Only 1 in 4 papers shares code behind the science

Credit: Szymek Drobniak
Share the code and data behind the research please. It’s easy, but it will have a major positive impact on progress and trust in science. That is the clear message from a new paper in PLOS Biology. An international team of ecologists found that currently, only about a quarter of the scientific papers in their field publicly shares computer code for analyses. “To make the science of ecology more transparent and reproducible, sharing is urgently needed.”
Open access, open source, open science. Although there is much talk about these important ‘open’ topics, the practice of sharing scientific data and especially accompanying code is lagging behind. And ecology is no exception.
“We urgently need to improve the reproducibility of ecological research,” explains lead author Antica Culina from the Netherlands Institute of Ecology (NIOO-KNAW). “The code is an essential part of the research process. If this code is shared with others, they can fully understand and evaluate the results. They can also use the code for their own work, accelerating scientific discovery.”
Start counting
Both the underlying data and the code to analyse it are needed to check and reuse scientific results. This might be particularly important in ecology, because of the sophisticated models used.
How many scientific journals encourage data and code sharing? And how many researchers actually share this? Together with fellow ecologists from Bielefeld University, Oxford University and Exeter University, Culina started counting.
Numbers talk
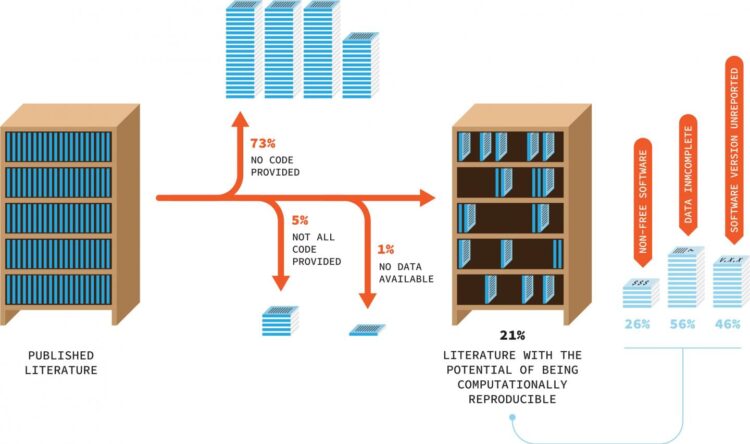
The numbers talk straight language. Culina: “Our results, combined with previous findings, indicate that less than 20% of ecological research is computationally reproducible.” From a random sample of hundreds of scientific articles on ecology, 79% had data available but only 27% was accompanied by code. Put together, this results in only about 20% of articles that is ‘computationally reproducible’. The actual numbers are probably even lower, as the team only looked into articles from journals that at least encourage code sharing. But it doesn’t end there.
A large part of the remaining literature with code and data available did not use free software (26%), did not report the software version (46%), and based on previous work by Roche and colleagues it is likely that many of the datasets (56%) are incomplete.
“On the positive side,” adds Culina, “more and more journals are adopting code-sharing policies, most of the published code is written in software that can be used by anyone who wants it, and ever more code is published in trusted ‘repositories’.”
To be open
The researchers used:
- a random sample of 346 articles about nonmolecular subjects from 14 ecological journals,
- articles published between 2015 and 2019 under mandatory or encouraged code-sharing policies. (This means that the percentages mentioned are probably overestimating the truly reproducible literature.)
They found out that:
- more and more ecological journals have mandatory or encouraged code-sharing policies, up from 15% in 2015 to 75% in 2020,
- still, code-sharing policies are not adhered to by most people.
Address it
The international research team hopes that these results will encourage journals, institutions, funding agencies and researchers to address this “alarming situation”. They also share helpful hints of how to do this. As Culina puts it: “We specifically call for a drastic increase in code availability, and we reach out to journals, authors and reviewers to contribute to this much needed change.” And no worries: “It is actually quite simple to share your code. Science thrives on collaboration and openness – let’s help ecology to thrive.”
###
With more than 300 staff members and students, the Netherlands Institute of Ecology (NIOO-KNAW) is one of the largest research institutes of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (KNAW). The institute specialises in water and land ecology. As of 2011, the institute is located in an innovative and sustainable research building in Wageningen, the Netherlands. NIOO has an impressive research history that stretches back 65 years and spans the entire country, and beyond.
Media Contact
Froukje Rienks
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.