Credit: ©Science China Press
Since the first discovery of photocatalytic water splitting on a TiO2 electrode under ultraviolet (UV) light, TiO2 materials have been widely investigated over the past few decades due to their unique properties such as nontoxicity, abundance, easy availability, and stability. For the moment, TiO2 materials present great potentials in the applications from the conventional areas (e.g., pigment, cosmetic, and toothpaste) to the latest developed areas including catalysis, energy storage and conversion, biomedicine, environmental remediation and so on. Beyond all question, TiO2 materials render new candidates to overcome the energy, environment, and health challenges facing humanity today.
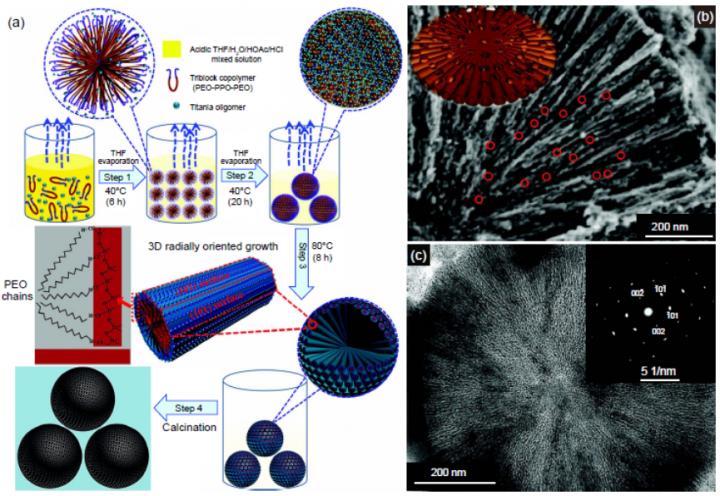
Recently, various TiO2 nanomaterials with different structures have been fabricated and applied in different areas and reveal excellent performances. Among them, mesoporous TiO2 materials, especially with hierarchically mesoporous structures, have received increasing interest due to their attractive features, such as high surface areas, large pore volumes, tunable pore structures, and nano-confined effects. Those features enable the high performance of hierarchically mesoporous TiO2 materials in many areas. The high surface area can provide abundant active-sites for surface- or interface-related processes such as adsorption and catalysis. The large pore volume has shown great potential in the loading of guest species and the accommodation of structural change. And the porous structure can facilitate the diffusion of reactants and products, which is benefit for the reaction kinetics.
In a new review published in National Science Review, scientists at the Department of Chemistry in Fudan University, China, present the latest advances in the synthesis of hierarchically mesoporous TiO2 materials for energy and environmental applications. Co-authors Wei Zhang, Yong Tian, Haili He, Li Xu, Wei Li, and Dongyuan Zhao summarize the general synthetic strategies (template-free, soft-template, and hard-template and multiple-template routes) for hierarchically mesoporous TiO2 materials firstly. After that, they review the representative morphologies of hierarchically mesoporous TiO2 materials (nanofibers, nanosheets, microparticles, films, spheres, core-shell structures, and multi-level architectures), meanwhile, the corresponding synthetic mechanisms and the key factors for the controllable synthesis of hierarchically mesoporous TiO2 materials with different architectures are highlighted. Moreover, they discuss the applications of hierarchically mesoporous TiO2 materials in terms of energy storage and environmental protection, including photocatalytic degradation of pollutants, photocatalytic fuel generation, photoelectrochemical water splitting, chemical catalysis, lithium-ion batteries and sodium-ion batteries. Finally, the author outline the challenges and future directions of research and development in this area.
###
This research received funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Ministry of Science and Technology of China and Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality.
See the article:
Wei Zhang, Yong Tian, Haili He, Li Xu, Wei Li, and Dongyuan Zhao
Recent Advances in Synthesis of Hierarchically Mesoporous TiO2 Materials for Energy and Environmental Applications
Natl Sci Rev, doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwaa021
https:/
The National Science Review is the first comprehensive scholarly journal released in English in China that is aimed at linking the country’s rapidly advancing community of scientists with the global frontiers of science and technology. The journal also aims to shine a worldwide spotlight on scientific research advances across China.
Media Contact
Wei Li
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




