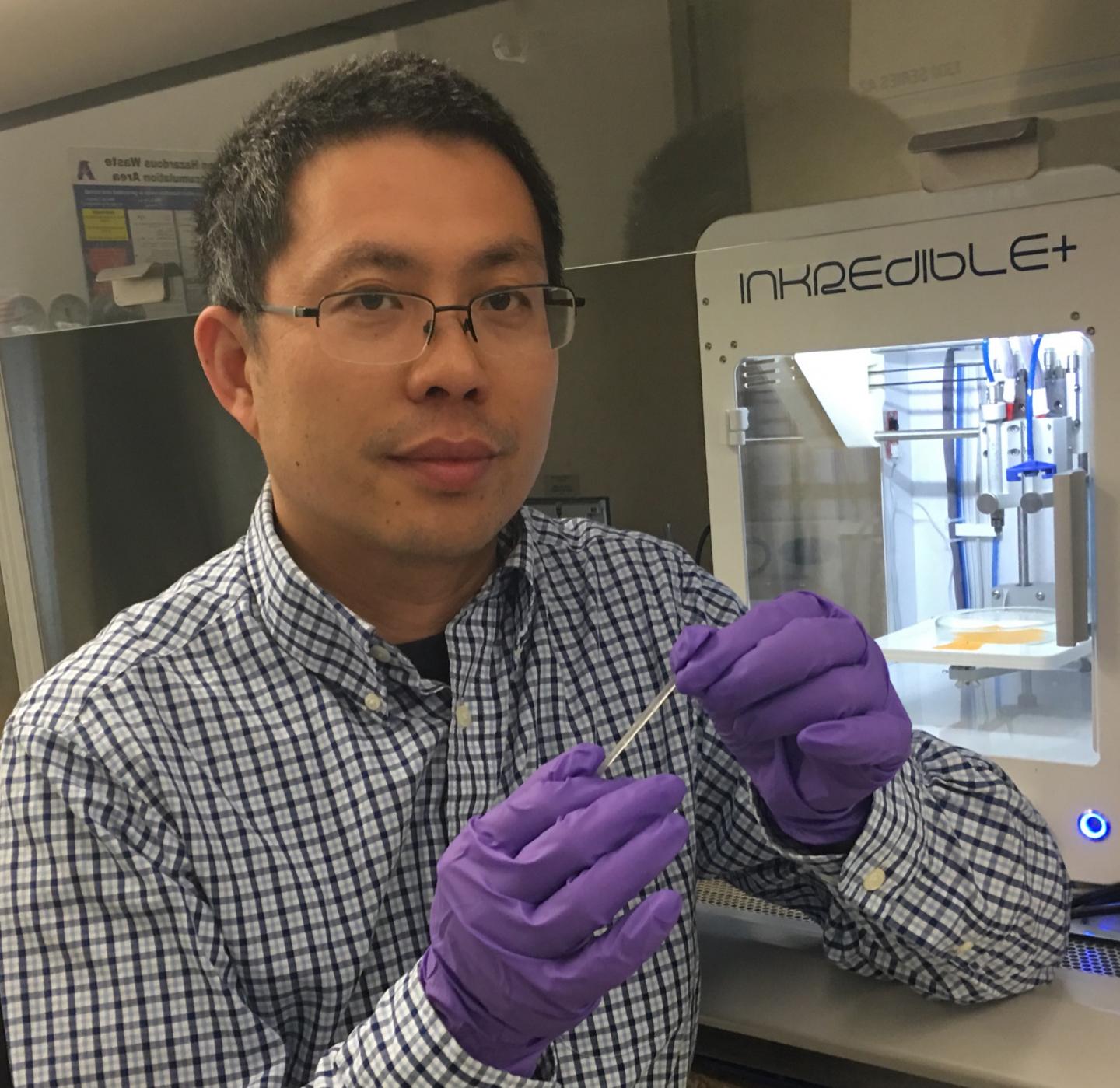
Researchers at The University of Texas at Arlington have developed a highly elastic biodegradable hydrogel for bio-printing of materials that mimic natural human soft tissues. Bio-printing uses live cells within the scaffolding of the new tissues and could potentially transform cell printing.
A provisional patent application has been filed on this new material, which will be able to generate multiple types of human soft tissues, including skin, skeletal muscles, blood vessels and heart muscles.
"Soft tissue bio-printing suffers from significant challenges as the hydrogels were often brittle and un-stretchable and could not mimic the mechanical behavior of human soft tissues," said Yi Hong, UTA professor of bioengineering and leader of the project.
"To overcome these challenges, we developed a simple system using a single cross-linking mechanism activated by visible light to achieve a highly elastic and robust, biodegradable and biocompatible hydrogel for cell printing," Hong added.
The researchers have described their findings in a new journal paper published recently in the American Chemical Society's ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces as "Highly Elastic Biodegradable Single-Network Hydrogel for Cell Printing." The paper was also selected as an American Chemical Society Editors' Choice.
A tri-block biodegradable polymer of polycaprolactone – poly (ethylene glycol) – polycaprolactone (PCL-PEG-PCL) with two end groups of acrylates and a visible-light water-soluble initiator forms this hydrogel for cell printing.
"Polycaprolactone and poly (ethylene glycol) are already widely used in Food and Drug Administration – approved devices and implants, which should facilitate quick translation of the material into pre-clinical and clinical trials in the future," Hong said.
"The tunability of the mechanical properties of this hydrogel to match different soft tissues is a real advantage," he added.
Michael Cho, UTA chair of bioengineering, congratulated Hong and his colleagues on this research.
"These colleagues may have created a new way of thinking about hydrogel bio-printing research," Cho said. "This work is also critical in advancing UTA's strategic theme of health and the human condition through cross-disciplinary work."
###
Dr. Gaohao Dai of Northeastern University in Boston also participated in this work and the prestigious paper.
Media Contact
Louisa Kellie
[email protected]
817-524-8926
@utarlington
http://www.uta.edu
Original Source
https://www.uta.edu/news/releases/2018/05/Yi%20Hong%20hydrogel%20for%20bioprinting.php http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b01294